GLP-1 (Glucagon-Like Peptide-1) injections harness the body’s mechanisms to regulate blood sugar levels and appetite, offering a promising approach to disease management. In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the science behind GLP-1 injections, their benefits, how they work, and their potential side effects.
Contents
How Does GLP-1 Injection Work?
 GLP-1 (Glucagon-Like Peptide-1) injections work by mimicking the action of the naturally occurring hormone GLP-1 in the body. It plays a crucial role in regulating blood sugar levels and appetite. Here’s an overview of how GLP-1 injections function:
GLP-1 (Glucagon-Like Peptide-1) injections work by mimicking the action of the naturally occurring hormone GLP-1 in the body. It plays a crucial role in regulating blood sugar levels and appetite. Here’s an overview of how GLP-1 injections function:
- Enhancing Insulin Secretion
GLP-1 is an incretin hormone, which means it’s released in response to eating and helps to lower blood sugar levels. One of its key actions is to stimulate the pancreas to produce insulin when blood sugar levels are high. GLP-1 injections enhance this natural insulin secretion, but only when blood sugar levels are elevated. And, reducing the risk of hypoglycemia (abnormally low blood sugar levels).
- Suppressing Glucagon Secretion
Alongside boosting insulin production, GLP-1 also suppresses the secretion of glucagon. Glucagon is a hormone that has the opposite effect of insulin, causing the liver to release stored glucose into the bloodstream. By inhibiting glucagon, GLP-1 injections help lower blood sugar levels.
- Slowing Gastric Emptying
GLP-1 injections slow down the rate at which the stomach empties its contents into the small intestine. This slower gastric emptying helps moderate the rise in blood sugar levels after eating and leads to a more prolonged feeling of fullness. This can help in appetite control and potentially aid in weight loss.
- Appetite Regulation
GLP-1 injections have been found to affect areas of the brain that regulate appetite and food intake, leading to a reduced appetite. This can be particularly beneficial for individuals with obesity or those who need to manage their weight. It is often a concern in type 2 diabetes management.
It’s important to note that GLP-1 injections are typically used in conjunction with other diabetes management strategies. They are primarily used in the treatment of type 2 diabetes. And, in some cases, for weight management in individuals with obesity.
Which GLP-1 Is Best For Diabetes?
Determining the “best” GLP-1 (Glucagon-Like Peptide-1) receptor agonist for diabetes management depends on various factors. Generally, several GLP-1 receptor agonists are available, each with its own set of characteristics. Here’s a brief overview of some commonly used GLP-1 receptor agonists:
- Exenatide (Byetta/Bydureon): Available in a twice-daily injection (Byetta) or a once-weekly injection (Bydureon). It’s effective in lowering blood sugar levels and promoting weight loss but may require more frequent dosing.
- Liraglutide (Victoza/Saxenda): Given as a once-daily injection. It’s known for its effectiveness in blood sugar control and has been approved for cardiovascular risk reduction in individuals with type 2 diabetes. Saxenda, a higher dose of liraglutide, is approved for weight management.
- Dulaglutide (Trulicity): Requires once-weekly injection. It is popular due to its convenience and has also shown benefits in reducing cardiovascular risk in people with type 2 diabetes.
- Semaglutide (Ozempic/Rybelsus): Available as a once-weekly injection (Ozempic) or a daily oral pill (Rybelsus). Semaglutide has demonstrated significant efficacy in lowering blood sugar and promoting weight loss, with Ozempic being particularly noted for its effectiveness in weight management.
- Albiglutide (Tanzeum) and Lixisenatide (Adlyxin): Other options, each with their dosing schedules and profiles.
Individuals must consult with their healthcare provider to choose the most suitable GLP-1 receptor agonist based on their medical history, lifestyle, treatment goals, and individual preferences. The healthcare provider will also consider any potential side effects and how the medication fits into the overall diabetes management plan.
How Can I Take GLP-1 Injections?
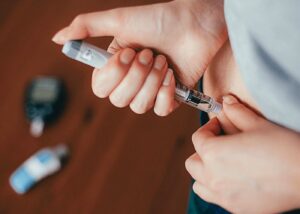 Taking a GLP-1 (Glucagon-Like Peptide-1) injection involves several steps, and it’s important to follow them carefully to ensure the medication is administered correctly and safely. Here’s a general guide on how to take a GLP-1 injection.
Taking a GLP-1 (Glucagon-Like Peptide-1) injection involves several steps, and it’s important to follow them carefully to ensure the medication is administered correctly and safely. Here’s a general guide on how to take a GLP-1 injection.
- Prepare the Injection Site
The injection is usually given subcutaneously. It means into the fatty layer just beneath the skin. Common injection sites include the abdomen, thigh, or upper arm. Avoid areas where the skin is bruised, tender, or hard.
- Clean the Injection Site
Use an alcohol swab to clean the area where you will inject the medication. Let the skin dry before you inject.
- Prepare the Injection Pen
If you’re using a new pen, you might need to attach a new needle. Remove the protective caps from the needle and pen. Depending on the type of pen, you may need to prime it to ensure it’s working correctly.
- Set the Dose
Follow the instructions for your specific medication to set the dose on the injection pen.
- Inject the Medication
Pinch up a section of skin at the cleaned injection site. Insert the needle fully into the pinched-up area at the angle recommended in the instructions (usually 90 degrees). Press the button on the pen to inject the medication. Hold the button down and leave the needle in place for the count recommended in your instructions (usually about 5-10 seconds) to make sure you get the full dose.
- Remove the Needle
Pull the needle out of the skin and release the pinched skin. If there’s bleeding, you can gently press on the injection site with a cotton ball or tissue. Do not rub the area.
- Dispose of the Needle Safely
Place the used needle in a sharps disposal container. Never reuse needles or share your injection pen with others.
Overall, it’s important to rotate injection sites with each dose to reduce the risk of lipodystrophy (changes in fat tissue) and localized skin reactions. Also, be aware of how to identify and manage potential side effects, and know when to seek medical attention.
What Are Some Risks And Considerations Of GLP-1 Injections?
 GLP-1 injections are generally safe and effective for the treatment of type 2 diabetes and, in some cases, obesity. However, like all medications, they come with potential risks and considerations. Here’s an overview:
GLP-1 injections are generally safe and effective for the treatment of type 2 diabetes and, in some cases, obesity. However, like all medications, they come with potential risks and considerations. Here’s an overview:
Gastrointestinal Side Effects
The most common side effects of GLP-1 receptor agonists are gastrointestinal. These can include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, constipation, and abdominal pain. These side effects are often mild and tend to decrease over time.
Hypoglycemia
While GLP-1 receptor agonists have a lower risk of causing hypoglycemia (low blood sugar) compared to some other diabetes medications, the risk can increase when they are used in combination with other drugs that lower blood sugar, such as insulin or sulfonylureas.
Pancreatitis
There have been reports of acute pancreatitis in patients using GLP-1 receptor agonists. Symptoms can include severe abdominal pain, nausea, and vomiting. It’s important to seek immediate medical attention if these symptoms occur.
Allergic Reactions
As with any medication, there’s a risk of allergic reactions, which could range from mild skin reactions to more severe responses like anaphylaxis. It’s important to be aware of the signs of an allergic reaction and seek medical help if they occur.
Thyroid Tumors
In animal studies, some GLP-1 receptor agonists have been linked to a type of thyroid tumor called medullary thyroid carcinoma. While it’s unclear if this risk applies to humans, patients with a personal or family history of medullary thyroid carcinoma or Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia syndrome type 2 (MEN 2) should not use GLP-1 receptor agonists.
Kidney Effects
GLP-1 receptor agonists can affect kidney function, leading to kidney problems including kidney failure. This is more likely in patients who already have kidney disease.
Cardiovascular Health
While some GLP-1 receptor agonists have been shown to reduce cardiovascular risk in people with type 2 diabetes, the impact on heart health can vary depending on the specific medication and the individual’s overall health profile.
Injection Site Reactions
Some people may experience reactions at the site of injection, such as redness, itching, or swelling.
Pregnancy and Breastfeeding
The safety of GLP-1 receptor agonists during pregnancy and breastfeeding is not well-established. They should be used only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus or infant.
It’s important to remember that individual responses to medications can vary. The decision to use a GLP-1 receptor agonist should be based on a thorough discussion between the patient and their healthcare provider.
Conclusion
In conclusion, GLP-1 injections offer a promising and effective treatment for managing type 2 diabetes and assisting with weight loss. These medications work by mimicking natural hormones to regulate blood sugar levels, reduce appetite, and slow down digestion. While they come with potential side effects, their benefits in improving diabetes control and promoting heart health can be significant.
Overall, it’s crucial to consult with the healthcare provider, discuss the risks and benefits, and closely follow the recommended guidelines for safe and effective use. Do you want to get rid of diabetes? Join our online diabetes treatment program and reverse Diabetes naturally through lifestyle changes such as a Personalized Diet plan, Exercise, Yoga, dieticians, and health coaches.