Pancreatic diabetes, also known as secondary diabetes, is a form of diabetes that occurs as a result of damage to the pancreas, affecting its ability to produce insulin. This condition can arise from various causes, such as chronic pancreatitis, pancreatic cancer, or surgical removal of the pancreas. Managing pancreatic diabetes presents unique challenges, and a comprehensive treatment approach is essential to improve the quality of life for affected individuals. In this blog, we will delve into the causes, symptoms, and various treatment strategies for pancreatic diabetes.
Understanding Pancreatic Diabetes
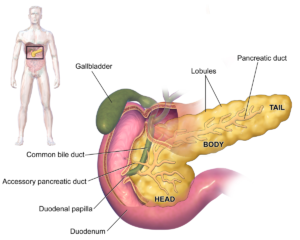
Pancreatic diabetes differs from type 1 and type 2 diabetes, as it is not primarily characterized by autoimmune destruction of insulin-producing cells or insulin resistance. Instead, it is a consequence of pancreatic dysfunction. The pancreas plays a crucial role in blood sugar regulation by producing insulin, and any damage to this organ can lead to diabetes.
Causes:
- Chronic Pancreatitis: Chronic inflammation of the pancreas can result in damage to the insulin-producing cells, leading to pancreatic diabetes. Alcohol abuse, gallstones, and certain genetic factors can contribute to chronic pancreatitis.
- Pancreatic Cancer: Pancreatic cancer can affect the pancreas’s ability to produce insulin. The growth of cancerous cells can disrupt normal pancreatic function, impacting both insulin and digestive enzyme production.
- Pancreatectomy: Surgical removal of all or part of the pancreas (pancreatectomy) may be necessary in some medical conditions, such as severe pancreatic trauma or tumors. This can lead to insufficient insulin production and subsequent diabetes.
Symptoms:
The symptoms of pancreatic diabetes are similar to those of other forms of diabetes and may include:
- Increased thirst and hunger
- Frequent urination
- Unexplained weight loss
- Fatigue
- Blurred vision
Best Pancreatic Diabetes Treatment Methods
The treatment of pancreatic diabetes typically involves managing both the underlying pancreatic condition and the resulting diabetes. Here are some key treatment methods:
Pancreatic Enzyme Replacement Therapy (PERT)
Pancreatic Enzyme Replacement Therapy (PERT) is a crucial component of the treatment for individuals with pancreatic diabetes, addressing the challenges related to impaired digestion.
- The pancreas produces enzymes, such as amylase, lipase, and protease, which are essential for breaking down carbohydrates, fats, and proteins in the digestive process.
- In pancreatic diabetes, where the pancreas is compromised, the production of these digestive enzymes is often insufficient, leading to malabsorption and nutrient deficiencies.
- PERT involves the supplementation of these digestive enzymes through oral medications, assisting in the breakdown of food and facilitating nutrient absorption in the small intestine.
Patients typically take enzyme capsules with meals to ensure proper digestion. This therapy helps alleviate symptoms like diarrhea, steatorrhea (excess fat in the stool), and weight loss associated with malabsorption.
Islet Cell Transplantation
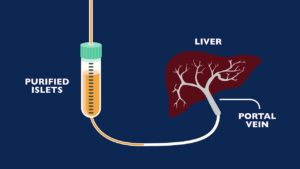
Islet cell transplantation represents a cutting-edge approach to treating pancreatic diabetes, focusing on restoring insulin production by introducing healthy islet cells into the pancreas. Islets of Langerhans contain beta cells, responsible for insulin secretion.
- In this procedure, islets are isolated from a donor pancreas and then transplanted into the recipient’s liver, where they can establish new blood vessel connections and begin producing insulin.
- While islet cell transplantation is not yet a widely established treatment, it shows promise, particularly in cases of severe pancreatic diabetes where traditional therapies may be insufficient.
The goal is to improve glycemic control, reduce the need for exogenous insulin, and enhance overall quality of life. Ongoing research aims to refine the transplantation process, address immune system challenges to prevent rejection and extend the duration of successful outcomes.
Artificial Pancreas Systems
Artificial Pancreas Systems (APS) represent a revolutionary advancement in diabetes management, offering a more automated and precise approach to insulin delivery. These systems integrate continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) with an insulin pump, creating a closed-loop system that adjusts insulin doses in real time based on the individual’s blood glucose levels.
- This technology aims to mimic the natural function of a healthy pancreas more closely, providing a continuous and dynamic response to changing glucose levels.
- The CGM component constantly measures blood glucose levels, sending this information to a control algorithm.
- The algorithm, in turn, calculates and administers the appropriate insulin dose through the insulin pump. APS technology has shown promise in improving glycemic control, reducing the risk of hypoglycemia, and offering greater flexibility to individuals with pancreatic diabetes.
While research and development in this field are ongoing, the potential benefits of APS systems include enhanced quality of life, reduced diabetes-related complications, and a more streamlined and efficient approach to diabetes management.
Regenerative Medicine
Regenerative medicine explores innovative approaches to repair or replace damaged tissues, and this includes efforts to regenerate insulin-producing cells in the pancreas.
- Stem cell therapy is a key focus in this field, aiming to stimulate the regeneration of beta cells or replace damaged pancreatic tissue with functional cells.
- While still in the experimental stages, early research suggests that certain types of stem cells, such as mesenchymal stem cells, may have the potential to differentiate into insulin-producing cells.
The goal of regenerative medicine in the context of pancreatic diabetes is to restore normal pancreatic function, reducing or eliminating the need for exogenous insulin.
However, challenges such as immune system response, ethical considerations, and the optimization of cell differentiation protocols need to be addressed. Ongoing research and clinical trials are exploring the safety and efficacy of regenerative approaches, offering hope for future breakthroughs in the treatment of pancreatic diabetes.
Alternative Therapies
Complementary and alternative therapies have gained attention as potential adjuncts to traditional treatments for pancreatic diabetes. While these approaches are not meant to replace conventional medical interventions, some individuals find them beneficial in managing symptoms and improving overall well-being.
Acupuncture: Acupuncture involves the insertion of thin needles into specific points of the body to stimulate energy flow. Some studies suggest that acupuncture may help in managing pain, a common symptom associated with chronic pancreatitis, which can lead to pancreatic diabetes. However, more research is needed to establish its effectiveness in the context of diabetes management.
Yoga: Yoga combines physical postures, breathing exercises, and meditation. It may contribute to stress reduction and improved overall health, factors that can positively impact blood glucose levels. While yoga alone is not a substitute for medical treatments, incorporating it into a comprehensive diabetes management plan may offer holistic benefits.
Herbal Supplements: Certain herbal supplements, such as bitter melon, fenugreek, and aloe vera, have been explored for their potential anti-diabetic properties. However, it’s crucial to approach herbal supplements with caution, as their efficacy and safety can vary, and interactions with other medications may occur. Consulting with a healthcare provider before incorporating herbal supplements into the treatment plan is advisable.
It’s essential to note that while these alternative therapies may provide additional support, they should be approached with an understanding of their limitations and in consultation with healthcare professionals.
Insulin Therapy
Insulin therapy is the cornerstone of treatment for pancreatic diabetes due to the impaired insulin production resulting from pancreatic damage. The goal is to mimic the body’s natural insulin secretion patterns, providing the necessary hormone to regulate blood sugar levels effectively.
- Different types of insulin are used, such as rapid-acting, short-acting, intermediate-acting, and long-acting insulin, to replicate the body’s varied insulin needs throughout the day.
- Individuals with pancreatic diabetes may be prescribed a combination of insulin types to achieve optimal blood glucose control.
- The dosage and timing of insulin injections are tailored to each patient’s specific requirements, often considering factors like meal timings and physical activity.
- Frequent monitoring of blood glucose levels is crucial to adjusting insulin dosages, ensuring they align with the body’s changing needs, and maintaining stable blood sugar levels over time.
Oral Medications
While insulin is a primary treatment, some oral medications may be considered in conjunction with insulin therapy to improve blood sugar control in pancreatic diabetes. Sulfonylureas, such as glipizide and glyburide, stimulate the pancreas to produce more insulin. These medications may be used when there is still some residual insulin production.
- Meglitinides, like repaglinide and nateglinide, work similarly to sulfonylureas but have a shorter duration of action. They are taken before meals to stimulate insulin release in response to food intake.
- Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitors, including sitagliptin and saxagliptin, enhance insulin secretion while suppressing glucagon, a hormone that raises blood sugar levels. These medications can be beneficial in managing post-meal glucose levels in pancreatic diabetes.
Lifestyle Modifications

Adopting a healthy lifestyle is integral to managing pancreatic diabetes.
- Dietary choices play a crucial role, and individuals are often advised to follow a well-balanced diet that includes a variety of nutrient-rich foods. A registered dietitian can create a personalized meal plan, considering factors such as calorie intake, carbohydrate distribution, and the need for specific nutrients.
- Regular physical activity is also vital for managing blood sugar levels. Exercise helps the body use insulin more effectively, reducing the reliance on external insulin or medications. However, exercise plans should be tailored to individual capabilities and health conditions.
- Additionally, managing body weight is essential, as excess weight can contribute to insulin resistance. Weight loss, if necessary, should be achieved through a combination of a healthy diet and regular physical activity.
- Alcohol consumption should be moderated, as excessive alcohol intake can exacerbate pancreatic damage.
- Quitting smoking is strongly recommended, as smoking has detrimental effects on overall health and can worsen complications associated with pancreatic diabetes.
Regular Follow-up and Monitoring
Consistent follow-up and monitoring play a pivotal role in the ongoing management of pancreatic diabetes. Regular check-ups with healthcare providers allow for the assessment of treatment effectiveness, the identification of potential complications, and the adjustment of therapeutic strategies.
Blood Glucose Monitoring: Continuous monitoring of blood glucose levels is critical for fine-tuning insulin dosages and ensuring glycemic control. Advances in technology, such as continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) systems, provide real-time data and insights into glucose fluctuations, facilitating more precise adjustments to the treatment plan.
Medication Adjustments: As the condition and individual needs evolve, healthcare providers may need to modify medication regimens. This may involve adjusting insulin doses, introducing new oral medications, or exploring alternative therapies based on the individual’s response to treatment.
Nutritional Assessment: Regular evaluations by dietitians help tailor dietary plans to the specific needs of individuals with pancreatic diabetes. Nutritional assessments take into account factors such as digestive enzyme supplementation, nutrient absorption, and any dietary restrictions or preferences.
Psychosocial Support: Living with a chronic condition like pancreatic diabetes can have emotional and psychological impacts. Regular check-ins with healthcare providers, as well as participation in support groups or counseling, can address the mental health aspects of diabetes management. Support in coping with stress, anxiety, and depression is integral to achieving holistic well-being.
Conclusion
Pancreatic diabetes presents a unique set of challenges, requiring a multidimensional approach to treatment. By addressing the underlying causes, implementing insulin therapy, incorporating oral medications, and making necessary lifestyle modifications, individuals with pancreatic diabetes can achieve better blood sugar control and improve their overall quality of life. A collaborative effort between healthcare providers, dietitians, and individuals themselves is vital for the successful management of this complex condition.
Do you want to get rid of diabetes? Join our online diabetes treatment program and reverse Diabetes naturally through lifestyle changes such as a Personalized Diet plan, Exercise, Yoga, dieticians, and health coaches.

