In the realm of diabetes management, the spotlight often falls on insulin, the hormone crucial for regulating blood sugar levels. However, another player in this intricate metabolic symphony is gaining recognition for its pivotal role—glucagon. Glucagon, often referred to as insulin’s counterpart, plays a crucial role in maintaining glucose balance in the body. In this blog, we will delve into the fascinating world of glucagon treatment, exploring its functions, applications, and the potential it holds for individuals managing diabetes and other metabolic disorders.
Contents
What Is Glucagon Treatment?
 Glucagon treatment involves the therapeutic administration of the hormone glucagon to address imbalances in blood sugar levels. This plays a crucial role in the regulation of glucose in the body, acting in opposition to insulin. While insulin facilitates the uptake of glucose into cells, glucagon stimulates the liver to release stored glucose into the bloodstream, thus elevating blood sugar levels. In medical contexts, glucagon treatment is often employed as a rapid and effective intervention for severe hypoglycemia.
Glucagon treatment involves the therapeutic administration of the hormone glucagon to address imbalances in blood sugar levels. This plays a crucial role in the regulation of glucose in the body, acting in opposition to insulin. While insulin facilitates the uptake of glucose into cells, glucagon stimulates the liver to release stored glucose into the bloodstream, thus elevating blood sugar levels. In medical contexts, glucagon treatment is often employed as a rapid and effective intervention for severe hypoglycemia.
This treatment can be administered through injections and is particularly vital in emergencies, offering a prompt response to restore glucose balance and prevent potential complications associated with low blood sugar. Additionally, ongoing research explores the broader applications of glucagon treatment, hinting at its potential in addressing various metabolic disorders beyond diabetes.
What Are The Functions Of It?
Glucagon, a hormone produced by the alpha cells of the pancreas, serves several crucial functions in maintaining glucose homeostasis and supporting overall metabolic balance in the body. Its primary functions include:
- Glucose Release from the Liver: One of the central roles of glucagon is to stimulate the liver to break down glycogen into glucose molecules and release them into the bloodstream. This process, known as glycogenolysis, contributes to an increased concentration of glucose in the blood.
- Gluconeogenesis: Glucagon promotes gluconeogenesis, a process in which the liver synthesizes new glucose molecules from non-carbohydrate sources, such as amino acids and glycerol. This further adds to the pool of circulating glucose during periods of low blood sugar.
- Inhibition of Glycogen Synthesis: Glucagon inhibits glycogen synthesis, preventing the storage of glucose in the form of glycogen. This helps to maintain glucose availability for energy production, especially during fasting or between meals.
- Promotion of Lipolysis: Glucagon stimulates the breakdown of fats (lipolysis) in adipose tissue, releasing fatty acids into the bloodstream. These fatty acids can be used as alternative energy sources, particularly when glucose levels are low.
- Inhibition of Insulin Secretion: Glucagon and insulin have opposing actions in regulating blood sugar. While insulin promotes glucose uptake and storage, glucagon inhibits insulin secretion, preventing an excess decrease in blood glucose levels.
Overall, the functions of glucagon work in tandem with insulin to ensure a delicate balance of glucose in the bloodstream. And, providing the body with a steady and regulated energy supply. Imbalances in this system can lead to conditions such as hypoglycemia or hyperglycemia, highlighting the critical role of both hormones in maintaining metabolic equilibrium.
How To Be Prepared For The Glucagon Treatment?
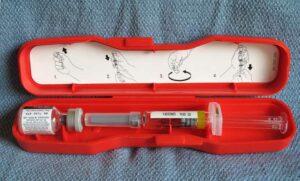 Being prepared for glucagon treatment involves a combination of understanding how to use glucagon in emergencies and ensuring that those around you are familiar with the process. Here’s a guide to being prepared for glucagon treatment:
Being prepared for glucagon treatment involves a combination of understanding how to use glucagon in emergencies and ensuring that those around you are familiar with the process. Here’s a guide to being prepared for glucagon treatment:
Education and Training
- Patients: Individuals with diabetes or those at risk of severe hypoglycemia should receive a thorough education on how to use glucagon. This includes understanding when and how to administer it.
- Caregivers and Family Members: Those close to individuals at risk should also be trained on the proper administration of glucagon. Knowledge of the steps involved and familiarity with the emergency kit is crucial.
Emergency Kit Accessibility
- Home and Workplace: Ensure that the emergency glucagon kit is easily accessible in places where the individual spends a significant amount of time. Such as at home and in the workplace.
- Carry It Everywhere: For individuals with diabetes, carrying a portable glucagon kit is essential. This is particularly important for those who may experience hypoglycemic episodes away from home.
Regular Check and Expiry Dates
- Check Regularly: Periodically check the contents of the glucagon emergency kit to ensure that all components, including the syringe and vial, are present and in good condition.
- Monitor Expiry Dates: Glucagon kits have expiration dates. So be vigilant about these dates and replace the kit before it expires.
Communication
- Inform Others: Make sure that people in your immediate surroundings, such as family members, friends, and coworkers, are aware of the existence and location of the glucagon kit. This is especially important in case of an emergency where you might not be able to administer it yourself.
Emergency Action Plan
- Develop a Plan: Work with healthcare providers to establish a clear emergency action plan. This plan should include steps to take in the event of severe hypoglycemia when to administer glucagon, and when to seek additional medical assistance.
Regular Medical Follow-Up
- Doctor’s Guidance: Regularly consult with healthcare providers to review the overall management plan, including the use of glucagon. They can guide adjustments to medication, diet, and other factors that may impact the risk of hypoglycemia.
Being well-prepared for glucagon treatment involves a combination of education, accessibility, and communication. Regular training, open communication with healthcare providers, and proactive management can significantly contribute to a swift and effective response in case of a hypoglycemic emergency.
Can Glucagon Be Given Orally?
Glucagon is primarily administered through injection and is not available in an oral form. The reason for this lies in the digestive processes of the stomach. This can break down and render the hormone ineffective if taken orally.
Glucagon is a peptide hormone, and like insulin, it is a protein that would be degraded by stomach acids and digestive enzymes if ingested. Therefore, to ensure its effectiveness, it is typically administered through intramuscular or subcutaneous injection. These injection methods allow for the hormone to be absorbed directly into the bloodstream, bypassing the digestive system.
It’s worth noting that developments and innovations in medical research and technology can occur. And there may be updates or new formulations of medications lately. It’s always advisable to consult with a healthcare professional for the most current information on medications and treatments.
What Are Some Pros And Cons Of Glucagon Treatment?
 The following are some pros and cons of glucagon treatment to consider:
The following are some pros and cons of glucagon treatment to consider:
Pros
- Rapid Blood Sugar Increase: Glucagon treatment acts quickly to raise blood sugar levels. And, making it a crucial intervention for severe hypoglycemia when immediate action is necessary.
- Emergency Lifesaver: Glucagon is a life-saving treatment in situations where an individual with diabetes is unconscious or unable to consume oral carbohydrates. It provides a way to increase blood sugar without the need for the person to swallow or eat.
- Portable and Easy to Administer: Glucagon emergency kits are designed to be portable and user-friendly, often coming with step-by-step instructions. This makes it accessible to both individuals with diabetes and their caregivers.
- Effective for Severe Hypoglycemia: Glucagon is particularly effective in cases of severe hypoglycemia that do not respond well to oral sugar intake. It provides a reliable means of elevating blood sugar levels rapidly.
Cons
- Injection Administration: Glucagon is currently available in injectable forms. This may be intimidating or challenging for some individuals to administer, especially in high-stress situations.
- Side Effects: Like any medication, glucagon may have side effects, though they are generally rare. Potential side effects may include nausea and vomiting. It’s essential to be aware of these possibilities and monitor for adverse reactions.
- Limited Shelf Life: Glucagon emergency kits have a limited shelf life, and the contents need to be checked regularly to ensure they are not expired. Replacement of expired kits is necessary to maintain efficacy in emergencies.
- Potential for Overdose: In some cases, if too much glucagon is administered, it may lead to hyperglycemia (excessively high blood sugar levels). This can have its own set of complications.
- Not a Long-Term Solution: While glucagon is crucial for emergencies, it is not a substitute for ongoing diabetes management. Addressing the underlying causes of hypoglycemia and working with healthcare professionals to adjust insulin and medication regimens is essential for long-term control.
It’s important to note that the pros and cons can vary depending on individual circumstances. Hence, decisions about the use of glucagon should be made in consultation with healthcare providers. Clear communication with healthcare professionals, proper education on administration, and addressing concerns can help individuals and their caregivers feel more confident in managing severe hypoglycemia with glucagon treatment.
Conclusion
In conclusion, exploring the multifaceted realm of glucagon treatment reveals its pivotal role in the intricate orchestration of metabolic health. From its rapid response as a lifeline in severe hypoglycemic emergencies to its potential applications beyond diabetes, glucagon emerges as a dynamic player in maintaining glucose balance. The journey through the nuances of its functions, innovations in therapy, and the firsthand experiences of individuals underscores its significance.
As research continues to unfold, the future holds promise for further advancements, reshaping the narrative of glucagon treatment and offering new avenues for enhanced patient well-being.
Do you want to get rid of diabetes? Join our online diabetes treatment program and reverse Diabetes naturally through lifestyle changes such as a Personalized Diet plan, Exercise, Yoga, dieticians, and health coaches.