In the intricate landscape of diabetes management, one often overlooked complication is diabetic glaucoma, a condition that can lead to vision impairment or even blindness if not addressed promptly. As individuals with diabetes are already at an increased risk of developing various eye-related issues, understanding and managing diabetic glaucoma becomes paramount. This blog aims to shed light on the intricacies of diabetic glaucoma and, most importantly, effective diabetic glaucoma treatment options that can help preserve and protect your precious eyesight.
Contents
How Diabetes Is Related To Glaucoma?
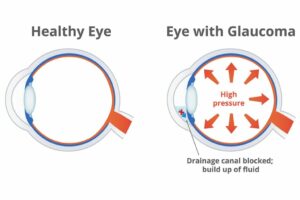 Diabetes and glaucoma are both medical conditions that can have a significant impact on eye health, and they are interrelated in several ways. Here’s a breakdown of how these two conditions are connected:
Diabetes and glaucoma are both medical conditions that can have a significant impact on eye health, and they are interrelated in several ways. Here’s a breakdown of how these two conditions are connected:
- Increased Risk
Individuals with diabetes are at an elevated risk of developing various eye-related complications, including glaucoma. The risk increases with the duration of diabetes and poor blood sugar control.
- Optic Nerve Damage
Glaucoma is characterized by damage to the optic nerve. This is responsible for transmitting visual information from the eye to the brain. Diabetes can contribute to the development of glaucoma by affecting the blood vessels that supply the optic nerve, leading to impaired blood flow and damage.
- Influence on Intraocular Pressure (IOP)
Elevated intraocular pressure (IOP) is a significant risk factor for glaucoma. Diabetes can impact the drainage system of the eye, leading to an increase in IOP. This elevated pressure can contribute to the development and progression of glaucoma.
- Vascular Complications
Diabetes is associated with vascular complications, and the blood vessels in the eyes are no exception. Changes in blood vessel structure and function can affect the circulation within the eye, contributing to the development of glaucoma.
- Inflammation and Oxidative Stress
Diabetes is characterized by chronic inflammation and oxidative stress. These conditions can contribute to the damage of ocular tissues, including the optic nerve, creating an environment conducive to glaucoma development.
- Peripheral Neuropathy
Diabetes can lead to peripheral neuropathy, affecting the nerves in various parts of the body, including the eyes. Peripheral neuropathy may impact the autonomic nerves that regulate intraocular pressure, potentially contributing to glaucoma.
Individuals with diabetes need to be proactive in managing their overall health. By understanding the relationship between diabetes and glaucoma, individuals can take steps to minimize the risk and preserve their vision.
What Are Some Medical Diabetic Glaucoma Treatments?
The management of diabetic glaucoma involves a combination of medical, surgical, and lifestyle interventions. Here are some medical treatments commonly employed for diabetic glaucoma:
Medication for Intraocular Pressure (IOP) Control
Medications aimed at controlling intraocular pressure (IOP) play a central role in managing diabetic glaucoma. Various types of eye drops are prescribed to lower IOP by either enhancing the drainage of fluid from the eye or reducing the production of aqueous humor. Prostaglandin analogs, beta-blockers, alpha agonists, and carbonic anhydrase inhibitors are commonly used classes of eye drops. These medications work by different mechanisms to improve the outflow of fluid. Thereby alleviating the pressure exerted on the optic nerve.
Oral Medications
In addition to topical eye drops, oral medications may be considered to further address intraocular pressure. Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors, when taken orally, can help reduce the production of aqueous humor and contribute to lowering IOP. Oral medications are often prescribed in conjunction with eye drops to achieve better control over intraocular pressure. However, these medications may have systemic side effects, and their usage is carefully monitored by healthcare professionals.
Combination Eye Drops
As a progressive approach to managing diabetic glaucoma, ophthalmologists may prescribe a combination of different eye drops. This strategy aims to enhance the efficacy of intraocular pressure reduction by utilizing multiple medications with complementary mechanisms of action. The combination therapy can provide a synergistic effect, offering better control over IOP compared to a single medication. This approach is particularly useful when monotherapy is insufficient in achieving the desired reduction in intraocular pressure.
Neuroprotective Medications
 Emerging research in the field of glaucoma explores the potential benefits of neuroprotective medications for preserving the health of the optic nerve. These drugs aim to shield nerve cells from damage and apoptosis, which are crucial aspects of glaucoma progression. While neuroprotective medications are still undergoing clinical trials and are not yet widely adopted in routine practice, they represent a promising avenue for future diabetic glaucoma treatment.
Emerging research in the field of glaucoma explores the potential benefits of neuroprotective medications for preserving the health of the optic nerve. These drugs aim to shield nerve cells from damage and apoptosis, which are crucial aspects of glaucoma progression. While neuroprotective medications are still undergoing clinical trials and are not yet widely adopted in routine practice, they represent a promising avenue for future diabetic glaucoma treatment.
Laser Therapy
This therapy is a common and effective approach for managing diabetic glaucoma by modulating intraocular pressure. Laser trabeculoplasty is a procedure that utilizes a focused laser beam to treat the trabecular meshwork, enhancing drainage and reducing IOP. Another laser procedure, known as laser peripheral iridotomy (LPI), involves creating a small hole in the peripheral iris to facilitate better fluid flow.
Selective Laser Trabeculoplasty (SLT)
Selective Laser Trabeculoplasty (SLT) is a newer form of laser treatment that specifically targets cells in the trabecular meshwork without causing thermal damage to surrounding tissues. SLT is considered a safe and effective option for lowering intraocular pressure and is suitable for individuals with diabetic glaucoma. This procedure can be repeated if necessary. Its selective nature reduces the risk of complications, making it a valuable tool in the management of glaucoma.
Surgery
When medical and laser interventions are insufficient to manage diabetic glaucoma, surgical procedures may be considered. Trabeculectomy is a traditional surgical approach that creates a new drainage pathway for aqueous humor, reducing intraocular pressure. Glaucoma drainage devices, such as shunts or tubes, can also be implanted to improve fluid drainage. Minimally invasive glaucoma surgery (MIGS) represents a group of newer surgical techniques that aim to reduce intraocular pressure with minimal trauma to the eye.
Intravitreal Injections
Intravitreal injections are a treatment option for managing diabetic macular edema, a condition that may coexist with glaucoma in individuals with diabetes. Anti-vascular endothelial growth factor (anti-VEGF) agents, such as bevacizumab or ranibizumab, are injected into the vitreous cavity to inhibit abnormal blood vessel growth and reduce macular edema. While these injections primarily target diabetic macular edema, they indirectly contribute to the overall management of diabetic eye complications, including glaucoma.
It’s important to note that the choice of treatment depends on various factors. Hence, treatment plans are often tailored to each patient’s specific needs. Regular follow-up appointments with an ophthalmologist are essential to monitor the progress of diabetic glaucoma and adjust the treatment plan as needed.
What Is The Best Drink For Diabetic Glaucoma Treatment?
 While there isn’t a specific drink that can treat diabetic glaucoma, maintaining a well-balanced and nutritious diet is essential for overall health, including eye health. Proper nutrition can contribute to managing diabetes and potentially supporting eye health. Here are some recommendations for beverages that individuals with diabetes and glaucoma may consider as part of a healthy lifestyle:
While there isn’t a specific drink that can treat diabetic glaucoma, maintaining a well-balanced and nutritious diet is essential for overall health, including eye health. Proper nutrition can contribute to managing diabetes and potentially supporting eye health. Here are some recommendations for beverages that individuals with diabetes and glaucoma may consider as part of a healthy lifestyle:
- Herbal Teas
Herbal teas, such as chamomile or green tea, can be good options. These teas are naturally caffeine-free and may have antioxidants that can contribute to general health. However, it’s important to avoid adding sugar to your tea, and moderation is key.
- Green Smoothies
Green smoothies made with leafy greens like spinach or kale, along with low-carb fruits like berries, can provide essential nutrients. Be mindful of the fruit content to manage carbohydrate intake. Also, consider using water or unsweetened almond milk as a base.
- Vegetable Juices
Freshly squeezed vegetable juices, such as carrot or beet juice, can be nutrient-rich. However, it’s crucial to be cautious with fruit juices due to their high sugar content. Consider diluting fruit juices with water or choosing whole fruits instead.
- Low-Glycemic Smoothies
Create smoothies using ingredients with a low glycemic index, such as non-starchy vegetables, berries, and a source of protein like Greek yogurt or protein powder. This can help manage blood sugar levels while providing essential nutrients.
- Milk Alternatives
Unsweetened almond milk, coconut milk, or soy milk can be suitable alternatives to cow’s milk. Choose those labeled as “unsweetened” to avoid added sugars.
It’s important to note that while certain foods and drinks may support overall health, they are not a substitute for medical treatment or professional advice. Before making significant changes to your diet, especially if you have diabetes, it’s advisable to consult with a healthcare professional or a registered dietitian.
Conclusion
In conclusion, diabetic glaucoma treatment requires a multifaceted approach that encompasses medical treatments, lifestyle adjustments, and regular monitoring. Understanding the interplay between diabetes and glaucoma is crucial for preserving vision. From medication and laser therapies to surgical interventions and a focus on overall health, individuals can take proactive steps to safeguard their eyesight.
Regular eye exams, proper nutrition, and adherence to prescribed treatments are essential components of a comprehensive strategy. By staying informed and working closely with healthcare professionals, those facing diabetic glaucoma can navigate the path to maintaining their eye health and overall well-being. Do you want to get rid of diabetes? Join our online diabetes treatment program and reverse Diabetes naturally through lifestyle changes such as a Personalized Diet plan, Exercise, Yoga, dieticians, and health coaches.