Diabetes, a chronic condition affecting millions worldwide, not only alters blood sugar levels but also impacts various bodily functions. One of the lesser-known but serious complications of diabetes is foot infections. These infections can range from mild skin irritations to severe infections leading to amputation. The high blood sugar levels in diabetics impair blood circulation and weaken the immune system, making it harder for the body to heal wounds and fight infections. This blog aims to shed light on diabetic foot infection treatment strategies and prevention.
Contents
What Causes Diabetic Foot Infection?
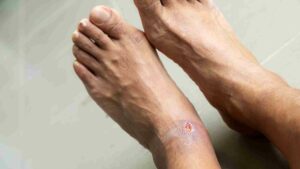 Diabetic foot infections are primarily caused by a combination of factors related to diabetes. Here are the key causes:
Diabetic foot infections are primarily caused by a combination of factors related to diabetes. Here are the key causes:
- Peripheral Neuropathy
Diabetes often leads to nerve damage, known as peripheral neuropathy. This condition reduces sensation in the feet, making it difficult for individuals to feel injuries, blisters, or sores. Without proper sensation, minor injuries can go unnoticed and untreated, leading to infections.
- Immune System Dysfunction
Diabetes can weaken the immune system, making it less effective at fighting off infections. This immune deficiency means that once bacteria enter a wound or sore on the foot, the body has a harder time containing and eliminating the infection.
- Skin Changes and Ulcers
Diabetics often experience skin changes, including dryness and cracking. It can create entry points for bacteria. Chronic high blood sugar can also lead to the formation of foot ulcers, which are prone to infection.
- Injury and Foot Deformities
Injuries to the foot, such as cuts, blisters, or sores, can become infected, especially in diabetics. Additionally, diabetes can cause foot deformities (like hammertoes or bunions), which can create pressure points prone to ulcers and infection.
- Athlete’s Foot and Other Infections
Fungal infections like athlete’s foot can cause cracks and breaks in the skin, which can lead to bacterial infections.
- Poor Hygiene and Inadequate Foot Care
Inadequate foot care, such as not regularly washing and inspecting the feet, can increase the risk of infection.
Individuals with diabetes need to manage their blood sugar levels, inspect their feet daily, wear proper footwear, and seek prompt medical attention for any foot injuries or abnormalities to prevent infections. Regular check-ups with healthcare professionals, including podiatrists, are also crucial for preventing diabetic foot infections.
Medical Approaches For Diabetic Foot Infection Treatment
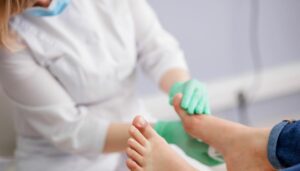 Diabetic foot infection treatment involves a multifaceted medical approach aimed at controlling the infection, promoting healing, and preventing complications such as amputation. Here are the key strategies:
Diabetic foot infection treatment involves a multifaceted medical approach aimed at controlling the infection, promoting healing, and preventing complications such as amputation. Here are the key strategies:
Wound Care and Debridement
Effective wound care is crucial in treating diabetic foot infections. This involves cleaning the wound and removing dead tissue, a process known as debridement. Debridement can be performed using various techniques, including surgical, mechanical, chemical, or autolytic (using dressings that promote the natural breakdown of dead tissue). Proper wound care also involves applying appropriate dressings to keep the wound environment moist, which promotes healing.
Antibiotic Therapy
Antibiotics are a cornerstone of treatment for diabetic foot infections, especially when there is evidence of significant soft tissue or bone infection. The choice of antibiotics depends on the severity of the infection and the types of bacteria suspected or identified. For mild infections, oral antibiotics are often sufficient. However, more severe infections may require intravenous antibiotics. It’s important to use antibiotics judiciously to prevent antibiotic resistance.
Blood Sugar Control
Maintaining optimal blood sugar levels is essential in the treatment of diabetic foot infections. High blood sugar can impair the immune system and slow down the healing process. Effective blood sugar management involves medication, diet, and lifestyle changes, and it’s critical for the overall treatment and prevention of complications.
Off-loading and Pressure Relief
To promote healing, it’s important to reduce pressure on the infected foot. This can be achieved through off-loading techniques such as using special footwear, orthotic devices, or casts. These methods help redistribute pressure away from the ulcer, reducing the risk of further injury and aiding in the healing process.
Surgery
Surgical intervention in the treatment of diabetic foot infections is often considered when other treatments have failed, or when the infection is severe and poses a risk of spreading. Minor surgical procedures might involve debridement, which is the removal of dead or infected tissue. In more severe cases, where the infection has caused extensive tissue damage or has led to gangrene, partial or total amputation of a toe, foot, or part of the leg might be necessary. The primary goal of such surgeries is to remove the source of infection completely and to prevent its spread.
Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy (HBOT)
HBOT is a treatment that involves breathing 100% oxygen in a pressurized chamber. This increased pressure allows the lungs to gather more oxygen than would be possible at normal air pressure. The blood then carries this oxygen throughout the body, helping to fight bacteria and stimulate the release of substances called growth factors and stem cells, which promote healing. HBOT is particularly beneficial for diabetic patients with chronic, non-healing foot ulcers.
Vascular Surgery
Poor circulation is a common complication in diabetes and can significantly impede the healing of foot infections. In such cases, vascular surgery may be required to improve blood flow to the affected area. Procedures can include angioplasty, where a small balloon is inserted and inflated in the narrowed area of the blood vessel to open it up, or vascular bypass surgery, where blood flow is redirected around a blocked artery. By restoring proper blood circulation, these procedures can facilitate wound healing and reduce the risk of future diabetic foot infections.
Pain Management
These infections can be quite painful, and effective pain management can improve the patient’s quality of life significantly. Pain management strategies might include the use of over-the-counter pain relievers like acetaminophen or ibuprofen, and in more severe cases, prescription pain medications. Additionally, local wound care practices and certain medications can help alleviate pain associated with the wound itself.
By integrating these medical approaches, the treatment of diabetic foot infections can be more effective, reducing the risk of complications and improving outcomes for patients with diabetes.
How To Prevent Diabetic Foot Infections?
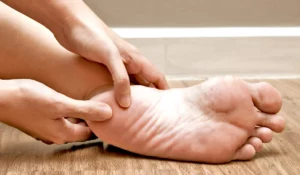 Preventing diabetic foot infections involves a combination of good diabetes management, regular foot care, and lifestyle modifications. Here are key strategies to help prevent these infections:
Preventing diabetic foot infections involves a combination of good diabetes management, regular foot care, and lifestyle modifications. Here are key strategies to help prevent these infections:
- Regular Foot Inspections: Check your feet daily for any signs of cuts, blisters, redness, swelling, or nail problems. Use a mirror to inspect all areas of your feet or ask someone for help if you are unable to do it yourself. Early detection of potential problems can prevent serious infections.
- Moisturize Your Feet: Dry skin can lead to cracks and fissures, which can become entry points for bacteria. Apply a thin coat of plain petroleum jelly, unscented hand cream, or other products recommended by your doctor. Avoid putting moisturizer between your toes, as this can increase the risk of fungal infections.
- Wear Properly Fitted Shoes: Ill-fitting shoes can cause blisters and sores that may lead to infections. Choose well-fitting, comfortable shoes that provide support and cushioning. Break new shoes in slowly to prevent blisters.
- Keep Your Feet Clean and Dry: Wash your feet daily with lukewarm water and mild soap. Dry your feet thoroughly, especially between the toes, where moisture can get trapped, leading to fungal infections.
- Avoid Walking Barefoot: Walking without shoes, even indoors, increases the risk of injury to your feet. Always wear shoes or slippers to protect your feet from cuts and abrasions.
- Trim Nails Carefully: Cut your toenails straight across and file the edges with an emery board or nail file. Avoid cutting nails too short as this can lead to ingrown toenails and infections.
- Avoid Smoking: Smoking affects circulation and can exacerbate circulatory problems, making it harder for wounds to heal and increasing the risk of infections.
- Exercise Regularly: Regular exercise improves blood circulation, which is essential for wound healing and can reduce the risk of foot infections. Choose low-impact exercises like walking, swimming, or cycling, and always wear appropriate footwear.
- Educate Yourself and Others: Be informed about the risks and prevention of diabetic foot infections. Sharing this knowledge with family and friends can also help in maintaining good foot care practices.
By incorporating these preventative measures into daily routines, individuals with diabetes can significantly reduce their risk of developing foot infections.
Conclusion
In conclusion, diabetic foot infection treatment is crucial for individuals. It involves a combination of proper wound care, appropriate medical treatments, and lifestyle changes. Regular foot inspections, maintaining optimal blood sugar levels, wearing well-fitting shoes, and practicing good foot hygiene are key. Additionally, treatments like surgery, hyperbaric oxygen therapy, and vascular surgery are important for severe cases.
Remember, early detection and prompt treatment are vital. Do you want to get rid of diabetes? Join our online diabetes treatment program and reverse Diabetes naturally through lifestyle changes such as a Personalized Diet plan, Exercise, Yoga, dieticians, and health coaches.

