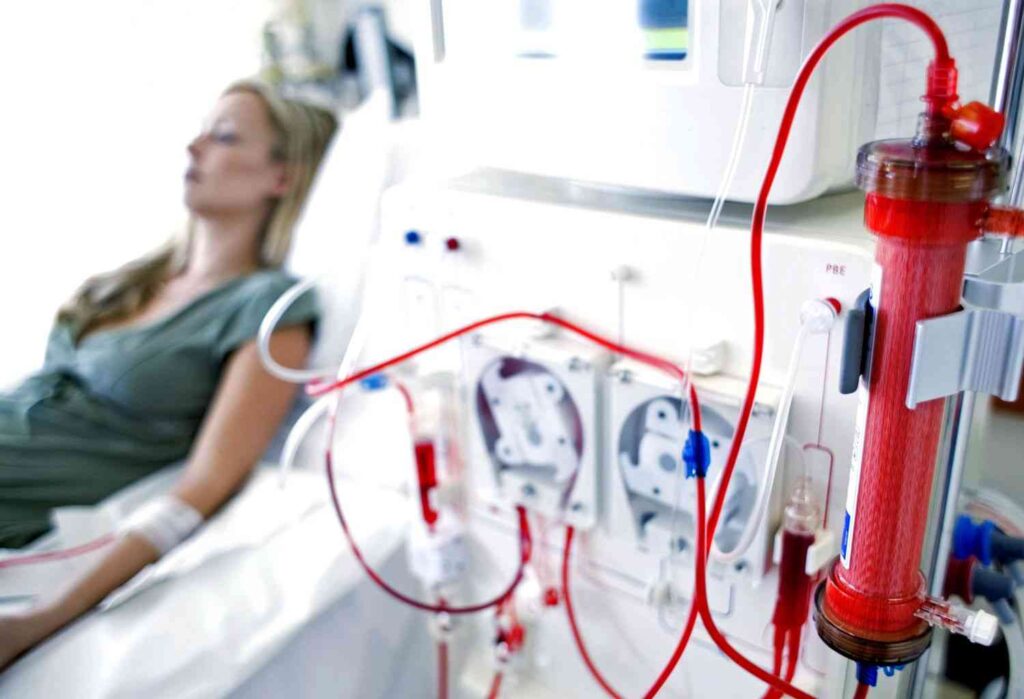
Diabetes is a complex condition that can lead to numerous health issues, including kidney damage that necessitates dialysis treatment. Understanding the intersection of diabetes management and dialysis is crucial for patients facing this dual challenge. This blog aims will discuss the challenges, offering insights and practical advice on diabetes dialysis treatment. From recognizing the challenges to deal with to adjusting your diet and lifestyle, we’ll guide you through the essential steps to maintain your health and quality of life.
Contents
Can A Diabetic Patient Survive On Dialysis?
 Yes, diabetic patients can survive on dialysis, although managing both diabetes and dialysis presents a complex challenge that requires meticulous attention to health management. Diabetes is a leading cause of kidney failure. For those whose kidneys have been significantly damaged, dialysis is a lifesaving treatment that filters and purifies the blood, compensating for the lost kidney function.
Yes, diabetic patients can survive on dialysis, although managing both diabetes and dialysis presents a complex challenge that requires meticulous attention to health management. Diabetes is a leading cause of kidney failure. For those whose kidneys have been significantly damaged, dialysis is a lifesaving treatment that filters and purifies the blood, compensating for the lost kidney function.
Survival rates for diabetic patients on dialysis have improved significantly over the years, thanks to advancements in medical technology, dialysis techniques, and comprehensive care. The key to improving and maintaining quality of life for diabetic dialysis lies in early detection of kidney damage and adherence to treatment protocols.
What Are The Best Diabetes Dialysis Treatment Options?
Managing diabetes in patients requiring dialysis involves a multi-faceted approach to treat both conditions effectively and improve the patient’s quality of life. Here’s an overview of the best practices in diabetes dialysis treatment:
Choosing the Right Type
The choice between hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis is influenced by various factors including the patient’s lifestyle, medical condition, and personal preferences. Hemodialysis is typically performed three times a week at a clinic, offering a rigorous but efficient means of removing waste products from the blood. This method requires careful scheduling and can be more taxing on the body, particularly for those with diabetes.
On the other hand, peritoneal dialysis allows for more flexibility and is done daily at home. And, making it easier to integrate into the patient’s lifestyle. It uses the lining of the abdomen to filter waste from the blood. This can be gentler and offer the patient more control over their dialysis schedule.
Tight Glucose Control
Effective management of blood glucose levels is paramount for diabetic patients undergoing dialysis. The fluctuating nature of glucose levels during dialysis sessions requires a tailored approach to insulin therapy and other diabetes medications. Continuous or frequent glucose monitoring systems are beneficial in these cases, allowing for real-time adjustments to treatment plans. The goal is to maintain glucose levels within a target range to prevent complications.
Dietary Management
 Nutritional management for patients with diabetes on dialysis is complex. The diet must limit certain nutrients to prevent complications from kidney disease, such as potassium, phosphorus, and fluids while managing carbohydrate intake to control blood sugar levels. This may involve choosing specific types of proteins, controlling portion sizes, and selecting low-potassium fruits and vegetables, all while balancing the need for enjoyable and varied meals.
Nutritional management for patients with diabetes on dialysis is complex. The diet must limit certain nutrients to prevent complications from kidney disease, such as potassium, phosphorus, and fluids while managing carbohydrate intake to control blood sugar levels. This may involve choosing specific types of proteins, controlling portion sizes, and selecting low-potassium fruits and vegetables, all while balancing the need for enjoyable and varied meals.
Cardiovascular Care
Cardiovascular disease is a leading cause of death among patients with diabetes and kidney failure. Managing risk factors such as hypertension and dyslipidemia is critical. This often involves a combination of lifestyle interventions (such as dietary changes and physical activity) and medications, including ACE inhibitors or ARBs to manage blood pressure, and statins to control cholesterol levels. Regular cardiovascular screenings and monitoring help identify and address issues early, improving the patient’s prognosis.
Regular Monitoring and Adjustments
Ongoing assessment of a patient’s response to dialysis and diabetes treatments allows healthcare providers to make necessary adjustments. This includes evaluating kidney function tests, blood glucose levels, and the effectiveness of dialysis. Adjustments may be required for medication dosages, dialysis frequency, or dietary recommendations based on these evaluations. This further help to ensure optimal treatment outcomes and to manage any side effects or complications.
Anemia Management
Anemia is a common issue for patients on dialysis due to reduced erythropoietin production by the kidneys. For diabetic patients, managing anemia is critical to maintain energy levels and prevent additional complications. Treatment strategies often include the use of erythropoiesis-stimulating agents (ESAs) to stimulate red blood cell production and iron supplements to support this process. Regular monitoring of hemoglobin levels helps to adjust these treatments and maintain them within target ranges.
Bone Health and Mineral Balance
Dialysis can disrupt the balance of minerals in the body, leading to bone health issues. Patients may require dietary adjustments to manage phosphate intake, the use of phosphate binders to prevent the absorption of phosphorus from food, and vitamin D supplements to improve calcium absorption and bone health. Monitoring and managing calcium and phosphorus levels are crucial to prevent bone disease and other complications.
Lifestyle Modifications
Encouraging patients to lead an active lifestyle within their physical limitations can have significant benefits. Physical activity can help manage blood glucose levels, improve cardiovascular health, and enhance overall well-being. Smoking cessation is also crucial, as smoking can exacerbate cardiovascular and kidney diseases. Support groups and mental health counseling can provide emotional support. And practical advice for managing the complexities of diabetes and dialysis.
It’s important to remember that the best treatment options are highly individualized. They depend on the patient’s overall health, stage of kidney disease, diabetes management needs, lifestyle, and personal preferences. A collaborative approach involving nephrologists, endocrinologists, dietitians, and diabetes educators is essential to optimize care for diabetic patients on dialysis.
Can Kidneys Start Working Again After Dialysis?
 The possibility of kidneys regaining function after starting dialysis depends largely on the type of kidney failure a patient has experienced: acute or chronic.
The possibility of kidneys regaining function after starting dialysis depends largely on the type of kidney failure a patient has experienced: acute or chronic.
Acute Kidney Failure (Acute Renal Failure)
In cases of acute kidney failure, the kidneys have suddenly stopped working effectively, often due to an event such as a severe infection, drug toxicity, or a blockage in the urinary tract. This condition can sometimes be reversible. If the underlying cause of acute kidney failure can be identified and treated successfully, there is a possibility that the kidneys can recover normal or near-normal function. The time needed for recovery can vary, ranging from a few days to several weeks or even months.
Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) leading to End-Stage Renal Disease (ESRD)
In contrast, chronic kidney disease is a long-term condition where kidney function deteriorates over time. By the time CKD progresses to end-stage renal disease (ESRD), where dialysis or a kidney transplant becomes necessary to sustain life, the damage to the kidneys is usually considered irreversible. In these cases, the kidneys are unlikely to regain enough function to eliminate the need for dialysis or transplantation.
However, there are rare instances where patients with certain types of kidney conditions may see an improvement in their kidney function while on dialysis. These cases are exceptional and often involve specific and sometimes rare conditions that may not apply to the majority of patients on dialysis due to chronic kidney disease. Patients with kidney failure need to have regular follow-ups with their nephrologist to monitor their kidney function and overall health.
Conclusion
In summary, diabetes dialysis treatment presents a unique set of challenges but with the right approach, including choosing the appropriate type of dialysis, maintaining tight glucose control, adhering to dietary restrictions, and making necessary lifestyle adjustments, patients can significantly improve their quality of life. Diabetes and chronic kidney disease are long-term conditions that often require ongoing treatment.
By working closely with healthcare professionals and utilizing available resources, patients can navigate these challenges successfully, maintaining stability in their health and well-being. Do you want to get rid of diabetes? Join our online diabetes treatment program and reverse Diabetes naturally through lifestyle changes such as a Personalized Diet plan, Exercise, Yoga, dieticians, and health coaches.