Sulfonylureas are a class of medications commonly prescribed to manage type 2 diabetes mellitus. Since their introduction in the 1950s, these drugs have played a crucial role in diabetes management by helping to regulate blood sugar levels. In this blog, we will explore the mechanisms of sulfonylurea medications, their uses, potential side effects, and considerations for patients and healthcare providers.
Contents
Mechanism of Action of Sulfonylurea Medications
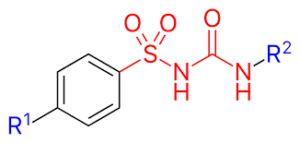
The mechanism of action of sulfonylurea medications involves several key steps in the regulation of insulin secretion and glucose metabolism. Here’s a detailed breakdown of their mechanisms:
Stimulation of Insulin Release:
- Beta Cell Interaction: Sulfonylureas interact with specific receptors on the beta cells of the pancreas, which are responsible for producing insulin.
- Closure of Potassium Channels: Upon binding, sulfonylureas inhibit ATP-sensitive potassium channels on the beta cell membrane. These channels are normally open and allow the efflux of potassium ions, leading to hyperpolarization of the cell.
Calcium Influx and Insulin Secretion:
- Depolarization of Beta Cells: Inhibition of potassium channels causes depolarization of the beta cell membrane.
- Calcium Influx: The depolarization triggers the opening of voltage-gated calcium channels, leading to an influx of calcium ions into the beta cell.
Insulin Granule Release:
- Exocytosis of Insulin Granules: The increase in intracellular calcium levels stimulates the exocytosis of insulin-containing granules from the beta cells into the bloodstream.
Enhanced Insulin Levels and Glucose Uptake:
- Increased Circulating Insulin: The released insulin enters the bloodstream, resulting in elevated levels of circulating insulin.
- Glucose Uptake: Insulin facilitates the uptake of glucose by peripheral tissues, particularly skeletal muscle and adipose tissue.
Lowering Blood Glucose Levels:
- Increased Cellular Glucose Utilization: The enhanced insulin action promotes the utilization of glucose by cells, leading to a reduction in blood glucose levels.
- Inhibition of Hepatic Glucose Production: Insulin also inhibits glucose production by the liver, further contributing to blood glucose control.
Duration of Action:
- Varied Durations: Different sulfonylurea medications have varying durations of action. Some have a short duration and are taken before meals, while others have a longer duration and may be taken once or twice a day.
Common Sulfonylurea Medications
Sulfonylurea medications are a class of drugs commonly used in the management of type 2 diabetes. They work by stimulating the release of insulin from the pancreas, helping to lower blood sugar levels. Here are details about some of the common sulfonylurea medications:
Glyburide (Micronase, Diabeta)
Glyburide, available under brand names such as Micronase and Diabeta, is an oral sulfonylurea medication widely used in the management of type 2 diabetes. This medication is typically administered in tablet form, and its dosing schedule may involve taking it once or twice a day, with or without food. One notable characteristic of glyburide is its long duration of action, providing sustained effects in controlling blood sugar levels. The mechanism of action involves stimulating insulin release from the pancreas, aiding in the uptake of glucose by cells. Glyburide is a valuable tool in the arsenal of antidiabetic medications, contributing to the overall strategy for glycemic control in individuals with type 2 diabetes.
Glipizide (Glucotrol)
Glipizide, marketed under the brand name Glucotrol, is another commonly prescribed sulfonylurea medication. It is available in immediate-release and extended-release oral tablets, offering flexibility in dosing. Immediate-release tablets are typically taken 30 minutes before a meal, while extended-release tablets are taken once a day with breakfast. Glipizide has a shorter duration of action compared to glyburide, making it suitable for specific patient profiles. By interacting with beta cells in the pancreas, glipizide facilitates insulin release, aiding in the regulation of blood glucose levels. Its versatility in dosing makes it a practical choice for individuals seeking tailored diabetes management.
Glimepiride (Amaryl)
Glimepiride, sold under the brand name Amaryl, is an oral sulfonylurea medication known for its long duration of action. Typically administered in tablet form, glimepiride is taken once a day with breakfast or the first main meal. The extended duration of action contributes to a sustained effect on insulin secretion and blood glucose regulation. Like other sulfonylureas, glimepiride stimulates insulin release from the pancreas, promoting glucose uptake by cells. Its once-daily dosing regimen enhances patient adherence and simplifies the management of type 2 diabetes. Glimepiride is often a preferred choice in the array of sulfonylurea medications due to its efficacy and convenience.
Tolbutamide (Orinase)
Tolbutamide, available under the brand name Orinase, is a short-acting sulfonylurea medication administered in oral tablet form. The dosing schedule typically involves taking it one to three times a day with meals. Tolbutamide’s mechanism of action includes interaction with beta cells in the pancreas, leading to insulin release and subsequent glucose uptake. Despite its shorter duration of action compared to some other sulfonylureas, tolbutamide remains a viable option, especially for individuals who may benefit from more frequent dosing throughout the day. It plays a role in the comprehensive approach to managing blood sugar levels in individuals with type 2 diabetes.
Gliclazide
Gliclazide is a sulfonylurea medication available in immediate-release and modified-release oral tablets. The immediate-release form is typically taken before meals, while the modified-release version is administered once a day. Gliclazide’s duration of action is influenced by its formulation, with the modified-release form providing a longer-lasting effect. By stimulating insulin release from the pancreas, gliclazide contributes to glucose regulation and helps manage type 2 diabetes. The dual availability of immediate and modified-release formulations offers healthcare providers flexibility in tailoring treatment plans to individual patient needs and optimizing glycemic control.
Uses of Sulfonylurea Medications
Sulfonylurea medications are commonly prescribed to individuals with type 2 diabetes to help manage their blood sugar levels. Here are the key uses of sulfonylurea medications outlined in points:
- Blood Sugar Regulation: Sulfonylureas play a crucial role in regulating blood glucose levels in individuals with type 2 diabetes by stimulating the release of insulin from the pancreas.
- Type 2 Diabetes Management: These medications are a mainstay in the management of type 2 diabetes, particularly when lifestyle modifications such as diet and exercise are insufficient for maintaining glycemic control.
- Combination Therapy: Sulfonylureas are often prescribed in combination with other antidiabetic medications, such as metformin or thiazolidinediones, to achieve better overall blood sugar management.
- Insulin Secretion Enhancement: The primary mechanism of sulfonylureas involves enhancing insulin secretion from beta cells in the pancreas, promoting the uptake of glucose by cells.
- Adjunct to Lifestyle Modifications: Sulfonylureas are used as an adjunct to lifestyle modifications, including dietary changes and increased physical activity, to optimize blood glucose control.
- Monotherapy or Combination Use: Sulfonylureas may be prescribed as monotherapy (single-drug treatment) or in combination with other antidiabetic medications, depending on the individual patient’s needs and the severity of their condition.
- Effective for Various Patient Profiles: Sulfonylureas can be effective across a range of patient profiles, including those who have recently been diagnosed with type 2 diabetes and those who have been managing the condition for an extended period.
- Reduction of Hyperglycemia Symptoms: By improving insulin action and glucose utilization, sulfonylureas help reduce the symptoms of hyperglycemia, such as excessive thirst, frequent urination, and fatigue.
Considerations for Patients of Sulfonylurea Medications

When considering sulfonylurea medications for the management of type 2 diabetes, patients should be aware of several important considerations. Here are key points for individuals taking sulfonylureas:
- Dosage and Administration: Follow the healthcare provider’s instructions regarding the dosage, timing, and frequency of sulfonylurea medication. Take the medication with or without food, as prescribed.
- Hypoglycemia Risk: Sulfonylureas can lower blood sugar levels, leading to hypoglycemia (low blood sugar). Be aware of symptoms such as sweating, shakiness, dizziness, confusion, and hunger. Understand the importance of regular meals and snacks to help prevent hypoglycemia.
- Monitoring Blood Glucose Levels: Regularly monitor blood glucose levels as directed by the healthcare provider to ensure the medication is effectively controlling blood sugar. Report any unusual patterns or readings to the healthcare team.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Continue making lifestyle changes, including a healthy diet and regular exercise, as recommended by healthcare professionals. Inform the healthcare provider about any significant changes in diet, physical activity, or other habits.
- Interactions with Other Medications: Inform healthcare providers about all medications, including over-the-counter drugs, herbal supplements, and vitamins, to avoid potential interactions. Some medications, such as certain antibiotics or antifungals, may interact with sulfonylureas.
- Kidney and Liver Function: Individuals with impaired kidney or liver function may require dosage adjustments or alternative medications. Regular monitoring of kidney and liver function is essential.
- Pregnancy and Breastfeeding: Inform healthcare providers if planning a pregnancy or if pregnant, as the safety of sulfonylureas during pregnancy is a consideration. Discuss the potential risks and benefits of breastfeeding while on sulfonylurea therapy.
- Allergic Reactions: Be aware of potential allergic reactions, such as rash, itching, or swelling, and seek medical attention if they occur. Report any adverse reactions promptly to the healthcare provider.
Potential Side Effects of Sulfonylurea Medications
While generally well-tolerated, sulfonylureas may cause side effects. Common side effects include weight gain and gastrointestinal issues such as nausea and diarrhea. Rare but serious side effects may include:
- Hypoglycemia Risk: This can cause low blood sugar levels, leading to symptoms like shakiness, sweating, and confusion.
- Weight Gain: This may contribute to weight gain in some individuals.
- Gastrointestinal Issues: Possible side effects include nausea and diarrhea.
- Allergic Reactions: Rarely, sulfonylureas can cause allergic reactions such as rash, itching, or swelling.
- Liver Function: Regular monitoring is essential, as sulfonylureas undergo liver processing.
- Blood Disorders: In rare cases, sulfonylureas may be associated with blood disorders.
It’s important for individuals taking sulfonylureas to be aware of these potential side effects and promptly report any concerns to their healthcare provider. Regular communication with healthcare professionals ensures effective management of diabetes while minimizing side effects.
Conclusion
Sulfonylurea medications have been a cornerstone in the management of type 2 diabetes for many decades. Understanding their mechanisms of action, common medications, uses, and potential considerations is essential for both healthcare providers and patients. As with any medication, an individualized approach to diabetes management, including lifestyle modifications and regular monitoring, remains crucial for achieving optimal outcomes. Patients are encouraged to maintain open communication with their healthcare team to address any concerns or issues related to sulfonylurea therapy.
Do you want to get rid of diabetes? Join our online diabetes treatment program and reverse Diabetes naturally through lifestyle changes such as a Personalized Diet plan, Exercise, Yoga, dieticians, and health coaches.