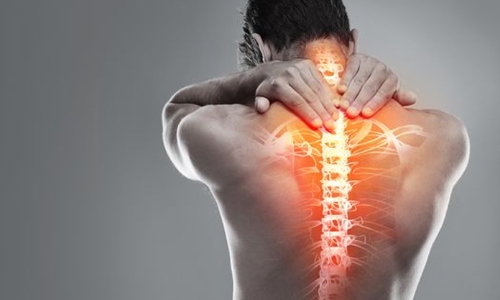
Diabetes, a chronic condition affecting millions worldwide, not only impacts blood sugar levels but also can lead to various physical discomforts, including body aches and pains. These discomforts can significantly affect the quality of life for those living with diabetes. In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the reasons behind these pains and most importantly, effective diabetes body aches and pains treatment.
Contents
Can Diabetes Make You Ache All Over?
 Yes, diabetes can indeed cause aches and pains throughout the body. This discomfort is often due to various complications and effects of diabetes, including:
Yes, diabetes can indeed cause aches and pains throughout the body. This discomfort is often due to various complications and effects of diabetes, including:
- Diabetic Neuropathy: One of the most common reasons for body aches in individuals with diabetes is neuropathy, particularly peripheral neuropathy. High blood sugar levels can damage nerves throughout the body, leading to pain, tingling, and numbness, typically in the hands and feet. However, this discomfort can sometimes be more widespread.
- Musculoskeletal Issues: Diabetes can lead to changes in the musculoskeletal system, causing conditions like frozen shoulder, carpal tunnel syndrome, and arthritis. These conditions can result in pain and stiffness in different parts of the body.
- Poor Circulation: Diabetes can affect blood circulation, leading to cramps and pains, especially in the legs. Poor circulation can also slow down the healing process, making individuals more susceptible to pain from injuries or infections.
- Inflammatory Conditions: High blood sugar levels can lead to chronic inflammation, contributing to widespread body aches and pains.
- Skin Conditions: Diabetic dermopathy and other skin conditions associated with diabetes can cause discomfort and pain on the skin’s surface.
- Kidney Disease: Diabetes can lead to kidney problems, which in some cases, might cause pain in the back or sides.
It’s important for individuals with diabetes experiencing widespread body aches to consult a healthcare professional. These symptoms might indicate the need for better blood sugar control or a specific treatment for diabetes-related complications.
What Are Some Diabetes Body Aches And Pains Treatment?
Yes, diabetes can lead to body aches and pains in various ways. High blood sugar levels can cause inflammation and nerve damage, leading to discomfort and pain in different parts of the body. Here are some treatments and management strategies for body aches and pains associated with diabetes:
Blood Sugar Control
Effective management of blood sugar levels is paramount in preventing or minimizing the body aches and pains associated with diabetes. Consistently high blood sugar levels can lead to complications such as diabetic neuropathy, where nerve damage causes pain, tingling, or numbness. By maintaining blood glucose within recommended ranges through medication, diet, and lifestyle adjustments, one can significantly reduce the risk of these painful complications.
Medications
- Pain Relievers: Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen, can be effective for managing mild to moderate pain. However, it’s essential to use these medications judiciously, as excessive use can lead to other health issues.
- Antidepressants: Certain antidepressants, particularly those in the tricyclic and SNRI categories, have been found effective in treating neuropathic pain in diabetic patients. They work by altering the chemical processes in the brain that cause pain.
- Anticonvulsants: Medications originally developed for epilepsy, like gabapentin and pregabalin, are frequently prescribed to treat nerve pain. They work by stabilizing electrical activity in the nerves and preventing pain signals from reaching the brain.
Physical Activity and Exercise
 Regular exercise is a cornerstone of diabetes management, offering multiple benefits including pain reduction. Exercise improves blood flow, reduces inflammation, and strengthens muscles, thereby helping to alleviate aches and pains. Low-impact exercises such as walking, swimming, or yoga can be particularly beneficial for those with joint pain or mobility issues. Exercise also enhances insulin sensitivity, which helps in better blood sugar control.
Regular exercise is a cornerstone of diabetes management, offering multiple benefits including pain reduction. Exercise improves blood flow, reduces inflammation, and strengthens muscles, thereby helping to alleviate aches and pains. Low-impact exercises such as walking, swimming, or yoga can be particularly beneficial for those with joint pain or mobility issues. Exercise also enhances insulin sensitivity, which helps in better blood sugar control.
Physical Therapy
A physical therapist can tailor an exercise program to address specific pain points and improve overall physical function. Physical therapy might include stretching exercises to improve flexibility, strength training to build muscle support around painful joints, and aerobic exercises to enhance circulation. Additionally, physical therapists can provide education on proper body mechanics and posture to reduce strain on the body.
Diet and Nutrition
A diet rich in nutrients, low in sugar, and unhealthy fats, can play a vital role in managing diabetes and associated pains. Foods high in antioxidants, like berries, leafy greens, and nuts, can combat inflammation. Omega-3 fatty acids, found in fish like salmon and flaxseeds, have been shown to reduce inflammation as well. Magnesium-rich foods, such as spinach, legumes, and whole grains, can also help as magnesium can alleviate muscle pain and cramps.
Weight Management
Excess weight puts additional stress on the body, especially on weight-bearing joints like the hips and knees, which can exacerbate pain. For overweight individuals with diabetes, weight loss can significantly reduce the strain on these joints, thus alleviating pain. Moreover, weight loss can improve insulin sensitivity, making diabetes easier to manage. A combination of diet modifications and regular exercise is typically the most effective approach to achieve sustainable weight loss.
Topical Treatments
Topical treatments can be a valuable addition to pain management in diabetes. Creams and ointments containing capsaicin, a compound found in chili peppers, can be effective in reducing pain sensations. Capsaicin works by decreasing the intensity of pain signals sent through the nerves. Lidocaine patches or creams are another option; they provide local numbness and can be particularly helpful for localized neuropathic pain.
Alternative Therapies
- Acupuncture: This traditional Chinese medicine technique involves inserting thin needles into specific points on the body. Acupuncture is believed to stimulate the nervous system and can be effective in relieving chronic pain, including diabetic neuropathy. It is thought to work by releasing natural pain-relieving chemicals in the body and by promoting blood flow.
- Massage Therapy: Massage can help reduce muscle tension and improve circulation, which in turn can alleviate pain. It can be particularly beneficial for diabetic patients who suffer from muscle stiffness and soreness. However, diabetic patients need to use a skilled massage therapist who is aware of their condition, especially if they have any diabetes-related complications like neuropathy.
Foot Care
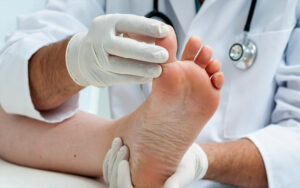 Diabetic neuropathy often affects the feet, making proper foot care essential. This includes regular inspection of the feet for cuts, sores, or blisters that may not be felt due to numbness. Proper foot hygiene, moisturizing, and wearing well-fitting, supportive shoes are also important to prevent complications. In some cases, custom orthotics may be recommended to alleviate pressure points and improve comfort while walking.
Diabetic neuropathy often affects the feet, making proper foot care essential. This includes regular inspection of the feet for cuts, sores, or blisters that may not be felt due to numbness. Proper foot hygiene, moisturizing, and wearing well-fitting, supportive shoes are also important to prevent complications. In some cases, custom orthotics may be recommended to alleviate pressure points and improve comfort while walking.
Regular Check-ups
Regular medical check-ups are crucial for monitoring the progression of diabetes and its associated symptoms, including body aches and pains. These check-ups can help in timely adjustments to treatment plans. Healthcare providers can also monitor for complications of diabetes that may contribute to pain, such as peripheral artery disease or kidney issues, and provide appropriate interventions.
Supplements
Some dietary supplements may help alleviate neuropathic pain in diabetes. Alpha-lipoic acid, a naturally occurring fatty acid, has shown promise in some studies for reducing symptoms of diabetic neuropathy. Vitamin B12 supplements can also be beneficial, especially since some diabetic patients on metformin are at risk for B12 deficiency. However, it’s important to discuss with a healthcare provider before starting any supplements, as they may interact with other medications or have side effects.
Incorporating these diabetes body aches and pains treatment can be instrumental in reducing body aches and pains. It’s always important for individuals with diabetes to consult with their healthcare team. This will help to ensure that any new treatment or approach is safe and appropriate for their specific health situation.
Conclusion
In conclusion, effectively managing body aches and pains associated with diabetes involves a multifaceted approach. Diabetes body aches and pains treatment including proper blood sugar levels, utilizing both medication and physical therapy, adopting a healthy diet, engaging in regular exercise, and employing stress management techniques, individuals can significantly alleviate their discomfort. Additionally, exploring alternative therapies, practicing diligent foot care, and considering supplements under medical guidance can further enhance pain management.
It’s essential to remember that each person’s experience with diabetes is unique, and what works for one may not work for another. Therefore, it’s crucial to work closely with healthcare professionals to tailor a pain management plan. Do you want to get rid of diabetes? Join our online diabetes treatment program and reverse Diabetes naturally through lifestyle changes such as a Personalized Diet plan, Exercise, Yoga, dieticians, and health coaches.