Diabetes Mellitus, commonly known as diabetes, is a chronic metabolic disorder characterized by elevated blood glucose levels. While medication plays a crucial role in managing diabetes, non-pharmacological interventions are equally important in achieving optimal health outcomes. This blog explores various Non-Pharmacological Management of Diabetes Mellitus that can be incorporated into their daily lives to better manage their condition.
Contents
What Does “Non-Pharmacological Management” Mean?
Non-pharmacological management refers to the use of interventions and strategies that do not involve the administration of medications or drugs for the treatment or control of a medical condition. In the context of diabetes mellitus, non-pharmacological management focuses on lifestyle modifications and behavioral changes to help control blood glucose levels and improve overall health without relying solely on medication.
The goal of non-pharmacological management is to address various aspects of an individual’s lifestyle, including diet, physical activity, stress management, and other behavioral factors, to positively impact the course of the disease and its associated complications. This approach recognizes the importance of a holistic and comprehensive strategy in managing chronic conditions like diabetes.
Why Do People Prefer Non-Pharmacological Management of Diabetes Mellitus?

People often prefer non-pharmacological management of diabetes mellitus for various reasons, as these approaches offer a range of benefits that contribute to overall well-being. Here are some common reasons why individuals with diabetes may choose non-pharmacological interventions:
- Reduced Side Effects: Many individuals experience side effects from diabetes medications. Non-pharmacological interventions, such as lifestyle modifications, are generally associated with fewer side effects compared to medications. This can improve the overall quality of life for individuals managing diabetes.
- Holistic Approach: Non-pharmacological management emphasizes a holistic approach to health, addressing various aspects of an individual’s lifestyle, including diet, exercise, and stress management. This comprehensive strategy aligns with the idea of treating the whole person rather than focusing solely on the symptoms of the disease.
- Empowerment and Control: Non-pharmacological interventions empower individuals to take an active role in managing their diabetes. Through lifestyle changes, individuals can gain a sense of control over their health and reduce their reliance on medications, fostering a greater sense of autonomy.
- Prevention of Complications: Lifestyle modifications can contribute to the prevention or delay of complications associated with diabetes, such as cardiovascular issues, neuropathy, and kidney problems. By addressing risk factors through non-pharmacological means, individuals aim to minimize the long-term impact of the disease.
- Personalized Approach: Non-pharmacological management allows for a more personalized approach to diabetes care. Individuals can work with healthcare professionals to tailor lifestyle changes to their specific needs, preferences, and cultural considerations.
- Cost Considerations: Medications for diabetes management can be expensive. Non-pharmacological interventions, such as dietary changes and regular physical activity, maybe more cost-effective for some individuals, especially those facing financial constraints.
- Improved Overall Health: Adopting a healthy lifestyle can lead to improvements in overall health beyond diabetes management. Weight loss, better cardiovascular health, and increased energy levels are common positive outcomes associated with non-pharmacological interventions.
- Long-Term Sustainability: Non-pharmacological interventions often promote sustainable lifestyle changes. Unlike medications, which may need adjustment over time, healthy habits such as a balanced diet and regular exercise can be maintained in the long term.
- Psychosocial Benefits: Engaging in non-pharmacological interventions, such as group exercise or mindfulness activities, can provide social support and contribute to improved mental well-being. This social aspect can be an important motivator for individuals managing diabetes.
It’s important to note that the preference for non-pharmacological management may vary among individuals, and the most effective approach often involves a combination of lifestyle modifications and medication as determined by healthcare professionals.
Non-Pharmacological Management of Diabetes Mellitus
This approach is crucial for individuals with diabetes as it complements pharmacological interventions and contributes to a comprehensive management plan. Here are key components of non-pharmacological management for diabetes:
Dietary Modifications

Carbohydrate Management: Carbohydrates are a primary source of energy, and managing their intake is crucial for individuals with diabetes. Focusing on complex carbohydrates, such as whole grains, vegetables, and legumes, provides sustained energy without causing rapid spikes in blood sugar levels. Limiting simple sugars, found in sweets and sugary beverages, helps control blood glucose fluctuations.
Portion Control: Controlling portion sizes is essential for preventing overconsumption of calories and managing blood sugar levels. Eating smaller, well-balanced meals throughout the day can help prevent post-meal spikes. This approach also supports weight management, a critical factor in diabetes control.
Glycemic Index (GI): Understanding the glycemic index of foods helps individuals make informed choices. Foods with a lower glycemic index release glucose more gradually, preventing sudden spikes in blood sugar. Choosing low-GI foods, such as whole grains and certain fruits, contributes to stable blood glucose levels.
Regular Physical Activity
Aerobic Exercise: Regular aerobic activities, including brisk walking, jogging, or cycling, have a profound impact on insulin sensitivity. Exercise facilitates the uptake of glucose by cells, reducing blood sugar levels. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise per week for optimal benefits.
Strength Training: Incorporating resistance or strength training exercises helps build muscle mass. Increased muscle mass enhances glucose utilization, supporting better blood sugar control. Strength training also contributes to overall metabolic health and aids in weight management.
Flexibility Exercises: Activities like yoga or stretching exercises promote flexibility and relaxation. While not directly impacting blood glucose levels, these exercises contribute to overall well-being by reducing stress, which can indirectly affect diabetes control.
Weight Management
Healthy Weight: Maintaining a healthy weight is paramount for individuals with diabetes. Even modest weight loss can significantly improve insulin sensitivity and blood sugar control. Weight management is often achieved through a combination of dietary modifications and regular physical activity.
Nutritional Counseling: Seeking guidance from a registered dietitian or nutritionist provides personalized advice on dietary choices and meal planning. Nutritional counseling helps individuals create sustainable and tailored meal plans that align with their specific health needs and diabetes management goals.
Stress Management
Mindfulness and Relaxation Techniques: Chronic stress can elevate blood sugar levels. Mindfulness practices, such as meditation and deep breathing exercises, promote relaxation and stress reduction. These techniques not only benefit mental health but also positively impact blood glucose control.
Adequate Sleep: Quality sleep is essential for overall health, including diabetes management. Lack of sleep can affect insulin sensitivity and contribute to elevated blood sugar levels. Establishing a regular sleep routine and addressing sleep-related issues are critical components of stress management.
Monitoring Blood Sugar Levels
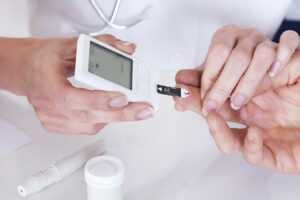
Regular Monitoring: Consistent monitoring of blood glucose levels provides valuable insights into how lifestyle factors, including diet and physical activity, impact diabetes control. Regular monitoring empowers individuals to make informed decisions about their daily routines and make necessary adjustments.
Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM): Advanced technologies, such as continuous glucose monitoring devices, offer real-time data on blood glucose levels. CGM devices provide a more comprehensive understanding of fluctuations throughout the day, enabling individuals to fine-tune their management strategies.
Smoking Cessation and Limiting Alcohol Intake
Quitting Smoking: Smoking is associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular complications in individuals with diabetes. Quitting smoking not only supports overall cardiovascular health but also contributes to improved blood circulation and better diabetes management.
Moderate Alcohol Consumption: If individuals with diabetes choose to consume alcohol, moderation is key. Excessive alcohol intake can lead to fluctuations in blood sugar levels. Understanding the impact of alcohol on diabetes and making informed choices aligns with a holistic approach to health.
Education and Support
Diabetes Education Programs: Participating in diabetes education programs enhances knowledge about the condition, its management, and lifestyle changes. Education empowers individuals to make informed decisions, fostering a sense of control over their health.
Support Groups: Joining diabetes support groups provides a sense of community and shared experiences. Emotional well-being is a crucial aspect of diabetes management, and having a supportive network can offer encouragement and motivation.
Behavioral Changes
Goal Setting: Establishing realistic and achievable goals is vital for the success of lifestyle changes. Setting specific, measurable, and time-bound goals helps individuals track their progress and stay motivated on their diabetes management journey.
Behavioral Therapy: In some cases, behavioral therapy or counseling may be beneficial to address psychological aspects of diabetes management. Coping with the emotional challenges associated with diabetes can positively influence adherence to lifestyle changes.
Social and Environmental Factors
Social Support: Creating a supportive network of family and friends is essential. Also, Social support encourages individuals to maintain healthy habits and provides emotional support during the ups and downs of managing diabetes.
Environmental Modifications: Making adjustments to the environment, such as having readily available nutritious snacks and incorporating physical activity into daily routines, fosters a health-conscious lifestyle. Creating an environment that supports healthy choices contributes to the long-term sustainability of lifestyle modifications.
Regular Medical Check-ups
Consistent visits to healthcare professionals are critical for ongoing monitoring and adjustments to the management plan. Regular check-ups enable healthcare providers to assess the effectiveness of non-pharmacological interventions and make necessary modifications based on individual health needs.
Conclusion:
In the management of diabetes mellitus, a holistic approach that combines pharmacological and non-pharmacological strategies is key to achieving optimal health outcomes. Implementing lifestyle modifications such as a balanced diet, regular physical activity, stress management, and maintaining a healthy weight can significantly contribute to effective diabetes control. By adopting these non-pharmacological interventions, individuals with diabetes can empower themselves to lead healthier, more fulfilling lives. Always consult with healthcare professionals for personalized advice based on individual health needs and conditions.
Do you want to get rid of diabetes? Join our online diabetes treatment program and reverse Diabetes naturally through lifestyle changes such as a Personalized Diet plan, Exercise, Yoga, dieticians, and health coaches.