Diabetes is a chronic condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It requires careful management and lifestyle adjustments to ensure a good quality of life. Fortunately, there are numerous ways to effectively care for diabetes, ranging from dietary changes to regular exercise and medication adherence. This blog’ll explore 15 essential strategies for managing and preventing diabetes complications.
Contents
- 1 What is Diabetes?
- 2 10 Steps for Diabetes Care
- 2.1 Monitor Blood Sugar Levels Regularly
- 2.2 Follow a Healthy Diet
- 2.3 Control Portion Sizes
- 2.4 Stay Hydrated
- 2.5 Engage in Regular Physical Activity
- 2.6 Maintain a Healthy Weight
- 2.7 Take Medications as Prescribed
- 2.8 Get Quality Sleep
- 2.9 Quit Smoking
- 2.10 Schedule Regular Check-ups
- 2.11 Build a Support Network
- 3 Conclusion
What is Diabetes?

Diabetes is a chronic medical condition characterized by elevated levels of glucose (sugar) in the blood. Glucose is the primary source of energy for the body’s cells and is derived from the foods we eat. However, in diabetes, the body either does not produce enough insulin (a hormone that helps regulate blood sugar levels) or cannot effectively use the insulin it produces. This results in high blood sugar levels, which, if left uncontrolled, can lead to serious health complications.
There are several types of diabetes, including:
- Type 1 Diabetes: Type 1 diabetes, also known as insulin-dependent diabetes or juvenile diabetes, typically develops during childhood or adolescence.
- Type 2 Diabetes: Type 2 diabetes is the most common form of diabetes and usually develops in adulthood, although it is increasingly being diagnosed in children and adolescents.
- Gestational Diabetes: Gestational diabetes occurs during pregnancy when the body cannot produce enough insulin to meet the increased demands of pregnancy.
- Other Forms of Diabetes: There are other less common forms of diabetes, such as monogenic diabetes (caused by mutations in a single gene) and secondary diabetes (resulting from other medical conditions or medications).
Common symptoms of diabetes include frequent urination, excessive thirst, unexplained weight loss, fatigue, blurred vision, slow wound healing, and recurrent infections. However, some individuals with diabetes may not experience noticeable symptoms, especially in the early stages of the disease.
10 Steps for Diabetes Care
Managing diabetes requires a comprehensive approach that includes various lifestyle adjustments and medical interventions. Here are 10 essential steps for diabetes care to help you effectively control your blood sugar levels, prevent complications, and improve your overall quality of life.
Monitor Blood Sugar Levels Regularly
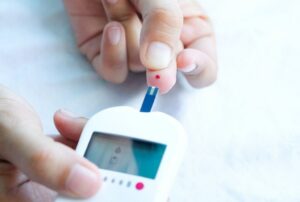
- Importance of Monitoring: Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels is crucial for effectively managing diabetes. It provides valuable insight into how your body responds to various factors such as food, exercise, and medication.
- Frequency of Testing: Depending on your treatment plan and individual needs, your healthcare provider may recommend testing your blood sugar levels multiple times a day. This helps you track patterns and make necessary adjustments to your diabetes management routine.
- Types of Monitoring Devices: There are various devices available for blood sugar monitoring, including glucometers, continuous glucose monitors (CGMs), and flash glucose monitoring systems. Discuss with your healthcare provider to determine which device is most suitable for your needs.
Follow a Healthy Diet
- Emphasis on Nutrient-Dense Foods: A healthy diet for diabetes management should focus on consuming nutrient-dense foods that provide essential vitamins, minerals, and fiber. Include a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats in your meals.
- Carbohydrate Management: Pay attention to carbohydrate intake and choose complex carbohydrates that are digested more slowly, such as whole grains, legumes, and non-starchy vegetables. Monitor portion sizes and spread carbohydrate consumption evenly throughout the day to help regulate blood sugar levels.
- Limit Sugary and Processed Foods: Minimize your intake of sugary beverages, sweets, and processed foods that are high in added sugars and refined carbohydrates. These foods can cause rapid spikes in blood sugar levels and contribute to insulin resistance over time.
Control Portion Sizes
- Understanding Portion Sizes: Become familiar with standard serving sizes for different food groups to help you control portion sizes effectively. Use measuring cups, food scales, or visual cues to gauge appropriate serving sizes.
- Mindful Eating Practices: Practice mindful eating techniques such as slowing down during meals, chewing food thoroughly, and paying attention to hunger and fullness cues. This can help prevent overeating and promote better portion control.
- Plate Method: Use the plate method as a visual guide for creating well-balanced meals. Fill half your plate with non-starchy vegetables, one-quarter with lean protein, and one-quarter with whole grains or starchy vegetables.
- Avoiding Oversized Portions: Be mindful of portion sizes when dining out or eating packaged foods, as restaurant meals and pre-packaged snacks often contain larger portions than necessary. Consider sharing entrees or asking for a to-go container to portion out leftovers before eating.
Stay Hydrated

- Importance of Hydration: Proper hydration is essential for overall health and well-being, including diabetes management. Water plays a key role in regulating body temperature, transporting nutrients, and flushing out waste products.
- Hydration Guidelines: Aim to drink at least eight 8-ounce glasses of water per day, but adjust your fluid intake based on factors such as climate, physical activity level, and individual hydration needs.
- Choosing Hydrating Beverages: Opt for hydrating beverages such as water, herbal tea, or infused water instead of sugary drinks or caffeinated beverages, which can contribute to dehydration and affect blood sugar control.
- Monitoring Fluid Intake: Pay attention to signs of dehydration such as dark-colored urine, dry mouth, fatigue, or dizziness. If you’re experiencing symptoms of dehydration, increase your fluid intake and consider consuming electrolyte-rich beverages or foods.
Engage in Regular Physical Activity
- Benefits of Exercise: Regular physical activity is essential for managing diabetes, as it helps improve insulin sensitivity, lower blood sugar levels, and maintain a healthy weight. It also reduces the risk of cardiovascular complications associated with diabetes.
- Types of Exercise: Incorporate a variety of aerobic exercises, such as walking, jogging, cycling, swimming, or dancing, into your weekly routine. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise per week, spread out over several days.
- Strength Training: Include strength training exercises two to three times per week to build muscle mass, improve metabolism, and enhance overall physical function. Focus on exercises that target major muscle groups, such as squats, lunges, push-ups, and weightlifting.
- Flexibility and Balance Training: Don’t forget to incorporate flexibility and balance exercises into your routine to improve mobility, prevent injuries, and enhance overall well-being. Consider activities such as yoga, tai chi, or Pilates to improve flexibility, balance, and mind-body awareness.
Maintain a Healthy Weight
- Setting Realistic Goals: Set realistic and achievable weight loss goals based on your individual needs, preferences, and medical history. Aim for gradual weight loss of 1-2 pounds per week, as rapid weight loss can be unsustainable and may increase the risk of nutrient deficiencies.
- Healthy Eating Habits: Focus on adopting healthy eating habits that promote weight loss and overall well-being, such as eating smaller, more frequent meals, incorporating more fruits and vegetables into your diet, and avoiding mindless snacking.
- Regular Physical Activity: Combine healthy eating habits with regular physical activity to support weight loss efforts and improve overall health. Engage in a combination of aerobic exercise, strength training, and flexibility exercises to maximize calorie burning and promote muscle growth.
Take Medications as Prescribed
- Adherence to Treatment Plan: Taking medications as prescribed by your healthcare provider is essential for managing diabetes and preventing complications. Follow the recommended dosage, frequency, and timing instructions carefully to ensure optimal effectiveness.
- Types of Diabetes Medications: There are several types of medications available for diabetes management, including oral medications, injectable insulin, and other injectable medications that work in different ways to lower blood sugar levels. Work closely with your healthcare provider to determine the most appropriate treatment regimen for your needs.
- Potential Side Effects: Be aware of potential side effects associated with diabetes medications and report any unusual symptoms or reactions to your healthcare provider promptly. Some common side effects may include hypoglycemia (low blood sugar), weight gain, gastrointestinal upset, or allergic reactions.
Get Quality Sleep

- Importance of Sleep: Quality sleep is essential for overall health and well-being, including diabetes management. During sleep, the body undergoes important restorative processes that support immune function, hormone regulation, and cellular repair.
- Recommended Sleep Duration: Aim for seven to nine hours of quality sleep per night, as recommended by the National Sleep Foundation. However, individual sleep needs may vary, so pay attention to how you feel during the day to determine if you’re getting enough sleep.
- Establishing a Bedtime Routine: Create a relaxing bedtime routine to signal to your body that it’s time to wind down and prepare for sleep. This may include activities such as taking a warm bath, reading a book, practicing relaxation techniques, or listening to calming music.
Quit Smoking
- Impact of Smoking on Diabetes: Smoking is detrimental to overall health and can worsen diabetes complications such as heart disease, stroke, nerve damage, and kidney disease. It also increases insulin resistance and makes blood sugar control more difficult.
- Benefits of Quitting Smoking: Quitting smoking is one of the most important steps you can take to improve your health and well-being, especially if you have diabetes. Within hours of quitting, your body begins to experience positive changes such as improved circulation and reduced blood pressure.
- Smoking Cessation Resources: Take advantage of smoking cessation resources and support services to help you quit successfully. These may include nicotine replacement therapies, prescription medications, counseling, support groups, or smartphone apps designed to aid in smoking cessation.
Schedule Regular Check-ups
- Importance of Regular Check-ups: Regular check-ups with your healthcare provider are essential for monitoring your diabetes and overall health. These appointments allow your healthcare team to assess your progress, identify any potential issues, and make necessary adjustments to your treatment plan.
- Frequency of Check-ups: The frequency of check-ups may vary depending on your individual needs and diabetes management goals. Typically, people with diabetes should have regular follow-up appointments every three to six months, or as recommended by their healthcare provider.
Build a Support Network
- Importance of Support: Managing diabetes can be challenging, but you don’t have to do it alone. Build a strong support network of family, friends, healthcare providers, and fellow individuals with diabetes who understand your condition and can provide encouragement, advice, and practical assistance when needed.
- Family and Friends: Share your diabetes journey with your loved ones and educate them about your condition, treatment plan, and support needs. Involve family members and friends in your diabetes care routine and communicate openly about how they can help.
- Healthcare Team: Develop a collaborative relationship with your healthcare team, including your primary care physician, endocrinologist, diabetes educator, registered dietitian, and other specialists. Work together to develop a comprehensive diabetes care plan that meets your individual needs and preferences.
- Support Groups: Join diabetes support groups, either in-person or online, to connect with others who are managing similar challenges. Share experiences, exchange tips and strategies, and provide mutual support and encouragement to one another.
- Online Communities: Participate in online communities and forums dedicated to diabetes management and prevention. These virtual support networks provide a platform for sharing information, asking questions, and connecting with peers from around the world.
Conclusion
Caring for diabetes requires a holistic approach encompassing dietary modifications, regular physical activity, medication adherence, stress management, and regular medical monitoring. By implementing these 15 essential strategies for diabetes care, you can effectively manage your condition, prevent complications, and enjoy a fulfilling life despite diabetes. Remember to work closely with your healthcare team to tailor a diabetes care plan that meets your individual needs and preferences. With dedication, education, and support, you can take control of your diabetes and thrive.
Do you want to get rid of diabetes? Join our online diabetes treatment program and reverse Diabetes naturally through lifestyle changes such as a Personalized Diet plan, Exercise, Yoga, dieticians, and health coaches.