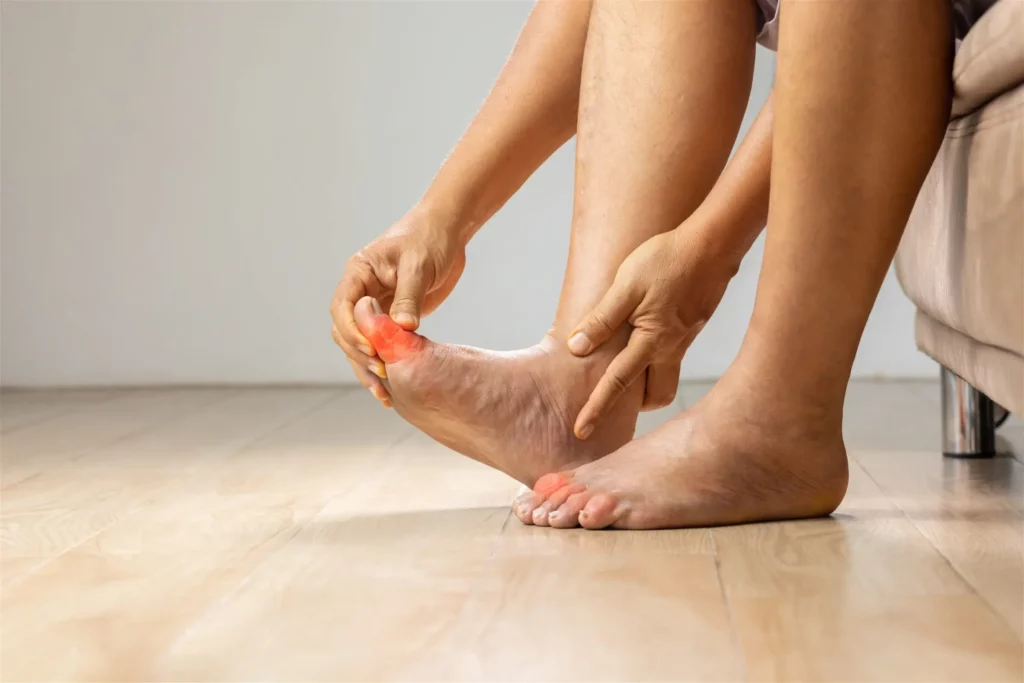
Diabetic foot neuropathy, a common and serious complication of diabetes, can lead to a loss of sensation in the feet, increasing the risk of injuries and infections. This condition not only affects physical health but can also have a significant impact on quality of life. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and available treatments is crucial for individuals living with diabetes. In this guide, we delve into several diabetic foot neuropathy treatments.
Contents
What is Diabetic Foot Neuropathy?
 Diabetic foot neuropathy refers to a type of nerve damage that occurs as a complication of diabetes. High levels of glucose in the blood over an extended period can lead to damage to the nerves, particularly those in the feet. This damage can result in a range of symptoms, including numbness, tingling, burning sensations, and weakness in the feet. As the condition progresses, individuals may experience a loss of sensation, making it difficult to detect injuries or infections.
Diabetic foot neuropathy refers to a type of nerve damage that occurs as a complication of diabetes. High levels of glucose in the blood over an extended period can lead to damage to the nerves, particularly those in the feet. This damage can result in a range of symptoms, including numbness, tingling, burning sensations, and weakness in the feet. As the condition progresses, individuals may experience a loss of sensation, making it difficult to detect injuries or infections.
The impact of diabetic foot neuropathy extends beyond physical discomfort, affecting mobility and overall quality of life. Individuals with this condition may face challenges in performing daily activities. Managing diabetic foot neuropathy requires a multidisciplinary approach to prevent further nerve damage and complications.
What Is The Best Diabetic Foot Neuropathy Treatment?
The diabetic foot neuropathy treatment typically involves a combination of medical approaches aimed at managing symptoms, slowing the progression of nerve damage, and preventing complications. Some of the most common medical approaches include:
1. Medications
- Pain relievers: Over-the-counter pain medications such as acetaminophen or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) may provide relief from mild to moderate neuropathic pain.
- Prescription medications: Antidepressants such as tricyclic antidepressants (amitriptyline, nortriptyline) or serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (duloxetine, venlafaxine) and anticonvulsants such as pregabalin and gabapentin are often prescribed to help manage neuropathic pain.
- Topical treatments: Creams, gels, or patches containing capsaicin or lidocaine may provide localized pain relief.
2. Nerve-stimulating medications
- Medications such as alpha-lipoic acid may help improve nerve function and reduce symptoms of neuropathy.
3. Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS)
- TENS therapy involves the use of a small device that delivers low-voltage electrical currents to the affected area, helping to relieve pain and improve nerve function.
4. Physical therapy
- Physical therapy techniques such as stretching exercises, massage, and balance training can help improve muscle strength, flexibility, and coordination, reducing the risk of falls and injuries.
5. Orthopedic devices
- Custom-made orthotic inserts or braces may help alleviate pressure on the feet, reduce pain, and prevent further damage.
6. Surgical interventions
- In severe cases of diabetic neuropathy where conservative treatments have failed, surgical procedures such as decompression surgery or nerve removal may be considered to relieve pressure on nerves or alleviate severe pain.
Individuals with diabetic neuropathy need to work closely with their healthcare providers to develop a personalized diabetic foot neuropathy treatment plan tailored to their specific symptoms and needs. Additionally, maintaining optimal blood sugar control, adopting a healthy lifestyle, and practicing good foot care are crucial components of managing diabetic neuropathy and preventing complications.
How Can I Prevent Diabetic Foot Neuropathy?
 Preventing diabetic foot neuropathy involves a proactive approach to managing diabetes and minimizing the risk factors associated with nerve damage. Here are some key strategies to help prevent diabetic foot neuropathy:
Preventing diabetic foot neuropathy involves a proactive approach to managing diabetes and minimizing the risk factors associated with nerve damage. Here are some key strategies to help prevent diabetic foot neuropathy:
Maintain optimal blood sugar levels
Consistently high blood sugar levels can damage nerves over time, leading to neuropathy. Work closely with your healthcare team to establish and maintain target blood sugar levels through a combination of medication, dietary adjustments, and regular physical activity. Monitor your blood sugar levels as recommended and adjust your treatment plan as needed to keep levels within the target range.
Manage other health conditions
Conditions such as high blood pressure and high cholesterol can exacerbate nerve damage and impair circulation, increasing the risk of diabetic foot neuropathy. Follow your healthcare provider’s recommendations for managing these conditions. This may include medications, lifestyle changes, and regular monitoring.
Quit smoking
Smoking narrows blood vessels and reduces blood flow to the extremities, including the feet. This can exacerbate existing nerve damage and increase the risk of complications such as ulcers and infections. Seek support and resources to quit smoking, such as nicotine replacement therapy, counseling, or support groups.
Exercise regularly
Regular physical activity improves blood circulation, helps control blood sugar levels, and promotes overall health. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise per week, along with strength training exercises at least two days per week. If you have neuropathy-related foot pain or other limitations, consult with your healthcare provider or a physical therapist to develop a safe and effective exercise plan.
Inspect feet daily
Daily foot inspections are crucial for identifying any signs of injury or infection early on. Use a mirror or enlist the help of a family member or caregiver to check the bottoms of your feet if necessary. Look for cuts, bruises, blisters, redness, swelling, or changes in skin color or temperature. Report any abnormalities to your healthcare provider promptly.
Practice proper foot care
Keep your feet clean and dry to prevent infections. Wash your feet daily with lukewarm water and mild soap, and pat them dry thoroughly, paying special attention to the areas between the toes. Apply moisturizer to prevent dry skin, but avoid applying it between the toes to prevent moisture buildup. This can increase the risk of fungal infections. Trim your toenails straight across and file any sharp edges to prevent ingrown toenails.
Choose appropriate footwear
Select shoes that fit well and provide adequate support and cushioning. Opt for shoes with a wide toe box to prevent pressure and friction on the toes. Avoid high heels, pointy-toed shoes, and shoes with seams or stitching that could rub against the skin and cause irritation. Wear moisture-wicking socks to keep your feet dry and reduce the risk of fungal infections.
Protect feet from extreme temperatures
Extreme temperatures can affect circulation and increase the risk of injury. Avoid exposing your feet to hot surfaces, such as heating pads or hot water, as well as cold temperatures. Wear appropriate footwear and protective gear when walking on hot pavement or cold surfaces, and use caution to prevent burns or frostbite.
Attend regular foot exams
 Schedule regular foot exams with a healthcare provider, preferably a podiatrist or diabetes specialist, to assess your foot health and identify any issues early on. Your healthcare provider can perform comprehensive foot exams, including checking for sensation, circulation, and structural abnormalities, and provide personalized recommendations for foot care and preventive measures.
Schedule regular foot exams with a healthcare provider, preferably a podiatrist or diabetes specialist, to assess your foot health and identify any issues early on. Your healthcare provider can perform comprehensive foot exams, including checking for sensation, circulation, and structural abnormalities, and provide personalized recommendations for foot care and preventive measures.
By implementing these preventive measures and staying vigilant about foot care, individuals with diabetes can reduce their risk of developing diabetic foot neuropathy and maintain optimal foot health. Consistency and proactive management are key to preventing complications and preserving quality of life.
Can You Live a Long Life With Diabetic Neuropathy?
Yes, it is possible to live a long life with diabetic neuropathy. While diabetic neuropathy can significantly impact daily life due to symptoms such as pain, numbness, and loss of sensation in the feet and legs, proactive management strategies can help individuals effectively cope with the condition. Optimal diabetes management is key. Controlling blood sugar levels can help slow the progression of neuropathy and reduce the risk of complications.
Moreover, addressing neuropathic pain through a combination of medications, physical therapy, and lifestyle adjustments can improve quality of life and overall well-being. While living with diabetic neuropathy may present challenges, still people can lead fulfilling lives. Many individuals with diabetic neuropathy continue to enjoy active and productive lives, maintaining longevity and overall health with proper management and support
Conclusion
In conclusion, with diabetic foot neuropathy treatment including proactive management, and proper care, individuals can lead fulfilling lives and maintain overall health. By prioritizing optimal diabetes management, practicing regular foot care, managing neuropathic pain, adopting a healthy lifestyle, and seeking support from healthcare providers and loved ones, individuals can mitigate the risks associated with diabetic neuropathy and prevent complications.
While the condition may require adjustments and perseverance, it is possible to enjoy a long and rewarding life despite the challenges posed by diabetic foot neuropathy. Do you want to get rid of diabetes? Join our online diabetes treatment program and reverse Diabetes naturally through lifestyle changes such as a Personalized Diet plan, Exercise, Yoga, dieticians, and health coaches.

