Diabetes, a chronic condition affecting millions worldwide, not only alters lifestyle but also brings a host of complications, one of which is diabetic foot. This condition, characterized by poor blood circulation and reduced sensation in the feet, can lead to severe consequences if not managed properly. So, in this guide, we aim to provide vital information on the prevention and diabetic foot treatment, emphasizing the importance of early detection, proper care, and lifestyle modifications.
Contents
What Is The First Rule Of Diabetic Foot Care?
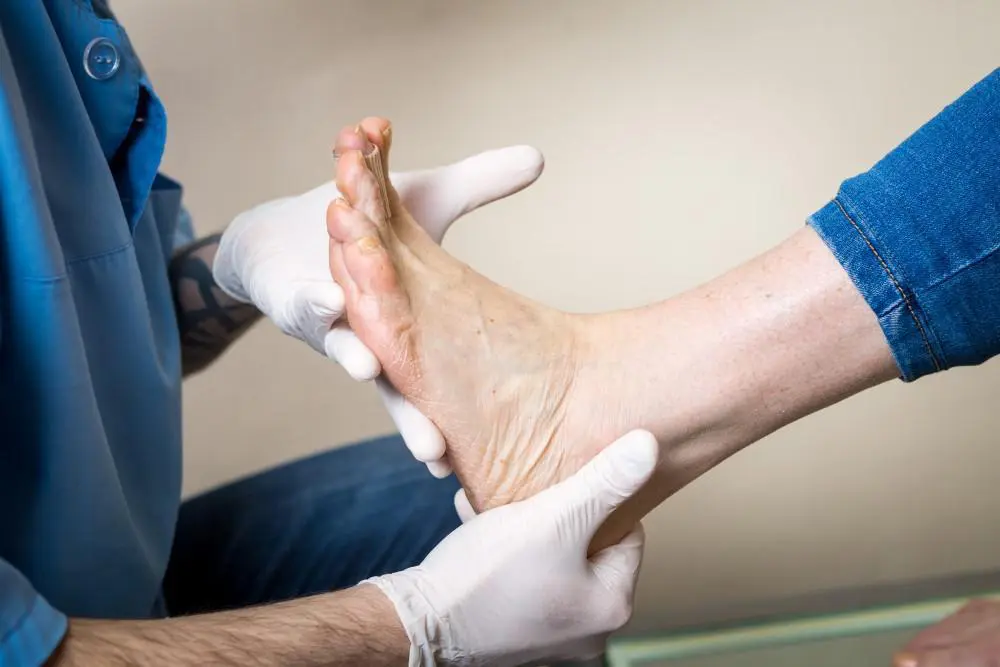
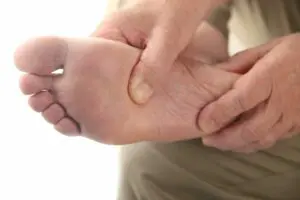 The first and foremost rule of diabetic foot care is regular inspection and monitoring of the feet. This involves checking your feet every day for cuts, blisters, red spots, swelling, and infected toenails. Individuals with diabetes may have reduced sensation in their feet due to neuropathy. This means they might not feel a foot injury.
The first and foremost rule of diabetic foot care is regular inspection and monitoring of the feet. This involves checking your feet every day for cuts, blisters, red spots, swelling, and infected toenails. Individuals with diabetes may have reduced sensation in their feet due to neuropathy. This means they might not feel a foot injury.
Therefore, it’s crucial to visually inspect the feet every day to catch any problems early before they develop into serious complications. Regular inspection helps in the early detection of potential issues and ensures prompt treatment, reducing the risk of infection and further complications.
What Are The Best Diabetic Foot Treatment Options?
The best treatment options for diabetic foot largely depend on the specific issues and complications that arise. However, there are several common approaches and strategies used in diabetic foot treatment and management:
Regular Inspection and Foot Care
Individuals with diabetes often experience neuropathy, which reduces sensation and makes it difficult to feel minor cuts or injuries. The daily inspection helps in the early detection of any problems. This is essential in preventing serious complications. During inspection, look for any cuts, blisters, red spots, swelling, or infected toenails. It’s also important to keep the feet clean and dry. However, avoid moisturizing between the toes to prevent fungal infections. Additionally, keeping the nails trimmed and smooth prevents ingrown toenails and cuts.
Wound Care
The presence of high blood sugar levels can impair the healing process, making even minor wounds a concern. If a cut or blister is found, it’s important to clean it with mild soap and water, apply an antibiotic cream, and cover it with a clean, dry bandage. Changing the bandage daily and monitoring the wound for signs of infection (like increased redness, swelling, pain, or discharge) is critical. If the wound does not start to heal within a few days, or if there are signs of infection, seeking medical attention is necessary.
Infection Control
Diabetic feet are more prone to infection, and an untreated infection can lead to serious complications, including the risk of amputation. Early recognition and treatment are vital. The signs of infection include redness, warmth, swelling, foul odor, and discharge from a wound. Infections are treated with antibiotics, either topical (applied to the skin) or systemic (oral or intravenous). Good glycemic control is also important in fighting infections.
Blood Sugar Control
 Effective control of blood sugar levels is essential in managing diabetic foot issues. High blood sugar can cause damage to blood vessels and nerves in the feet, leading to reduced sensation (neuropathy) and poor blood circulation. This impairs the ability to feel pain and slows down the healing process, increasing the risk of ulcers and infections. Maintaining blood sugar levels within target ranges can prevent or delay these complications. This involves adhering to prescribed medications, following a diabetic-friendly diet, regular monitoring of blood glucose levels, and maintaining a healthy lifestyle with regular exercise.
Effective control of blood sugar levels is essential in managing diabetic foot issues. High blood sugar can cause damage to blood vessels and nerves in the feet, leading to reduced sensation (neuropathy) and poor blood circulation. This impairs the ability to feel pain and slows down the healing process, increasing the risk of ulcers and infections. Maintaining blood sugar levels within target ranges can prevent or delay these complications. This involves adhering to prescribed medications, following a diabetic-friendly diet, regular monitoring of blood glucose levels, and maintaining a healthy lifestyle with regular exercise.
Proper Footwear
Special diabetic footwear is designed to reduce the risk of foot sores and ulcers. These shoes and insoles are made to accommodate the shape of the diabetic foot, distribute weight evenly, and minimize pressure points. They also provide adequate cushioning and support. Diabetic socks, typically seamless and non-constricting, help in preventing blisters and sores. They are made from fabrics that keep moisture away from the skin, reducing the risk of fungal infections.
Off-loading
Off-loading is a critical strategy in the treatment of foot ulcers, which are common in diabetic patients. It involves reducing pressure and stress on the ulcerated area to promote healing and prevent further injury. This can be achieved through various methods, such as wearing special footwear, using orthotic devices like insoles or cushions, and using assistive devices like crutches or wheelchairs. In some cases, a total contact cast or a removable cast walker may be recommended. These devices are designed to distribute weight away from the ulcerated area while still allowing some mobility.
Surgery
In certain cases of diabetic foot complications, surgical intervention might be necessary. This could range from minor procedures to the removal of dead or infected tissue. It helps in promoting healing and preventing the spread of infection, to more complex surgeries to correct deformities like bunions or hammertoes that can lead to ulcers. In severe cases, where there is extensive infection or gangrene, amputation of a toe, foot, or part of the leg may be required. Surgery can also involve vascular procedures to improve blood flow to the feet.
Physical Therapy and Rehabilitation
After undergoing foot surgery, or in cases where foot deformities or complications have impaired mobility, physical therapy becomes a crucial part of the treatment plan. Physical therapists can design specific exercises and routines to improve foot strength, flexibility, and function. Rehabilitation can also involve learning how to use assistive devices correctly and safely. Additionally, physical therapy plays a significant role in preventing future foot problems by teaching proper foot care techniques and encouraging activities that improve circulation and foot health.
Regular Check-ups with Healthcare Professionals
Regular appointments with healthcare providers are vital for managing diabetic foot. This includes routine check-ups with a primary care physician for overall diabetes management and regular visits to a podiatrist for specialized foot care. These professionals can provide essential guidance on foot care practices, monitor the condition of the feet, and intervene early if problems arise. They can also adjust treatment plans as needed and provide referrals to other specialists.
By addressing these aspects comprehensively, individuals with diabetes can effectively manage their foot health. Ultimately, reducing the risk of severe complications and improving their overall quality of life.
How To Prevent Diabetic Foot?
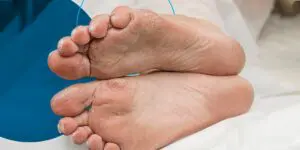 To prevent diabetic foot complications, it’s important to focus on a holistic approach that encompasses overall health and awareness. Here are some additional strategies:
To prevent diabetic foot complications, it’s important to focus on a holistic approach that encompasses overall health and awareness. Here are some additional strategies:
- Regular Glycemic Monitoring and Management
While controlling blood sugar levels has been mentioned, it’s worth emphasizing the importance of regular monitoring. Frequent checks allow for immediate adjustments in diet, medication, or lifestyle to keep blood sugar within target ranges.
- Education and Awareness
Educating yourself about diabetes and its potential complications is crucial. Understanding how diabetes affects your body can motivate adherence to treatment plans and preventive measures.
- Smoking Cessation
Smoking exacerbates blood circulation problems, increasing the risk of diabetic foot complications. Quitting smoking can significantly improve circulation and overall health. Seek support programs or smoking cessation aids if needed.
- Regular Exercise with Caution
Exercise improves blood circulation and helps in managing diabetes, but it’s important to choose activities that are less stressful on the feet, like swimming or cycling. Also, always check your feet for blisters or sores after exercise.
- Maintaining a Healthy Weight
Excess weight puts additional pressure on your feet and can lead to foot problems. Working towards a healthy weight through diet and exercise can significantly reduce the risk of diabetic foot complications.
- Avoiding Foot Trauma
Be cautious to avoid foot injuries. Wear appropriate protective footwear even at home and be careful while engaging in activities that could cause foot injuries.
- Avoiding Sitting with Crossed Legs
Sitting with your legs crossed for long periods can reduce blood flow to your feet. Try to maintain a position that encourages good circulation.
By integrating these strategies into daily life, individuals with diabetes can significantly reduce their risk of developing diabetic foot complications, ensuring better overall health and quality of life.
Is Walking Good For Diabetic Foot?
 Walking can be beneficial for individuals with diabetic foot, but it must be approached with caution. For those with diabetes, regular exercise, including walking, plays a crucial role in overall health management. It helps in controlling blood sugar levels, improving circulation, and maintaining a healthy weight, all of which are essential in managing diabetes and its complications. Improved blood flow is particularly beneficial for the feet, as it aids in healing and reduces the risk of complications.
Walking can be beneficial for individuals with diabetic foot, but it must be approached with caution. For those with diabetes, regular exercise, including walking, plays a crucial role in overall health management. It helps in controlling blood sugar levels, improving circulation, and maintaining a healthy weight, all of which are essential in managing diabetes and its complications. Improved blood flow is particularly beneficial for the feet, as it aids in healing and reduces the risk of complications.
However, it’s important for those with diabetic foot concerns to choose appropriate footwear and to check their feet regularly for any signs of blisters, cuts, or sores. On the other hand, if an individual with diabetes has significant neuropathy (loss of sensation in the feet), a history of foot ulcers, or poor circulation, walking might need to be monitored closely. Balancing the benefits of walking with the risk of potential foot injuries is key in safely incorporating this activity into a diabetic foot care regimen.
Conclusion
In conclusion, diabetic foot treatment requires a combination of diligent care, lifestyle adjustments, and professional medical guidance. From conducting daily foot inspections and practicing good foot hygiene to wearing the right footwear and carefully monitoring blood sugar levels, each step plays a vital role in prevention and treatment. While interventions like off-loading, surgery, or physical therapy might be necessary for some, simple measures are foundational for all.
Remember, the key to effectively managing diabetic foot lies in early detection, consistent care, and a proactive approach toward overall health. Do you want to get rid of diabetes? Join our online diabetes treatment program and reverse Diabetes naturally through lifestyle changes such as a Personalized Diet plan, Exercise, Yoga, dieticians, and health coaches.