Living with diabetes can present daily challenges, but with the right management strategies, individuals can lead fulfilling lives while minimizing the impact of the condition on their health. Effective management involves a combination of lifestyle adjustments, medication adherence, regular monitoring, and ongoing support from healthcare professionals. In this guide, we’ll explore various aspects of diabetes management, including diet, exercise, medication, monitoring, and psychological well-being, to empower individuals with diabetes to take control of their health.
Contents
What is Diabetes?

Diabetes is a chronic health condition characterized by elevated levels of glucose (sugar) in the blood. Glucose is a crucial source of energy for the body’s cells, and its levels are typically regulated by insulin, a hormone produced by the pancreas. In diabetes, either the pancreas does not produce enough insulin (Type 1 diabetes), or the body is unable to effectively use the insulin it produces (Type 2 diabetes). There is also a type called gestational diabetes, which occurs during pregnancy.
Type 1 Diabetes: Type 1 diabetes, often referred to as insulin-dependent diabetes or juvenile diabetes, is an autoimmune condition in which the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks and destroys insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas.
Type 2 Diabetes: Type 2 diabetes is the most common form of diabetes, accounting for the majority of diabetes cases worldwide. It occurs when the body becomes resistant to the effects of insulin or fails to produce enough insulin to meet its needs.
Gestational Diabetes: Gestational diabetes develops during pregnancy and is characterized by high blood sugar levels that occur for the first time during pregnancy. It usually resolves after childbirth, but women who have had gestational diabetes have an increased risk of developing Type 2 diabetes later in life.
Common Symptoms of Diabetes: The symptoms of diabetes can vary depending on the type and severity of the condition, but common signs and symptoms include:
- Increased thirst and urination
- Fatigue
- Unexplained weight loss (in Type 1 diabetes)
- Increased hunger
- Blurred vision
- Slow-healing wounds or frequent infections
- Tingling or numbness in the hands or feet
List of Management Strategies for Diabetes
Managing diabetes effectively involves a combination of lifestyle modifications, medication adherence, regular monitoring, and ongoing support from healthcare professionals. Here is a comprehensive list of management strategies for diabetes:
Dietary Management

Diet plays a pivotal role in managing diabetes effectively. Adopting a balanced and nutritious diet can help regulate blood sugar levels, control weight, and reduce the risk of diabetes-related complications. The key principles of dietary management for diabetes include:
Balanced Macronutrient Intake: Focus on consuming a balanced mix of carbohydrates, protein, and fats. Opt for complex carbohydrates with a low glycemic index to prevent rapid spikes in blood sugar levels. Include sources of lean protein such as poultry, fish, tofu, and legumes, and choose healthy fats from sources like avocados, nuts, seeds, and olive oil.
Fiber-Rich Foods: Include plenty of fiber-rich foods in your diet, such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, and nuts. Dietary fiber helps regulate blood sugar levels, promote satiety, and support digestive health. Aim for at least 25 to 30 grams of fiber per day from a variety of sources.
Limit Added Sugars and Refined Carbohydrates: Minimize the intake of foods and beverages high in added sugars, such as sugary drinks, sweets, desserts, and processed snacks. Also, reduce consumption of refined carbohydrates like white bread, white rice, and sugary cereals, which can cause rapid spikes in blood sugar levels.
Regular Meal Timing: Establish a consistent meal schedule with evenly spaced meals and snacks throughout the day. Avoid skipping meals or going long periods without eating, as this can lead to fluctuations in blood sugar levels and overeating later in the day.
Carbohydrate Counting: For individuals who use insulin therapy or certain diabetes medications, carbohydrate counting can be a useful strategy for managing blood sugar levels. Learn to estimate the carbohydrate content of foods and adjust insulin doses accordingly to match carbohydrate intake.
Regular Exercise

Physical activity is a cornerstone of diabetes management, offering numerous health benefits, including improved insulin sensitivity, blood sugar control, cardiovascular health, weight management, and stress reduction. Incorporating regular exercise into your daily routine can help manage diabetes effectively. Here are some key aspects of exercise management for diabetes:
Aerobic Exercise: Engage in moderate-intensity aerobic activities such as brisk walking, cycling, swimming, dancing, or jogging for at least 150 minutes per week, spread over several days. Aerobic exercise helps lower blood sugar levels by increasing glucose uptake by muscles and improving insulin sensitivity.
Strength Training: Include strength training exercises at least two days per week, targeting major muscle groups with exercises such as weightlifting, resistance band workouts, bodyweight exercises, or using weight machines. Strength training helps build muscle mass, which can enhance insulin sensitivity and metabolic health.
Flexibility and Balance Exercises: Incorporate flexibility and balance exercises into your routine to improve joint mobility, reduce the risk of injury, and enhance overall physical function. Activities such as yoga, tai chi, Pilates, and stretching exercises can help improve flexibility, balance, and relaxation.
Individualized Exercise Plan: Work with a certified fitness professional or exercise physiologist who has experience working with individuals with diabetes to develop an individualized exercise plan tailored to your fitness level, health status, goals, and preferences. Consider factors such as age, fitness level, existing health conditions, and any diabetes-related complications when designing your exercise program.
Medications
Medication adherence is crucial for effectively managing diabetes and achieving optimal blood sugar control. For individuals with Type 1 diabetes, insulin therapy is essential for regulating blood sugar levels, while individuals with Type 2 diabetes may require oral medications, injectable medications, or a combination of both to manage their condition. Here are some key considerations for medication management in diabetes:
Understanding Medications: Educate yourself about the medications prescribed to you, including their names, dosages, administration methods, and potential side effects. Understand how each medication works to lower blood sugar levels and improve insulin sensitivity or production.
Follow Prescribed Treatment Plan: Adhere to your healthcare provider’s prescribed treatment plan, including medication dosages, timing, and frequency. Take medications as directed, and do not skip doses or alter dosages without consulting your healthcare team.
Communicate with the Healthcare Team: Maintain open communication with your healthcare team regarding any concerns, questions, or difficulties you may have with your medications. Report any side effects, changes in symptoms, or challenges with adherence promptly so that adjustments can be made as needed.
Regular Medication Reviews: Schedule regular medication reviews with your healthcare provider to assess the effectiveness of your current treatment regimen, monitor for any adverse effects, and make adjustments as necessary. Be proactive in discussing any changes in your health status, lifestyle, or medication needs.
Medication Refills: Ensure that you have an adequate supply of medications on hand to prevent interruptions in treatment. Refill prescriptions promptly, and plan for travel or other situations that may disrupt your access to medications.
Blood Sugar Monitoring
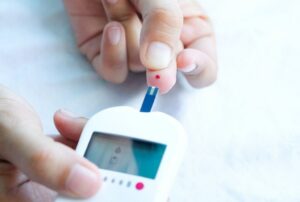
Regular blood sugar monitoring is a critical aspect of diabetes management, providing valuable insights into how various factors such as diet, exercise, medication, and lifestyle choices affect your blood glucose levels. Monitoring allows you to make informed decisions about your diabetes care and helps you maintain optimal blood sugar control. Here are some key components of blood sugar monitoring:
Frequency of Monitoring: Work with your healthcare team to determine the frequency of blood sugar monitoring that’s appropriate for your individual needs. Some individuals may need to check their blood sugar levels multiple times per day, while others may require less frequent monitoring. Factors such as the type of diabetes, treatment regimen, level of glycemic control, and risk of hypoglycemia or hyperglycemia will influence monitoring frequency.
Methods of Monitoring: There are several methods available for blood sugar monitoring, including traditional fingerstick blood glucose testing and continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) systems. Fingerstick testing involves pricking the finger with a lancet to obtain a small blood sample, which is then tested using a blood glucose meter. CGM systems continuously monitor glucose levels throughout the day and night using a sensor inserted under the skin, providing real-time data and trends.
Target Blood Sugar Levels: Establish target blood sugar ranges with your healthcare provider based on factors such as age, health status, diabetes type, treatment goals, and the presence of any complications. Target ranges typically include fasting/pre-meal blood sugar levels, postprandial (after-meal) blood sugar levels, and bedtime blood sugar levels.
Weight Management
Maintaining a healthy weight is essential for managing diabetes effectively, as excess weight, particularly abdominal obesity, is a significant risk factor for insulin resistance and Type 2 diabetes. Achieving and maintaining a healthy weight through a combination of dietary modifications, regular physical activity, and lifestyle changes can improve insulin sensitivity, blood sugar control, and overall health. Here are some key strategies for weight management in diabetes:
Set Realistic Goals: Establish realistic and achievable weight loss goals based on your current weight, health status, and individual preferences. Aim for gradual, sustainable weight loss of 1-2 pounds per week, as rapid weight loss can be difficult to maintain and may not be conducive to long-term success.
Calorie Control: Monitor your calorie intake and aim to create a calorie deficit by consuming fewer calories than you expend through physical activity and metabolism. Focus on nutrient-dense, low-calorie foods such as fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, whole grains, and healthy fats.
Behavioral Changes: Identify and address underlying behaviors and habits that contribute to overeating or sedentary behavior. Keep a food diary, practice stress-reduction techniques, plan meals and snacks, and seek support from friends, family, or a healthcare professional to help overcome barriers to weight management.
Monitor Progress: Track your progress regularly by monitoring changes in weight, body measurements, and body composition over time. Celebrate successes and acknowledge challenges, but avoid becoming discouraged by occasional setbacks. Focus on making gradual, sustainable lifestyle changes that promote long-term health and well-being.
Stress Management

Stress management is an often overlooked but important aspect of diabetes management. Chronic stress can contribute to elevated blood sugar levels through hormonal changes and unhealthy coping behaviors such as emotional eating or neglecting self-care routines. Effectively managing stress can help improve blood sugar control, reduce the risk of complications, and enhance overall well-being. Here are some key strategies for stress management in diabetes:
Identify Stressors: Identify sources of stress in your life, including both external stressors such as work deadlines, financial pressures, or relationship conflicts, and internal stressors such as negative self-talk or perfectionism. Understanding your stress triggers can help you develop targeted coping strategies.
Stress Reduction Techniques: Explore various stress reduction techniques to find what works best for you. Examples include deep breathing exercises, progressive muscle relaxation, meditation, mindfulness practices, guided imagery, yoga, tai chi, or spending time in nature. Experiment with different techniques and incorporate them into your daily routine.
Physical Activity: Regular physical activity is not only beneficial for blood sugar control but also for stress management. Exercise releases endorphins, which are natural mood lifters, and helps reduce levels of stress hormones such as cortisol. Engage in activities you enjoy, whether it’s walking, dancing, cycling, or playing a sport, to reap the stress-relieving benefits of exercise.
Healthy Coping Strategies: Develop healthy coping strategies to manage stress constructively. Practice assertive communication, problem-solving skills, time management techniques, and boundary-setting to address stressors proactively. Seek support from friends, family, or a support group, and don’t hesitate to ask for help when needed.
Mindful Eating: Practice mindful eating to cultivate a healthier relationship with food and reduce stress-related eating behaviors. Pay attention to hunger and fullness cues, savor the taste and texture of each bite, and eat without distractions to enhance awareness and enjoyment of meals.
Relaxation Techniques: Incorporate relaxation techniques into your daily routine to promote relaxation and reduce tension. Take breaks throughout the day to engage in activities that help you unwind, such as listening to music, reading, taking a warm bath, or practicing a hobby.
Prioritize Self-Care: Prioritize self-care activities that promote physical, mental, and emotional well-being. Get adequate sleep, maintain a healthy diet, stay hydrated, and schedule regular relaxation breaks. Set boundaries to protect your time and energy, and make time for activities that bring you joy and fulfillment.
Conclusion
Managing diabetes requires a holistic approach that encompasses dietary modifications, regular exercise, medication adherence, blood sugar monitoring, and attention to psychological well-being. By adopting these strategies and working closely with healthcare providers, individuals with diabetes can achieve better glycemic control, reduce the risk of complications, and improve their overall quality of life. Remember, diabetes management is a journey, and with dedication and perseverance, it is possible to thrive while living with this chronic condition.
Do you want to get rid of diabetes? Join our online diabetes treatment program and reverse Diabetes naturally through lifestyle changes such as a Personalized Diet plan, Exercise, Yoga, dieticians, and health coaches.