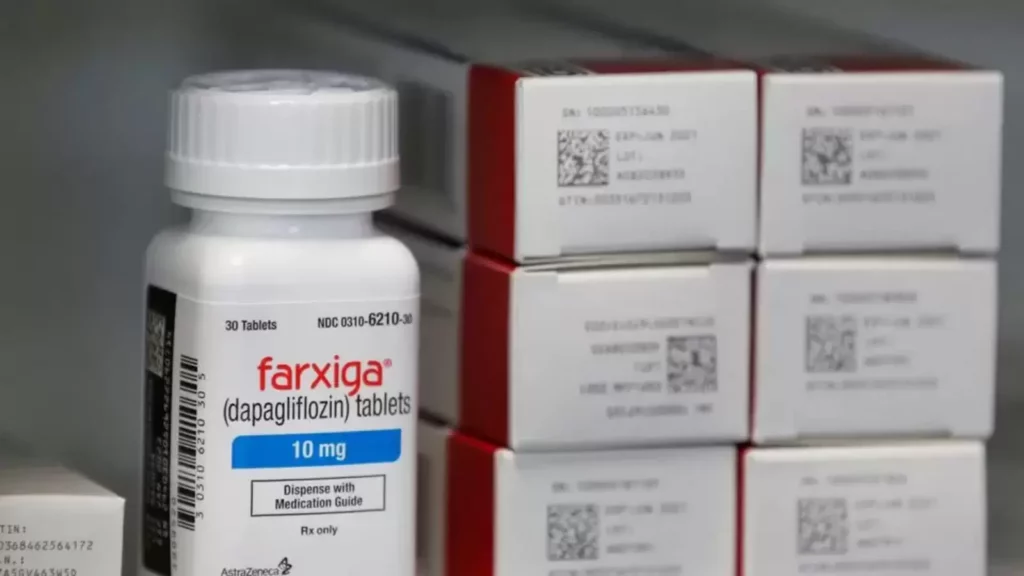
In the realm of pharmaceuticals, AstraZeneca stands out as a prominent player, particularly in the field of diabetes management. With a commitment to improving the lives of individuals living with diabetes, AstraZeneca has developed a range of medications aimed at addressing the diverse needs of patients. In this comprehensive guide, we delve into AstraZeneca diabetes medication, exploring its mechanisms of action, efficacy, safety profiles, and impact on patient care.
Contents
- 1 What is Diabetes?
- 2 AstraZeneca’s Commitment to Diabetes Care
- 3 Types of AstraZeneca Diabetes Medication
- 4 Dosage and Administration of AstraZeneca Diabetes Medication
- 5 Potential Side Effects of AstraZeneca Diabetes Medication
- 6 Considerations and Precautions of AstraZeneca Diabetes Medication
- 7 Conclusion
What is Diabetes?

Before delving into AstraZeneca’s offerings, it’s crucial to grasp the basics of diabetes. Diabetes mellitus refers to a group of metabolic disorders characterized by high blood sugar levels over a prolonged period. The two primary forms of diabetes are Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes, each with distinct etiologies and treatment approaches.
Type 1 diabetes typically results from autoimmune destruction of insulin-producing pancreatic beta cells, necessitating insulin replacement therapy. On the other hand, Type 2 diabetes often involves insulin resistance and impaired insulin secretion, with treatment ranging from lifestyle modifications to oral medications and injectable therapies.
AstraZeneca’s Commitment to Diabetes Care
Here are several aspects that highlight AstraZeneca’s comprehensive approach to diabetes care:
- Research and Development: AstraZeneca invests significantly in research and development to advance the understanding of diabetes and develop novel treatment options. Through collaborations with leading scientists, academic institutions, and research organizations, the company strives to identify innovative therapeutic targets and develop medications with improved efficacy, safety, and tolerability profiles.
- Patient Support Programs: AstraZeneca offers a range of patient support programs designed to empower individuals living with diabetes and help them navigate their treatment journey. These programs provide educational resources, lifestyle counseling, medication adherence support, and access to financial assistance programs to ensure that patients receive comprehensive care and support beyond pharmacotherapy.
- Healthcare Professional Education: AstraZeneca is committed to equipping healthcare professionals with the knowledge and tools they need to effectively manage diabetes in clinical practice. The company sponsors educational initiatives, training workshops, and online resources to enhance healthcare professionals’ understanding of diabetes pathophysiology, treatment guidelines, and patient-centered care approaches.
- Advocacy and Awareness: AstraZeneca actively engages in advocacy efforts to raise awareness about diabetes prevention, early detection, and management. By collaborating with patient advocacy organizations, healthcare institutions, and policymakers, the company works to promote public health initiatives, support community-based diabetes screening programs, and advocate for policies that improve access to diabetes care and resources.
- Collaborative Partnerships: AstraZeneca recognizes the importance of collaboration and partnerships in addressing the complex challenges associated with diabetes care. The company collaborates with healthcare providers, patient advocacy groups, government agencies, and other stakeholders to develop integrated care models, foster innovation in diabetes management, and drive positive outcomes for patients and communities affected by diabetes.
- Continuous Innovation: AstraZeneca is committed to continuous innovation in diabetes care, leveraging cutting-edge research and technology to develop next-generation therapies and solutions.
Types of AstraZeneca Diabetes Medication
AstraZeneca develops various types of diabetes medications, each belonging to different classes of antidiabetic drugs. Here are some of the key types of AstraZeneca diabetes medications:
- Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 (DPP-4) Inhibitors: Medications in this class include saxagliptin. DPP-4 inhibitors work by inhibiting the enzyme DPP-4, which degrades incretin hormones. By inhibiting DPP-4, these medications prolong the action of incretins, which stimulate insulin secretion and inhibit glucagon release, thereby lowering blood sugar levels.
- Sodium-Glucose Co-Transporter 2 (SGLT2) Inhibitors: AstraZeneca produces medications such as dapagliflozin, which belongs to the SGLT2 inhibitor class. SGLT2 inhibitors work by blocking the reabsorption of glucose in the kidneys, leading to increased urinary glucose excretion and lower blood sugar levels.
- Glucagon-like Peptide-1 (GLP-1) Receptor Agonists: GLP-1 receptor agonists mimic the action of endogenous GLP-1, a hormone that stimulates insulin secretion, inhibits glucagon release, slows gastric emptying, and promotes satiety. By activating GLP-1 receptors, these medications help regulate blood sugar levels. AstraZeneca produces exenatide extended-release, a once-weekly injectable GLP-1 receptor agonist.
- Combination Therapies: AstraZeneca also offers combination therapies that combine two or more antidiabetic agents in a single medication. For example, combination products may include a DPP-4 inhibitor with a metformin, or an SGLT2 inhibitor with a DPP-4 inhibitor.
These medications may be used alone or in combination with other antidiabetic drugs, depending on the individual patient’s needs, treatment goals, and comorbidities.
Dosage and Administration of AstraZeneca Diabetes Medication
here’s a more generalized version of the dosage and administration guidelines for AstraZeneca’s diabetes medications:
Dosage
- The dosage of AstraZeneca’s diabetes medications may vary depending on individual patient factors such as age, renal function, hepatic function, concomitant medications, and comorbidities.
- Healthcare providers typically initiate treatment with the lowest effective dose and titrate upwards as needed to achieve optimal glycemic control while minimizing side effects.
- Dosage adjustments may be necessary based on ongoing assessment of patient response, tolerability, and glycemic goals.
Administration
- AstraZeneca’s diabetes medications are administered orally or via subcutaneous injection, depending on the specific formulation.
- Oral medications are typically taken once daily, with or without food, as directed by a healthcare provider.
- Furthermore, Injectable medications may be administered weekly or as directed by a healthcare provider, with proper training provided to patients on correct injection technique and site rotation.
Guidance for Patients
- Patients should follow the prescribed dosage and administration instructions provided by their healthcare provider.
- Oral medications should be swallowed whole with a glass of water, and patients should avoid crushing or splitting tablets unless instructed otherwise.
- Injectable medications should be administered according to the recommended schedule, with proper disposal of needles and syringes to prevent injury and contamination.
- Furthermore, Patients should be educated on the importance of medication adherence, regular monitoring of blood glucose levels, and reporting any adverse effects or concerns to their healthcare provider.
Individualization of Treatment
- Treatment plans should be individualized based on patient-specific factors, including age, renal function, hepatic function, comorbidities, and lifestyle factors.
- Healthcare providers should regularly assess patient response to treatment and adjust dosages as needed to achieve and maintain optimal glycemic control while minimizing the risk of adverse effects.
Patient Counseling
- Healthcare providers should provide comprehensive counseling to patients on proper medication use, potential side effects, and strategies for managing diabetes effectively.
- Patients should be encouraged to actively participate in their treatment plan, including lifestyle modifications such as diet, exercise, and weight management, in addition to medication therapy.
Potential Side Effects of AstraZeneca Diabetes Medication

AstraZeneca’s diabetes medications, like all pharmaceuticals, have the potential to cause side effects. While many patients tolerate these medications well, it’s important for both healthcare providers and patients to be aware of potential adverse reactions. Here are some common side effects associated with AstraZeneca’s diabetes medications:
Common Side Effects:
- Gastrointestinal issues: Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and abdominal discomfort are common side effects of many diabetes medications.
- Genitourinary tract infections: Furthermore, some medications may increase the risk of urinary tract infections and genital fungal infections.
- Hypoglycemia: Low blood sugar levels can occur, especially if medications are not taken as prescribed or in conjunction with other glucose-lowering agents.
Less Common Side Effects:
- Allergic reactions: Rarely, patients may experience allergic reactions such as rash, itching, swelling, or difficulty breathing.
- Injection-site reactions: Injectable medications may cause local reactions such as redness, swelling, or pain at the injection site.
- Changes in laboratory values: Some medications may affect laboratory parameters such as kidney function tests, liver function tests, or lipid profiles.
Serious Side Effects:
- Pancreatitis: Inflammation of the pancreas can occur with certain diabetes medications, presenting with severe abdominal pain, nausea, and vomiting.
- Ketoacidosis: Furthermore, this serious condition can occur, particularly with certain classes of medications, and is characterized by high levels of ketones in the blood, leading to metabolic acidosis.
- Renal impairment: Some medications may affect kidney function, leading to worsening renal function or acute kidney injury in susceptible individuals.
Considerations and Precautions of AstraZeneca Diabetes Medication
When prescribing AstraZeneca’s diabetes medications, healthcare providers must consider various factors and precautions to ensure safe and effective treatment. Here are some important considerations and precautions associated with these medications:
- Renal Function: Some AstraZeneca diabetes medications require dose adjustments or should be avoided in patients with impaired renal function. Healthcare providers should assess renal function before initiating treatment and monitor it regularly, adjusting medication doses as necessary to prevent toxicity and optimize efficacy.
- Hepatic Function: Patients with hepatic impairment may require dose adjustments or close monitoring when using certain diabetes medications. Healthcare providers should evaluate hepatic function before initiating treatment and exercise caution when prescribing medications that are primarily metabolized in the liver.
- Concomitant Medications: AstraZeneca’s diabetes medications may interact with other medications, including antidiabetic agents, cardiovascular drugs, and drugs metabolized by the same enzymes or transporters. Healthcare providers should review patients’ medication lists carefully to identify potential drug interactions and adjust doses or select alternative therapies as needed.
- Hypoglycemia Risk: Some diabetes medications, particularly insulin secretagogues and combination therapies, may increase the risk of hypoglycemia, especially when used in combination with other glucose-lowering agents. Healthcare providers should educate patients about the signs and symptoms of hypoglycemia, as well as appropriate management strategies to prevent and treat low blood sugar levels.
- Genital and Urinary Tract Infections: SGLT2 inhibitors, such as dapagliflozin, have been associated with an increased risk of genital mycotic infections (e.g., yeast infections) and urinary tract infections. Healthcare providers should counsel patients about the signs and symptoms of these infections and recommend appropriate hygiene measures to minimize the risk.
Conclusion
AstraZeneca’s diabetes medications represent valuable additions to the armamentarium for managing diabetes mellitus. Through their diverse mechanisms of action, these medications offer patients effective options for achieving and maintaining glycemic control, while also addressing associated comorbidities and reducing the risk of complications. However, as with any pharmacotherapy, it is essential for healthcare providers to carefully evaluate each patient’s individual needs and considerations to optimize treatment outcomes and enhance overall well-being in diabetes management.
Do you want to get rid of diabetes? Join our online diabetes treatment program and reverse Diabetes naturally through lifestyle changes such as a Personalized Diet plan, Exercise, Yoga, dieticians, and health coaches.

