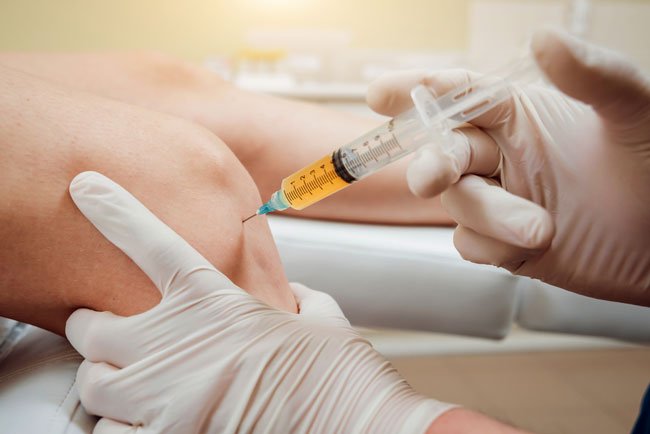
Cortisone shots, also known as corticosteroid injections, are commonly used to treat various inflammatory conditions, such as arthritis, tendonitis, bursitis, and certain skin conditions. While these injections can provide significant relief from pain and inflammation, they may also pose risks for individuals with diabetes. Understanding the relationship between cortisone shots and diabetes is crucial for managing the condition effectively while addressing other health concerns.
In this blog post, we’ll delve into the effects of cortisone shots on diabetes, explore the potential risks and benefits, and discuss strategies for mitigating any adverse effects.
Contents
What are Cortisone Shots?
Cortisone shots, also known as corticosteroid injections, are a type of medication administered directly into a specific area of the body to reduce inflammation and alleviate pain. These injections contain corticosteroids, synthetic drugs that mimic the effects of cortisol, a hormone naturally produced by the adrenal glands.
Cortisone shots are commonly used to treat various inflammatory conditions affecting joints, tendons, bursae (fluid-filled sacs between bones, muscles, and tendons), and soft tissues. Some of the most common conditions treated with cortisone shots include:
- Arthritis: Cortisone shots can provide relief for both osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis by reducing inflammation in the affected joints.
- Tendonitis: Inflammation of tendons, such as tennis elbow (lateral epicondylitis) or rotator cuff tendonitis, can be treated with cortisone injections to alleviate pain and swelling.
- Bursitis: Inflammation of the bursae, small fluid-filled sacs that cushion and lubricate joints, can be relieved with cortisone shots. Examples include trochanteric bursitis in the hip or subacromial bursitis in the shoulder.
- Skin Conditions: Certain skin conditions characterized by inflammation, such as psoriasis or eczema, may be treated with cortisone injections to reduce itching and inflammation.
- Allergic Reactions: Severe allergic reactions, such as contact dermatitis or allergic asthma, may require cortisone shots to quickly reduce inflammation and symptoms.
Cortisone shots are administered by a healthcare professional, typically a physician or an orthopedic specialist, using a syringe and needle. The injection is delivered directly into the affected area or near the site of inflammation, providing targeted relief. The procedure is usually performed in a medical office or outpatient setting and may involve the use of local anesthesia to minimize discomfort.
Working of Cortisone Shots for Diabetes
Cortisone shots, also known as corticosteroid injections, can have several effects on blood sugar levels and glucose metabolism, which can be particularly relevant for individuals with diabetes. Here’s a detailed explanation of how cortisone shots can affect diabetes:
- Glucose Metabolism Disruption: Corticosteroids like cortisone can interfere with glucose metabolism in several ways. They promote gluconeogenesis, a process in which the liver produces glucose from non-carbohydrate sources such as amino acids and fats. This can lead to an increase in blood glucose levels, contributing to hyperglycemia.
- Insulin Resistance: Corticosteroids can also induce insulin resistance, meaning that cells become less responsive to the effects of insulin. Insulin is the hormone responsible for regulating blood sugar levels by facilitating glucose uptake into cells. When cells become resistant to insulin, glucose uptake is impaired, leading to elevated blood sugar levels.
- Decreased Insulin Secretion: Corticosteroids can suppress the secretion of insulin from the pancreas, further contributing to hyperglycemia. This can be particularly problematic for individuals with diabetes who already have impaired insulin production or secretion.
- Increased Appetite and Weight Gain: Corticosteroids can also stimulate appetite and lead to weight gain. This can exacerbate insulin resistance and worsen glycemic control in individuals with diabetes.
- Stress Response: In addition to their direct effects on glucose metabolism, corticosteroids can activate the body’s stress response, releasing stress hormones such as cortisol and adrenaline. These hormones can further increase blood sugar levels by promoting gluconeogenesis and glycogenolysis (the breakdown of glycogen into glucose).
Dosage and Administration of Cortisone Shots for Diabetes
Cortisone shots, or corticosteroid injections, are administered in various dosages and can be delivered through different routes, depending on the specific medical condition being treated. For individuals with diabetes, careful consideration of the dosage and administration of cortisone shots is essential to minimize the impact on blood sugar levels and overall diabetes control. Here’s an overview of the dosage and administration considerations:
Dosage:
- Dosage Range: The dosage of cortisone shots can vary widely depending on factors such as the severity of the condition being treated, the size of the affected area, and individual patient factors.
- Low-Dose vs. High-Dose: In general, lower doses of cortisone are preferred for individuals with diabetes to minimize the risk of exacerbating hyperglycemia and insulin resistance. High doses of cortisone are more likely to lead to significant increases in blood sugar levels. They may require more aggressive management of diabetes medications.
- Single vs. Multiple Injections: Some individuals may require a single cortisone injection to achieve symptom relief. Others may require multiple injections spaced over time for more sustained therapeutic effects. Multiple injections may increase the cumulative dose of cortisone. It should be carefully monitored in individuals with diabetes.
Administration:
- Injection Site: Cortisone shots can be administered directly into the affected area or near the site of inflammation, depending on the medical condition being treated. Common injection sites include joints, tendons, bursae, and soft tissues.
- Intramuscular vs. Intra-articular: Cortisone shots can be delivered intramuscularly (into the muscle) or intra-articularly (into the joint space). Intra-articular injections are commonly used for conditions such as osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, and other joint-related inflammatory conditions.
- Local Anesthesia: Local anesthesia may be used to minimize discomfort during the injection procedure, particularly for intra-articular injections. Lidocaine or a similar numbing agent may be injected into the skin or soft tissues surrounding the injection site before administering the cortisone shot.
Risks for Individuals with Diabetes
For individuals with diabetes, cortisone treatment can pose several risks due to its effects on blood sugar levels and metabolism. Managing these risks effectively requires careful monitoring and adjustment of diabetes management strategies. Here are some of the key risks associated with cortisone treatment for individuals with diabetes:
- Hyperglycemia: Cortisone treatment can lead to elevated blood sugar levels, known as hyperglycemia. This occurs due to increased glucose production by the liver, decreased glucose uptake by cells, and inhibited insulin secretion. Persistent hyperglycemia can increase the risk of diabetes-related complications such as neuropathy, retinopathy, nephropathy, and cardiovascular disease.
- Worsening of Diabetes Control: Cortisone treatment can make it challenging to control blood sugar levels effectively in individuals with diabetes. Insulin resistance and decreased insulin secretion can lead to fluctuations in blood glucose levels. This makes it difficult to maintain stable glycemic control. Poorly managed diabetes can increase the risk of acute complications. These are such as hyperglycemic crises (e.g., diabetic ketoacidosis) and long-term complications. These are associated with chronic hyperglycemia.
- Increased Risk of Infections: Cortisone treatment can suppress the immune system’s response to infections, making individuals with diabetes more susceptible to bacterial, viral, and fungal infections. Poorly controlled diabetes can also impair immune function, further increasing the risk of infections. Infections can exacerbate diabetes control issues and may require prompt medical attention to prevent complications.
- Exacerbation of Cardiovascular Risk Factors: Cortisone treatment can contribute to cardiovascular risk factors such as hypertension, dyslipidemia (abnormal lipid levels), and obesity. These risk factors are already elevated in individuals with diabetes and can increase the risk of cardiovascular events such as heart attack and stroke. Managing cardiovascular risk factors through lifestyle modifications and appropriate medication management is essential for individuals with diabetes undergoing cortisone treatment.
- Bone Loss and Osteoporosis: Prolonged cortisone treatment can lead to bone loss and osteoporosis, particularly in individuals with diabetes who may already have an increased risk of bone-related complications. Osteoporosis can increase the risk of fractures and mobility issues, further impacting quality of life and overall health.
Managing Cortisone Shots and Diabetes

Managing cortisone shots and diabetes requires careful coordination between individuals with diabetes and their healthcare providers. By implementing appropriate strategies, individuals can minimize the impact of cortisone treatment on blood sugar levels and overall diabetes control. Here are some key management approaches:
Pre-Treatment Evaluation:
- Before receiving cortisone shots, individuals with diabetes should undergo a comprehensive evaluation by their healthcare provider. This evaluation should include a review of medical history, current diabetes management strategies, and an assessment of baseline blood sugar levels.
- Healthcare providers may also consider alternative treatment options or adjust the dosage and frequency of cortisone shots based on individual needs and diabetes control.
Blood Sugar Monitoring:
- Regular monitoring of blood glucose levels is essential for individuals with diabetes receiving cortisone shots. Monitoring should occur more frequently during and after treatment to track any changes in blood sugar levels.
- Individuals should follow their healthcare provider’s recommendations for monitoring blood glucose levels, which may involve self-monitoring with a glucometer or continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) system.
Diabetes Medication Adjustment:
- Depending on the individual’s response to cortisone treatment, adjustments to diabetes medications may be necessary to maintain optimal blood sugar control. This may include changes in insulin dosage, oral medications, or other diabetes management strategies.
- Healthcare providers may recommend temporary increases in insulin dosage or adjustments to oral medications to counteract the effects of cortisone on blood sugar levels.
Dietary Modifications:
- Following a balanced diet is important for managing blood sugar levels during cortisone treatment. Individuals should aim to consume a consistent amount of carbohydrates at each meal and snack. This is to help regulate blood sugar levels.
- Healthcare providers may recommend working with a registered dietitian or diabetes educator to develop a personalized meal plan. It takes into account the effects of cortisone on blood sugar levels.
Lifestyle Modifications:
- Engaging in regular physical activity can help improve insulin sensitivity and blood sugar control during cortisone treatment. Individuals should aim for a combination of aerobic exercise, strength training, and flexibility exercises as tolerated.
- Managing stress through relaxation techniques such as deep breathing, meditation, or yoga can also help stabilize blood sugar levels. It also improves overall well-being.
Regular Follow-Up:
- Regular follow-up appointments with healthcare providers are essential for monitoring diabetes control and any potential complications associated with cortisone shots. These appointments provide an opportunity to adjust treatment plans as needed and address any concerns or questions.
Conclusion
Cortisone shots can be effective in managing inflammatory conditionS. However, they may pose risks for individuals with diabetes due to their effects on blood sugar levels. By understanding the relationship between cortisone shots and diabetes and implementing appropriate management strategies, individuals with diabetes can minimize the risks and optimize their overall health and well-being. Open communication with healthcare providers and proactive self-care is essential for navigating this complex medical scenario effectively.
Do you want to get rid of diabetes? Join our online diabetes treatment program and reverse Diabetes naturally through lifestyle changes such as a Personalized Diet plan, Exercise, Yoga, dieticians, and health coaches.