Gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) is a condition that develops during pregnancy when the body cannot produce enough insulin to meet its increased needs, leading to high blood sugar levels. While managing gestational diabetes often involves lifestyle changes such as diet and exercise, sometimes medication is necessary to control blood glucose levels effectively. In this blog post, we will delve into the various medications used to manage gestational diabetes, their mechanisms of action, potential side effects, and considerations for their use.
Contents
What is Gestational Diabetes?

Gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) is a type of diabetes that develops during pregnancy. It is characterized by high blood sugar levels that occur for the first time during pregnancy and usually disappear after giving birth. Gestational diabetes occurs when the body cannot produce enough insulin to meet the increased insulin needs during pregnancy.
During pregnancy, the placenta, which connects the baby to the mother’s blood supply, produces hormones that help the baby grow and develop. Some of these hormones can interfere with the body’s ability to use insulin effectively, leading to insulin resistance. As a result, blood sugar levels can rise, leading to gestational diabetes.
Are Medicines Effective for Gestational Diabetes?
Medications can indeed be effective in managing gestational diabetes when lifestyle modifications alone are insufficient to control blood sugar levels. While lifestyle changes such as diet and exercise are often the first line of treatment, medications may be necessary in some cases to achieve optimal glycemic control and reduce the risk of complications for both the mother and the baby.
The effectiveness of medications for gestational diabetes can vary depending on various factors, including the severity of the condition, individual patient characteristics, treatment adherence, and the specific medication used.
List of Gestational Diabetes Medicines
Here’s a list of medications commonly used for the management of gestational diabetes:
Insulin Lispro (Humalog)
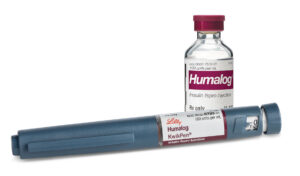
Insulin Lispro, commonly marketed under the brand name Humalog, is one of the insulin analogs frequently used as a medication for managing gestational diabetes.
Also, Insulin Lispro is a rapid-acting insulin analog that works to lower blood sugar levels quickly after meals. It is structurally similar to human insulin but has been modified to have a faster onset of action and shorter duration, making it particularly suitable for controlling postprandial (after-meal) glucose spikes.
For women with gestational diabetes, Insulin Lispro may be prescribed to help regulate blood sugar levels throughout the day, especially in situations where dietary modifications and lifestyle changes alone are insufficient to maintain optimal glycemic control.
Insulin Aspart (Novolog)
Insulin Aspart, commonly known by the brand name NovoLog, is another rapid-acting insulin analog used as a medication for managing gestational diabetes.
Here’s an overview of Insulin Aspart (NovoLog) as a gestational diabetes medicine:
- Rapid-Acting: Insulin Aspart is designed to have a rapid onset of action, typically beginning to lower blood sugar levels within 10 to 20 minutes after injection. This rapid onset makes it effective for controlling postprandial (after-meal) glucose spikes.
- Short Duration: Similar to Insulin Lispro, Insulin Aspart has a relatively short duration of action, typically lasting for about 3 to 4 hours. This shorter duration helps reduce the risk of hypoglycemia between meals.
- Flexibility: Insulin Aspart can be administered shortly before or immediately after meals, providing flexibility in dosing timing to match meal consumption.
- Dosing Adjustments: The dosage of Insulin Aspart is individualized based on factors such as blood sugar levels, carbohydrate intake, physical activity, and insulin sensitivity. Regular monitoring of blood glucose levels is essential to determine the appropriate dosage and make adjustments as needed.
Insulin Glulicine (Apidra)

Insulin Glulisine, commonly known by the brand name Apidra, is another rapid-acting insulin analog used as a medication for managing gestational diabetes.
Here’s an overview of Insulin Glulisine (Apidra) as a gestational diabetes medicine:
- Rapid-Acting: Insulin Glulisine is formulated to have a rapid onset of action, typically starting to lower blood sugar levels within 10 to 15 minutes after injection. This rapid onset makes it effective for controlling postprandial (after-meal) glucose spikes.
- Short Duration: Similar to other rapid-acting insulin analogs, Insulin Glulisine has a relatively short duration of action, typically lasting for about 3 to 4 hours. This shorter duration helps reduce the risk of hypoglycemia between meals.
- Flexibility: Insulin Glulisine can be administered shortly before or immediately after meals, providing flexibility in dosing timing to match meal consumption.
- Dosing Adjustments: The dosage of Insulin Glulisine is individualized based on factors such as blood sugar levels, carbohydrate intake, physical activity, and insulin sensitivity. Regular monitoring of blood glucose levels is essential to determine the appropriate dosage and make adjustments as needed.
- Safety Profile: Insulin Glulisine has been extensively studied and is generally considered safe for use during pregnancy when prescribed under medical supervision. As with other insulin therapies, it is crucial for pregnant women with gestational diabetes to closely monitor their blood sugar levels and adhere to their treatment plan to reduce the risk of complications for both the mother and the baby.
Insulin Glargine (Lantus)
Insulin Glargine, commonly marketed under the brand name Lantus, is a long-acting insulin analog used as a medication for managing gestational diabetes.
Here’s an overview of Insulin Glargine (Lantus) as a gestational diabetes medicine:
- Long-Acting: Insulin Glargine is formulated to provide a long duration of action, typically lasting for about 24 hours. It works gradually and consistently to help control blood sugar levels between meals and overnight.
- Basal Insulin: Insulin Glargine is often used as a basal insulin, which means it provides a background level of insulin to maintain stable blood sugar levels throughout the day. It is typically administered once daily at the same time each day.
- Steady Release: Insulin Glargine is designed to release insulin slowly and steadily over time, mimicking the basal insulin secretion of the pancreas in individuals without diabetes.
Insulin Detemir (Levemir)
Here’s a fresh perspective on Insulin Detemir (Levemir) as a medication for managing gestational diabetes:
- Duration of Action: Insulin Detemir is a long-acting insulin analog with a duration of action lasting up to 24 hours. It provides a steady release of insulin to help maintain stable blood sugar levels throughout the day and night. This consistent action makes it a valuable option for managing gestational diabetes, especially for women who require basal insulin coverage.
- Flexibility in Dosing: Insulin Detemir offers flexibility in dosing, allowing for once-daily or twice-daily administration depending on individual patient needs. This flexibility can accommodate varying insulin requirements throughout the day and simplify treatment regimens for pregnant women with gestational diabetes.
- Reduced Risk of Hypoglycemia: Insulin Detemir is associated with a lower risk of hypoglycemia (low blood sugar) compared to some other long-acting insulin analogs. This attribute is particularly beneficial for pregnant women with gestational diabetes, as hypoglycemia can pose risks to both the mother and the baby.
Metformin

Here’s a comprehensive look at Metformin as a medication for managing gestational diabetes:
- Mechanism of Action: Metformin is an oral medication classified as a biguanide. It works by decreasing glucose production in the liver, increasing insulin sensitivity in peripheral tissues like muscle and fat, and reducing glucose absorption in the intestines. These actions collectively help lower blood sugar levels.
- Treatment of Gestational Diabetes: Metformin is increasingly being used as an alternative or adjunct to insulin therapy for the management of gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM). It is typically considered when lifestyle modifications alone are insufficient to control blood sugar levels during pregnancy.
- Effectiveness: Studies have shown that Metformin can effectively lower blood sugar levels in women with gestational diabetes, potentially reducing the need for insulin therapy. It is particularly beneficial for women who are unable or unwilling to use insulin injections during pregnancy.
- Safety Profile: Metformin has a relatively favorable safety profile and is generally considered safe for use during pregnancy when prescribed under medical supervision. It does not cross the placenta to a significant extent, reducing the risk of fetal exposure. However, as with any medication, potential risks and benefits should be discussed with a healthcare provider.
- Dosage and Monitoring: The dosage of Metformin is individualized based on factors such as blood sugar levels, body weight, and renal function. It is typically initiated at a low dose and gradually increased as needed to achieve optimal glycemic control. Close monitoring of blood glucose levels is essential throughout pregnancy to assess the effectiveness of Metformin therapy.
Glyburide
Here’s an in-depth exploration of Glyburide as a medication for managing gestational diabetes:
- Mechanism of Action: Glyburide is an oral medication belonging to the sulfonylurea class. It works by stimulating insulin secretion from the pancreatic beta cells, thereby lowering blood sugar levels. Glyburide primarily acts to increase the release of endogenous insulin, which helps to control glucose levels in individuals with diabetes.
- Treatment of Gestational Diabetes: Glyburide has been used off-label for the treatment of gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) when lifestyle modifications alone are insufficient to achieve optimal blood sugar control during pregnancy. It is typically considered as an alternative to insulin therapy in certain cases, particularly for women who prefer oral medication over insulin injections.
- Effectiveness: Studies have shown that Glyburide can effectively lower blood sugar levels in women with gestational diabetes, thereby reducing the risk of maternal and fetal complications associated with uncontrolled diabetes during pregnancy. It is particularly beneficial for women who have difficulty with insulin injections or are unable to achieve glycemic targets with lifestyle modifications alone.
- Safety Profile: The safety of Glyburide use during pregnancy has been a topic of debate and ongoing research. While some studies suggest that Glyburide is safe and effective for the treatment of gestational diabetes, others raise concerns about potential adverse outcomes, such as increased neonatal hypoglycemia and macrosomia (large birth weight). Healthcare providers carefully weigh the potential risks and benefits of Glyburide therapy for every patient.
- Dosage and Monitoring: The dosage of Glyburide is individualized based on factors such as blood sugar levels, body weight, and response to treatment. It is typically initiated at a low dose and gradually titrated upward as needed to achieve optimal glycemic control. Close monitoring of blood glucose levels is essential throughout pregnancy to assess the effectiveness and safety of Glyburide therapy.
Tips To Take Gestational Diabetes Medicines
Managing gestational diabetes with medication requires careful attention to detail and adherence to your healthcare provider’s instructions. Here are some tips to help you take gestational diabetes medicines effectively:
- Understand Your Medications: Take the time to learn about the medications prescribed to you, including their names, dosages, how they work, and any potential side effects. Ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist if you have any questions or concerns.
- Follow Your Treatment Plan: Stick to the treatment plan outlined by your healthcare provider. This may include taking medications as prescribed, following a specific diet, monitoring your blood sugar levels regularly, and engaging in recommended physical activity.
- Take Medications as Prescribed: Take your medications exactly as prescribed by your healthcare provider. Follow the recommended dosage and timing instructions carefully. If you have any doubts about how to take your medications, consult your healthcare provider or pharmacist for clarification.
- Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of water throughout the day to stay hydrated. Adequate hydration can help support overall health and may also contribute to better blood sugar management.
- Communicate with Your Healthcare Provider: Keep open lines of communication with your healthcare provider. If you experience any side effects or difficulties with your medications, let them know promptly. Your healthcare provider can provide guidance and make adjustments to your treatment plan as needed.
- Plan Ahead: Ensure you have an adequate supply of medications on hand. Plad for refills to avoid running out of medication. If you need to travel or have any disruptions to your routine, make arrangements to ensure you can continue taking your medications as prescribed.
- Attend Regular Check-ups: Attend all scheduled prenatal appointments and check-ups with your healthcare provider. These appointments allow your healthcare provider to monitor your health, adjust your treatment plan as needed, and address any concerns you may have.
Conclusion
Managing gestational diabetes is essential for the health and well-being of both the mother and the baby. While lifestyle modifications such as diet and exercise play a crucial role, medication may be necessary in some cases to achieve optimal blood sugar control. Insulin therapy remains the cornerstone of treatment for gestational diabetes, but oral medications such as metformin and glyburide may be considered in certain situations. Close monitoring and collaboration between healthcare providers and patients are key to ensuring the safety and effectiveness of gestational diabetes medication.
Remember, the key to successful diabetes management lies in understanding the condition, being vigilant about monitoring, and making informed decisions about your health. Do you want to get rid of diabetes? Join our online diabetes treatment program and reverse Diabetes naturally through lifestyle changes such as a Personalized Diet plan, Exercise, Yoga, dieticians, and health coaches.