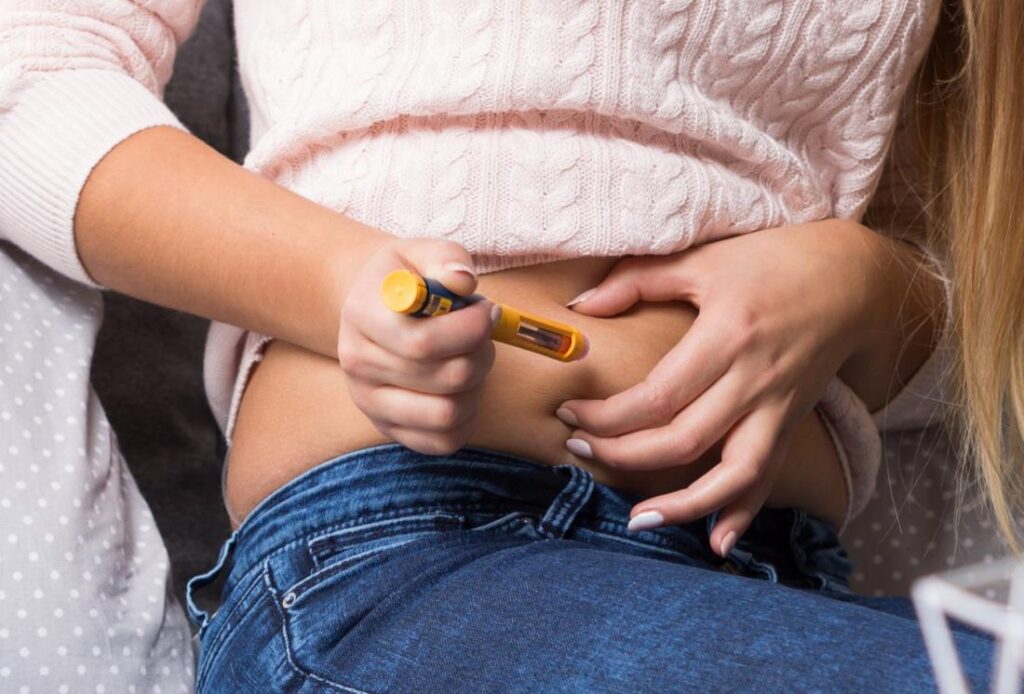
Insulin glulisine is a rapid-acting insulin analog used to control blood sugar levels in people with diabetes mellitus. This synthetic form of insulin acts quickly to regulate glucose levels after meals. In this blog, we will delve into the details of insulin glulisine injection, exploring its uses, benefits, and considerations for those who rely on it to manage their diabetes effectively.
Contents
What is Insulin Glulisine?
Insulin glulisine is a synthetic, rapid-acting insulin analog used in the treatment of diabetes mellitus. It is structurally similar to natural human insulin but has been modified to have a faster onset of action, quicker peak effect, and shorter duration of action. This rapid-acting insulin is designed to mimic the physiological response of the pancreas to mealtime glucose spikes, allowing for more effective control of blood sugar levels.
The development of insulin glulisine was aimed at addressing the limitations of traditional insulins, particularly in managing postprandial hyperglycemia (high blood sugar levels after meals). By acting more rapidly than regular human insulin, insulin glulisine helps prevent sharp increases in blood sugar levels following meals, thereby reducing the risk of complications associated with uncontrolled diabetes.
Insulin glulisine is administered via subcutaneous injection, typically before meals, to coincide with the rise in blood glucose levels that occurs after eating. Its rapid onset of action allows it to start lowering blood sugar levels within minutes after injection, making it an effective option for controlling postprandial hyperglycemia. However, its effects also wear off more quickly compared to regular human insulin, necessitating careful timing of injections to maintain stable blood sugar levels throughout the day.
How Does Insulin Glulisine Work?
Insulin glulisine works by mimicking the action of natural insulin in the body to regulate blood sugar levels. Here’s a detailed explanation of how it works:
- Injection and Absorption: Insulin glulisine is administered via subcutaneous injection, typically into the fatty tissue just beneath the skin. Once injected, the insulin is absorbed into the bloodstream at a relatively rapid rate compared to regular human insulin.
- Bloodstream Delivery: After entering the bloodstream, insulin glulisine travels to target cells throughout the body. These target cells include muscle cells, fat cells, and liver cells.
- Cellular Uptake of Glucose: Insulin glulisine binds to insulin receptors on the surface of target cells, triggering a series of biochemical reactions within the cells. One of the primary effects of insulin binding to its receptors is the translocation of glucose transporter proteins (GLUT4) from inside the cell to the cell membrane.
- Glucose Transport: The presence of GLUT4 proteins on the cell membrane allows for the facilitated transport of glucose molecules from the bloodstream into the interior of the cell. This process is essential for cells to utilize glucose as a source of energy or for storage.
- Blood Sugar Regulation: By promoting the uptake of glucose into cells, insulin glulisine helps to lower the concentration of glucose in the bloodstream. This action is particularly important after meals when blood sugar levels tend to rise due to the digestion and absorption of carbohydrates.
- Metabolic Effects: In addition to its effects on glucose uptake, insulin glulisine also exerts various metabolic effects on target cells. These include promoting the synthesis of glycogen (the storage form of glucose) in the liver and inhibiting the breakdown of stored glycogen into glucose (glycogenolysis). Insulin glulisine also inhibits the production of glucose by the liver (gluconeogenesis).
Uses of Insulin Glulisine
Insulin glulisine is primarily used in the management of diabetes mellitus, a chronic condition characterized by high blood sugar levels resulting from insufficient insulin production or impaired insulin function. Here are the key uses of insulin glulisine:
Control of Postprandial Hyperglycemia
One of the primary uses of insulin glulisine is to control blood sugar levels following meals, known as postprandial hyperglycemia. When insulin glulisine is administered before meals, it helps to counteract the rise in blood glucose that occurs after eating by facilitating the uptake of glucose into cells. This helps prevent sharp spikes in blood sugar levels and promotes better overall glycemic control.
Mealtime Insulin Therapy
Insulin glulisine is often prescribed as part of a comprehensive insulin regimen for individuals with type 1 diabetes or type 2 diabetes who require insulin therapy. It can be used in combination with long-acting basal insulins or oral diabetes medications to provide mealtime coverage and maintain stable blood sugar levels throughout the day.
Correction of High Blood Sugar Levels
In addition to its role in mealtime insulin therapy, insulin glulisine can also be used to correct high blood sugar levels (hyperglycemia) between meals or outside of mealtime. By acting rapidly to lower blood glucose levels, insulin glulisine helps bring elevated blood sugar levels back into the target range.
Flexible Dosing Options
Insulin glulisine offers flexibility in dosing, as it can be administered shortly before meals or even after meals, depending on individual preferences and mealtime insulin requirements. This flexibility allows for better customization of insulin therapy to match varying insulin needs throughout the day.
Insulin Pump Therapy
Insulin glulisine can also be used in insulin pump therapy, where it is continuously infused subcutaneously to provide basal insulin coverage throughout the day and deliver bolus doses to cover meals or correct high blood sugar levels. Its rapid onset of action and short duration make it suitable for use in insulin pumps.
Gestational Diabetes
In some cases of gestational diabetes (diabetes that develops during pregnancy), insulin therapy may be necessary to control blood sugar levels and reduce the risk of complications for both the mother and the baby. Insulin glulisine may be prescribed in such cases to help manage postprandial hyperglycemia and ensure optimal glycemic control during pregnancy.
Benefits of Insulin Glulisine
Insulin glulisine offers several benefits for individuals with diabetes, particularly in terms of its rapid onset of action, shorter duration of action, and flexibility in dosing. Here are the key benefits of insulin glulisine:
Rapid Onset of Action
Insulin glulisine has a rapid onset of action, typically starting to lower blood sugar levels within 15 minutes after injection. This rapid onset makes it particularly effective for controlling postprandial hyperglycemia, as it can quickly counteract the rise in blood glucose levels that occurs after meals. By acting faster than regular human insulin, insulin glulisine helps to minimize spikes in blood sugar levels, promoting better overall glycemic control.
Quick Peak Effect
In addition to its rapid onset, insulin glulisine also reaches peak concentration in the bloodstream more quickly compared to regular insulin. This quick peak effect allows it to exert its maximum glucose-lowering action shortly after injection, helping to address the immediate rise in blood sugar levels following meals.
Shorter Duration of Action
Insulin glulisine has a shorter duration of action compared to regular human insulin, meaning that its effects wear off more quickly. This shorter duration helps to reduce the risk of hypoglycemia (low blood sugar) between meals, as insulin activity diminishes within a few hours after injection. Individuals using insulin glulisine may have more flexibility in their dosing schedule, as they can adjust their insulin doses to match their mealtime requirements without the prolonged risk of hypoglycemia.
Flexibility in Dosing
Insulin glulisine offers flexibility in dosing, as it can be administered shortly before meals or even after meals, depending on individual preferences and mealtime insulin requirements. This flexibility allows for better customization of insulin therapy to match varying insulin needs throughout the day. It also provides individuals with diabetes greater control over their blood sugar levels, as they can adjust their insulin doses based on factors such as meal size, carbohydrate content, and anticipated physical activity.
Reduced Risk of Weight Gain
Rapid-acting insulins like insulin glulisine may be associated with a lower risk of weight gain compared to some other forms of insulin therapy. By more closely mimicking the physiological action of insulin in response to meals, insulin glulisine helps to regulate glucose metabolism without promoting excessive storage of calories as fat. This can be particularly beneficial for individuals who are concerned about weight management as part of their diabetes treatment.
Improved Quality of Life
The rapid onset, shorter duration, and flexibility in dosing offered by insulin glulisine can contribute to an improved quality of life for individuals with diabetes. By providing more precise control over blood sugar levels and minimizing the risk of hypoglycemia, insulin glulisine allows individuals to better manage their diabetes while accommodating their lifestyle and dietary preferences. This improved control can lead to greater confidence in diabetes management and a reduced burden of living with the condition.
Considerations When Using Insulin Glulisine Injection
While insulin glulisine offers several benefits for individuals with diabetes, there are important considerations to keep in mind when using this medication. Here are some key considerations:
Hypoglycemia Risk
Like all insulin therapies, insulin glulisine carries the risk of hypoglycemia (low blood sugar). Because it acts rapidly and has a shorter duration of action, there is a higher risk of hypoglycemia if the timing of insulin administration does not match meal consumption or if insulin doses are not adjusted appropriately. Individuals using insulin glulisine should be educated about the signs and symptoms of hypoglycemia and how to treat it promptly.
Injection Site Rotation
Rotating injection sites are important to prevent lipodystrophy (changes in fat tissue) and ensure consistent absorption of insulin. Continuous use of the same injection site can lead to poor insulin absorption and variability in blood sugar levels. Healthcare providers should educate patients on proper injection techniques and the importance of rotating injection sites regularly.
Meal Timing and Consistency
Because insulin glulisine is rapid-acting, it should be administered shortly before meals to coincide with the rise in blood sugar levels that occurs after eating. Meal timing and consistency are essential for optimizing blood sugar control and minimizing the risk of hypoglycemia. Individuals using insulin glulisine should be advised to adhere to a consistent meal schedule and monitor their blood sugar levels closely to adjust insulin doses as needed.
Individualized Dosing
The dose of insulin glulisine may vary depending on factors such as meal size, carbohydrate content, blood sugar levels, and insulin sensitivity. Healthcare providers should work closely with patients to determine the appropriate dose of insulin glulisine for optimal blood sugar control. Adjustments to insulin doses may be necessary based on changes in diet, physical activity, illness, or other factors that affect insulin requirements.
Pump Therapy Considerations
Insulin glulisine can be used in insulin pump therapy. This is where it is continuously infused subcutaneously to provide basal insulin coverage and deliver bolus doses to cover meals or correct high blood sugar levels. However, individuals using insulin glulisine in pump therapy should be vigilant about monitoring their blood sugar levels and adjusting pump settings as needed to prevent hyperglycemia or hypoglycemia.
Storage and Handling
Insulin glulisine should be stored according to the manufacturer’s recommendations, typically at cool room temperature (between 36°F and 86°F or 2°C and 30°C) and away from direct heat and sunlight. Insulin should not be frozen, exposed to extreme temperatures, or stored in the refrigerator door. Patients should also check the expiration date and inspect the appearance of insulin glulisine before each use to ensure its effectiveness and safety.
Conclusion
Insulin glulisine injection plays a vital role in the management of diabetes, offering rapid and effective control of postprandial blood sugar levels. Its fast onset of action, short duration of action, and flexibility in dosing make it a valuable option for individuals seeking to achieve tighter control over their diabetes.
However, it’s crucial to use insulin glulisine judiciously, following healthcare provider guidance and closely monitoring blood sugar levels to minimize the risk of complications. With proper education and support, insulin glulisine can empower individuals with diabetes to lead healthier and more fulfilling lives.
Do you want to get rid of diabetes? Join our online diabetes treatment program and reverse Diabetes naturally through lifestyle changes such as a Personalized Diet plan, Exercise, Yoga, dieticians, and health coaches.

