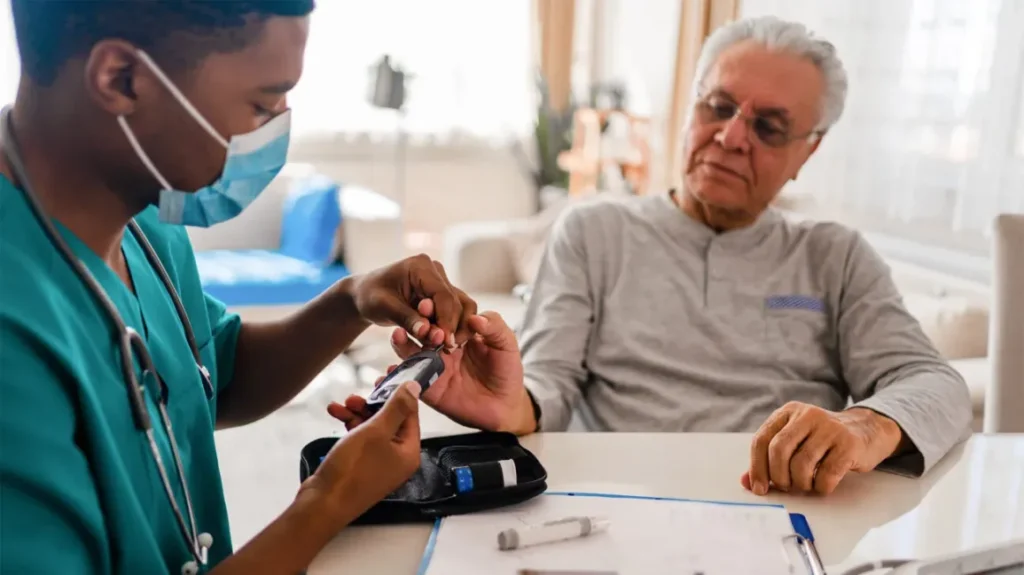
Diabetes, a chronic medical condition affecting millions worldwide, necessitates a multifaceted approach to its management. Characterized by high levels of blood sugar due to the body’s inability to produce or effectively use insulin, diabetes poses numerous health challenges. However, with advancements in medical science and a better understanding of the disease, managing diabetes has become more achievable than ever before. This comprehensive guide aims to shed light on various aspects of diabetes treatment, offering insights and strategies to those navigating this complex condition.
Contents
What Are Some Medical Approaches In Diabetes Treatment?
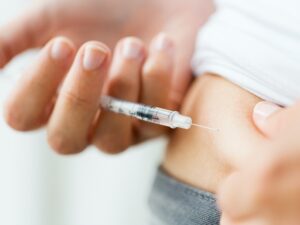 Medical approaches in diabetes treatment have evolved significantly, offering a range of options to manage this complex condition effectively. These approaches primarily focus on maintaining blood glucose levels within a target range, preventing complications, and enhancing overall quality of life. Here’s a detailed overview:
Medical approaches in diabetes treatment have evolved significantly, offering a range of options to manage this complex condition effectively. These approaches primarily focus on maintaining blood glucose levels within a target range, preventing complications, and enhancing overall quality of life. Here’s a detailed overview:
Insulin Therapy
It is used in some cases of Type 2 diabetes where blood glucose levels cannot be controlled with oral medications alone. Insulin is categorized based on how quickly it works and how long its effects last. Rapid-acting insulin begins working within minutes and is ideal for controlling blood sugar spikes during meals. Long-acting insulins provide a steady level of insulin throughout the day and night. The administration of insulin can be done through various methods, including syringes, pens, and pumps.
Oral Medications
Metformin is often the first medication prescribed and works by improving the body’s sensitivity to insulin and reducing the amount of glucose released by the liver. Sulfonylureas help increase insulin production from the pancreas. DPP-4 inhibitors work more subtly by affecting the incretin hormones. SGLT2 inhibitors are a newer class of drugs that cause the kidneys to remove sugar from the body through urine, lowering blood glucose levels.
Non-Insulin Injectable Medications
These include GLP-1 receptor agonists, which mimic the glucagon-like peptide-1 hormone. They stimulate insulin production when blood sugar levels are high and slow gastric emptying. This helps lower blood sugar levels after eating. Amylin analogs are another option used alongside insulin to control post-meal blood sugars, by slowing food’s movement through the stomach and inhibiting the release of glucagon.
Continuous Glucose Monitoring Systems
CGMs offer a way to constantly track glucose levels throughout the day and night. These devices typically consist of a small sensor inserted under the skin that measures interstitial glucose levels and transmits this information to a receiver. This constant monitoring can help in making more informed decisions about diet, exercise, and medication.
Insulin Pump Therapy
An insulin pump is a small device that delivers insulin continuously throughout the day, mimicking the way a healthy pancreas releases insulin. The pump can be programmed to deliver specific amounts of insulin based on meals, activity levels, and current blood sugar readings. This can lead to more stable blood glucose levels and reduced risk of hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia.
Pancreas and Islet Cell Transplantation
These are more invasive options and are typically considered when other treatments have failed. Pancreas transplantation can potentially cure Type 1 diabetes but comes with significant risks and the need for lifelong immune-suppressing drugs. Islet cell transplantation involves transferring insulin-producing cells from a donor pancreas into a person with diabetes. It can reduce the amount of insulin they need to inject.
Bariatric Surgery
This type of surgery, including procedures like gastric bypass and sleeve gastrectomy, is not only effective for weight loss but also for improving or even resolving Type 2 diabetes in severely obese patients. The surgery can lead to significant improvements in blood sugar control. And sometimes allowing patients to reduce or even stop their diabetes medications.
Each of these treatment options has its benefits and risks. Hence, the choice depends on various factors, including the type and severity of diabetes, individual health status, and personal preferences. Collaborative decision-making with healthcare providers is crucial in selecting the most appropriate treatment plan.
How Diabetes Can Be Controlled Naturally?
 Controlling diabetes naturally involves a combination of lifestyle modifications, dietary changes, and regular monitoring of blood glucose levels. These natural methods are particularly effective in managing Type 2 diabetes and can also supplement the treatment of Type 1 diabetes. Here are key strategies to control diabetes naturally:
Controlling diabetes naturally involves a combination of lifestyle modifications, dietary changes, and regular monitoring of blood glucose levels. These natural methods are particularly effective in managing Type 2 diabetes and can also supplement the treatment of Type 1 diabetes. Here are key strategies to control diabetes naturally:
Dietary Adjustments
Foods with a low glycemic index, like whole grains, legumes, and most fruits, are beneficial as they cause a slower rise in blood sugar levels. High-fiber foods, including vegetables, fruits, whole grains, and legumes, are excellent for blood sugar control. They delay the absorption of sugar and help maintain steady blood sugar levels. Including healthy fats from sources like nuts, seeds, avocados, and olive oil can also positively impact blood sugar levels.
Regular Physical Activity
Regular exercise is imperative in managing diabetes. Physical activities like walking, swimming, cycling, and yoga improve the body’s insulin sensitivity, thus helping control blood sugar. It’s recommended to engage in at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity weekly, coupled with strength training exercises. Regular exercise also aids in weight loss, which is beneficial for people with diabetes.
Weight Management
Weight management is critical, especially in Type 2 diabetes. Losing even a small percentage of body weight can improve blood sugar control significantly. A combination of healthy eating and regular exercise is the best strategy for losing and maintaining a healthy weight.
Stress Management
Stress affects blood sugar levels. Techniques like mindfulness, meditation, and deep breathing can reduce stress. Engaging in hobbies and activities that relax the mind can also help manage blood sugar levels effectively.
Adequate Sleep
Quality sleep is essential for good health and diabetes management. Lack of sleep can affect blood sugar levels and insulin sensitivity. Aim for 7-8 hours of uninterrupted sleep each night to help maintain stable blood sugar levels.
Avoiding Harmful Habits
Unhealthy habits like smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can exacerbate diabetes and its complications. Quitting smoking and limiting alcohol intake can significantly improve health and help in managing diabetes more effectively.
Regular Blood Sugar Monitoring
Keeping track of blood sugar levels helps in managing diabetes efficiently. It provides insights into how different foods, activities, and stress levels affect blood sugar. This information can be used to make necessary adjustments in diet and lifestyle.
Natural Supplements and Herbs
Some herbs and supplements, such as cinnamon, berberine, and alpha-lipoic acid, are believed to help with blood sugar control. However, it’s important to consult with a healthcare provider before using these, as they may interact with other medications.
Stay Hydrated
Adequate hydration is important in diabetes management. Drinking water helps maintain blood sugar levels and supports kidney function, allowing the body to excrete excess sugar through urine.
While these natural methods can significantly aid in diabetes management, they should complement, not replace, standard medical treatments prescribed by healthcare professionals. It’s important to consult with your doctor before making any significant changes to your diabetes management plan.
What Is The Importance Of Diabetes Treatment?
 The importance of diabetes treatment cannot be overstated, as it plays a crucial role in preventing complications and maintaining overall health and quality of life for individuals with diabetes. Here are some key reasons why diabetes treatment is vital:
The importance of diabetes treatment cannot be overstated, as it plays a crucial role in preventing complications and maintaining overall health and quality of life for individuals with diabetes. Here are some key reasons why diabetes treatment is vital:
- Preventing Acute Complications
These include hypoglycemia (low blood sugar) and hyperglycemia (high blood sugar), both of which can be dangerous if not promptly managed. Hypoglycemia can cause symptoms like confusion, fainting, or even seizures, while hyperglycemia can lead to diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) in Type 1 diabetes.
- Reducing the Risk of Long-Term Complications
Chronic high blood sugar levels can damage various organs and systems over time. This includes heart disease, kidney damage (diabetic nephropathy), eye damage (diabetic retinopathy), nerve damage (diabetic neuropathy), and poor circulation leading to wounds that don’t heal properly.
- Improving Quality of Life
Properly managed diabetes allows individuals to maintain a better quality of life. It helps in managing symptoms such as fatigue, excessive thirst, and frequent urination. And enables people to engage more fully in daily activities and maintain their productivity.
- Enhancing Physical Health
Good blood sugar control helps maintain overall physical health. It supports optimal energy levels, healthy skin, and weight management. It also reduces the risk of infections and other diabetes exacerbations, like skin conditions or yeast infections.
- Supporting Mental and Emotional Health
Living with diabetes can be challenging not just physically, but also mentally and emotionally. Effective treatment helps in reducing the stress and anxiety associated with managing a chronic condition and decreases the risk of depression.
- Prolonging Life Expectancy
Diabetes, particularly when poorly managed, can significantly reduce life expectancy due to its complications. Effective management of diabetes has been shown to increase lifespan and reduce mortality rates.
Overall, diabetes treatment is essential not only for controlling blood sugar levels but also for preventing a range of complications that can impact nearly every aspect of an individual’s health and well-being.
Conclusion
In conclusion, managing diabetes effectively is crucial for maintaining overall health and preventing serious complications. Whether through medical treatments like insulin and oral medications, lifestyle changes like diet and exercise, or natural methods, each aspect plays a vital role in controlling blood sugar levels. By understanding the different facets of diabetes treatment and embracing a holistic approach to care, individuals can lead healthier, more fulfilling lives.
It’s important to remember that while diabetes can be challenging, with the right strategies and support, it’s possible to manage the condition successfully. Do you want to get rid of diabetes? Join our online diabetes treatment program and reverse Diabetes naturally through lifestyle changes such as a Personalized Diet plan, Exercise, Yoga, dieticians, and health coaches.

