Living with diabetes means paying extra attention to your health, particularly when it comes to your feet. Diabetic individuals are more susceptible to foot problems due to the reduced blood flow and nerve damage (neuropathy) that often accompany this condition. One common issue is the care of toenails, which, if not properly managed, can lead to complications. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the crucial steps and best practices for diabetic toenails treatment, ensuring that you maintain healthy feet and avoid any serious problems.
Contents
What Does a Diabetic Toenail Look Like?
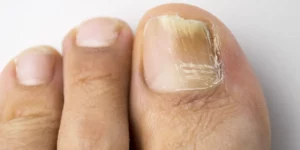 Diabetic toenails can exhibit several characteristic changes, largely due to the complications associated with diabetes, such as poor circulation and nerve damage. Here are some common signs to look out for in diabetic toenails:
Diabetic toenails can exhibit several characteristic changes, largely due to the complications associated with diabetes, such as poor circulation and nerve damage. Here are some common signs to look out for in diabetic toenails:
- Thickening of the Nails: One of the most noticeable changes is the thickening of the toenails. This can occur due to reduced circulation to the feet. This affects the health of the nails.
- Fungal Infections: Diabetics are more prone to fungal infections like athlete’s foot. It can cause the toenails to become discolored (often yellow or brown), brittle, and crumbly.
- Ingrown Toenails: Due to nerve damage (neuropathy), individuals with diabetes might not feel pain from improperly cut or ingrown toenails until they are significantly worsened.
- Changes in Nail Color: Toenails may turn yellowish, but other colors like brown or black can also appear, especially if there is a fungal infection or a subungual hematoma (bleeding under the nail) due to minor trauma.
- Increased Curvature: The nails might become more curved or rounded, a condition known as onychogryphosis. It can make them difficult to trim.
- Brittleness and Splitting: The nails might become more brittle, leading to splitting or cracking, which can expose the nail bed to infections.
- Slow Growth: Poor blood circulation can also cause the toenails to grow more slowly than usual.
- Deformities: In some cases, the toenails may develop deformities or unusual shapes.
It’s important to note that while these symptoms can be common in diabetic toenails, they can also be indicative of other health issues. Regular foot inspections and consultations with healthcare professionals, particularly for individuals with diabetes, are essential for proper diagnosis and treatment.
What Are Some Effective Diabetic Toenails Treatment Options?
 Managing diabetic toenails effectively is crucial to prevent complications such as infections or foot ulcers. Here are some best diabetic toenails treatment options and best practices:
Managing diabetic toenails effectively is crucial to prevent complications such as infections or foot ulcers. Here are some best diabetic toenails treatment options and best practices:
Proper Toenail Trimming
Proper toenail trimming is a cornerstone of diabetic foot care. Toenails should be trimmed straight across, rather than rounded, to prevent ingrown toenails, a common and painful condition. Cutting them too short should also be avoided as it can lead to infection. After trimming, it’s beneficial to gently file the edges with an emery board to smooth any sharp corners that might catch and tear. Individuals with diabetes should check their feet for any cuts or wounds after trimming, and if vision or flexibility is an issue, seeking assistance from a healthcare professional for nail care is recommended.
Regular Foot Inspections
Daily foot inspections are crucial for individuals with diabetes. This process involves checking the entire foot, including the toenails, for any changes or abnormalities such as cuts, sores, blisters, redness, or nail discoloration. This is important because diabetes can lead to reduced sensation in the feet, meaning injuries might not be immediately noticed. Using a mirror can help to see the bottom of the feet, or asking someone else to check can be helpful.
Maintain Good Foot Hygiene
Good foot hygiene involves washing the feet daily with mild soap and lukewarm water. It’s important to thoroughly dry the feet, especially between the toes, to prevent fungal infections. Moisturizing the feet is also key, but avoid applying lotion between the toes as this can create a moist environment conducive to fungal growth. Regular cleaning prevents harmful bacteria and reduces the risk of infections.
Wear Proper Footwear
Diabetics should wear shoes that fit well and protect their feet. Shoes that are too tight can cause pressure spots, leading to ulcers, while shoes that are too loose can cause friction and blisters. Diabetic shoes are specifically designed to reduce the risk of skin breakdown in diabetics with pre-existing foot disease. Additionally, wearing clean, dry socks, preferably those made from materials that wick away moisture, can further protect the feet.
Manage Blood Sugar Levels
Effective control of blood sugar levels is essential in reducing the risk of complications, including those affecting the feet and toenails. High blood sugar can lead to poor circulation and nerve damage, which makes it harder for foot injuries to heal and increases the risk of infection. Following a healthy diet, maintaining an exercise regimen, and adhering to prescribed diabetes medications are key strategies for managing blood sugar levels.
Visit a Podiatrist
Regular visits to a podiatrist are vital for anyone with diabetes. A podiatrist specializes in foot care and can provide critical support in managing the unique challenges that diabetics face with their feet. They can professionally trim toenails, especially for patients who have difficulty doing so themselves due to poor vision or physical limitations. Podiatrists also play a crucial role in the early identification and treatment of foot problems, such as ingrown toenails, fungal infections, or foot ulcers.
Avoid DIY Foot Procedures
 Diabetics should avoid do-it-yourself procedures for foot issues, such as attempting to remove corns, calluses, or warts at home. These procedures can easily lead to injuries or infections. Over-the-counter treatments for such conditions may not be suitable for diabetics and can cause skin burns or ulcers. Any foot problems should be evaluated and treated by a healthcare professional, preferably a podiatrist, to ensure safe and effective care.
Diabetics should avoid do-it-yourself procedures for foot issues, such as attempting to remove corns, calluses, or warts at home. These procedures can easily lead to injuries or infections. Over-the-counter treatments for such conditions may not be suitable for diabetics and can cause skin burns or ulcers. Any foot problems should be evaluated and treated by a healthcare professional, preferably a podiatrist, to ensure safe and effective care.
Orthotics or Special Shoes
In some cases, diabetics may benefit from custom-made orthotics or special shoes designed to accommodate specific foot conditions. These can help distribute pressure more evenly across the foot, reducing the risk of ulcers and other complications. Diabetic shoes are designed with a higher toe box to prevent pressure on the toes and toenails, and without seams that can rub against the skin. Orthotics can correct alignment issues and improve comfort. A podiatrist can assess the need for these aids and ensure they fit correctly.
Stay Active
Physical activity is important for overall health and is particularly beneficial for blood circulation in the legs and feet. Improved circulation aids in faster healing and reduces the risk of complications. However, diabetics should choose low-impact exercises to avoid foot injuries and should always wear appropriate footwear. Consulting with a healthcare provider before starting a new exercise regimen is essential to ensure the activities are safe and appropriate for their specific health conditions.
Seek Immediate Medical Attention for Injuries
Any injuries to the feet, such as cuts, sores, blisters, or infections, require immediate medical attention for individuals with diabetes. Due to reduced sensation and slower healing, what might seem like minor injuries can quickly escalate into serious complications. Early intervention by a healthcare professional can prevent infections, ulcers, and other severe consequences.
Laser Therapy and Other Advanced Treatments
For severe or stubborn toenail problems, such as chronic fungal infections, advanced treatments like laser therapy may be considered. Laser therapy can be effective in treating toenail fungus resistant to traditional medications. However, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare provider to understand the benefits and risks of these treatments. Other advanced treatments may include surgical interventions for ingrown toenails or severe deformities. These should only be considered under professional medical advice and as part of a comprehensive diabetic foot care plan.
Each diabetic individual’s needs can vary. So it’s important to have a personalized diabetic toenails treatment plan. Regular consultations with healthcare providers, including a podiatrist, are essential for effective management and to avoid complications associated with diabetic toenails.
How Do Diabetics Get Rid Of Toenail Fungus?
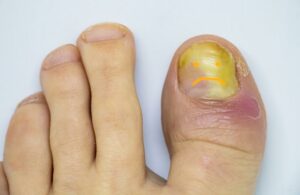 Treating toenail fungus in individuals with diabetes can be more challenging due to the potential for complications like reduced blood flow and nerve damage in the feet. However, there are several approaches to effectively manage and treat fungal infections:
Treating toenail fungus in individuals with diabetes can be more challenging due to the potential for complications like reduced blood flow and nerve damage in the feet. However, there are several approaches to effectively manage and treat fungal infections:
- Topical Antifungal Medications
These are applied directly to the affected nail and surrounding skin. Over-the-counter options include creams, ointments, and lacquers. However, their effectiveness can be limited for more severe infections or for nails that are very thickened.
- Oral Antifungal Medications
Oral treatments are often more effective than topical ones for treating toenail fungus. Common prescriptions include terbinafine (Lamisil) and itraconazole (Sporanox). These medications can have side effects and may interact with other drugs, so they must be used under medical supervision, especially in diabetics who often take multiple medications.
- Preventive Measures and Good Hygiene
Keeping the feet clean and dry is essential. Fungus thrives in moist environments, so reducing moisture around the feet can help prevent fungal growth. Socks should be changed regularly, especially if feet become sweaty. Also, shoes should be well-ventilated; alternating shoes can also give them time to dry out between wearings.
- Natural Remedies and Over-the-Counter Options
Some people use natural remedies like tea tree oil or vinegar soaks, but their effectiveness isn’t scientifically proven, and they should be used with caution. Before trying any home remedy, it’s best to consult with a healthcare provider.
- Avoiding Home Surgery
Never attempt to remove part of an infected toenail at home. This can lead to wounds and potentially serious infections. Diabetics need to approach toenail fungus treatment cautiously and under medical guidance. Over-the-counter treatments might not be as effective for severe infections, and some remedies might not be suitable due to the complexities of diabetes.
Consulting with a healthcare provider, particularly a podiatrist, is the safest way to determine the best treatment plan.
Conclusion
In conclusion, diabetic toenails treatment care requires a blend of vigilance, good hygiene practices, and professional medical guidance. Whether it’s through proper toenail trimming, maintaining clean and dry feet, wearing suitable footwear, or seeking timely treatment for fungal infections, each step plays a crucial role in preventing complications. Regular foot inspections and controlling blood sugar levels are essential components of this care.
Always consult with healthcare professionals, especially a podiatrist, to ensure safe and effective management of your foot health. Make sure to join our online diabetes treatment program and reverse Diabetes naturally through lifestyle changes.