Diabetes is a chronic condition that affects millions worldwide, characterized by high blood sugar levels either due to insufficient insulin production or the body’s inability to use insulin effectively. While medication and insulin therapy are vital components of diabetes management, dietary choices play a pivotal role in controlling blood sugar levels and overall health. In this guide, we’ll delve into the world of diabetes treatment foods, exploring the principles, strategies, and specific food choices that can help individuals with diabetes manage their condition effectively.
Contents
What is Diabetes?
Before delving into dietary recommendations, it’s essential to understand the different types of diabetes and how they affect the body. The two primary types of diabetes are type 1 and type 2, each with its unique characteristics and treatment approaches.
Type 1 Diabetes:
- Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune condition where the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks and destroys insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas.
- Individuals with type 1 diabetes require insulin injections to survive since their bodies cannot produce insulin.
- While diet plays a crucial role in managing blood sugar levels in type 1 diabetes, insulin therapy is the cornerstone of treatment.
Type 2 Diabetes:
- Type 2 diabetes is characterized by insulin resistance, where the body’s cells become resistant to the effects of insulin, leading to elevated blood sugar levels.
- Lifestyle factors, such as diet, exercise, and weight management, significantly influence the development and progression of type 2 diabetes.
- While some individuals with type 2 diabetes may require insulin therapy, others can manage their condition through lifestyle modifications, including dietary changes.
Why Do People Prefer Diabetes Treatment Foods?

People prefer diabetes treatment foods for several reasons, each stemming from the desire to effectively manage their condition and improve overall health. Here are some key factors driving the preference for these foods:
- Blood Sugar Control: One of the primary reasons people opt for diabetes treatment foods is to regulate blood sugar levels. These foods are typically low in simple sugars and refined carbohydrates, which can cause rapid spikes in blood glucose levels. Instead, they focus on complex carbohydrates, fiber, and nutrient-dense ingredients that help stabilize blood sugar levels over time.
- Health Benefits: Diabetes treatment foods are often rich in essential nutrients such as fiber, vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. These nutrients play crucial roles in supporting overall health, including cardiovascular health, immune function, and digestive health. By choosing nutrient-dense foods, individuals with diabetes can address nutritional deficiencies and reduce the risk of complications associated with the condition.
- Weight Management: Many diabetes treatment foods are low in calories and high in fiber, which can promote feelings of fullness and satiety. By incorporating these foods into their diet, individuals with diabetes can better control their appetite, manage portion sizes, and achieve or maintain a healthy weight. Weight management is particularly important for people with type 2 diabetes, as excess body weight can exacerbate insulin resistance and increase the risk of complications.
- Disease Prevention: A balanced diet rich in diabetes treatment foods can help reduce the risk of developing chronic diseases such as heart disease, stroke, and certain types of cancer. By prioritizing whole grains, lean proteins, fruits, vegetables, and healthy fats, individuals with diabetes can address risk factors associated with these conditions, including high cholesterol, hypertension, and inflammation.
Principles of Diabetes Treatment Foods
The principles of diabetes treatment foods are grounded in the understanding that dietary choices play a critical role in managing blood sugar levels and overall health in individuals with diabetes. These principles are designed to guide food selection, portion control, and meal planning to support optimal diabetes management. Here are the key principles:
Glycemic Control
- The glycemic index (GI) ranks carbohydrate-containing foods based on their effect on blood sugar levels. Foods with a low GI cause a gradual rise in blood sugar levels, while those with a high GI lead to rapid spikes.
- Choosing low-GI foods can help individuals with diabetes better manage their blood sugar levels and prevent sudden fluctuations.
Carbohydrate Counting
- Carbohydrate counting involves monitoring the number of carbohydrates in meals and snacks to regulate blood sugar levels.
- Consistent carbohydrate intake and portion control are essential for maintaining stable blood sugar levels throughout the day.
- Individuals with diabetes often work with healthcare providers or registered dietitians to determine their carbohydrate needs and learn how to adjust insulin doses accordingly.
Balanced Nutrition
- A balanced diet that includes a variety of nutrient-dense foods such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats is crucial for overall health and diabetes management.
- Adequate intake of fiber, vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants supports optimal metabolic function and helps prevent complications associated with diabetes.
- Meals should be balanced to include a combination of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats to provide sustained energy and prevent blood sugar fluctuations.
Portion Control

- Controlling portion sizes is important for managing blood sugar levels and preventing overeating, which can lead to weight gain and insulin resistance.
- Using measuring cups, food scales, or visual cues can help individuals with diabetes accurately portion their meals and snacks.
- Portion control extends beyond carbohydrates to include proteins, fats, and overall calorie intake, ensuring a balanced and nutritious diet.
Meal Timing and Frequency
- Consistent meal timing and spacing can help regulate blood sugar levels and prevent large fluctuations throughout the day.
- Eating smaller, balanced meals and snacks every few hours can help stabilize blood sugar levels and prevent overeating at subsequent meals.
- Some individuals with diabetes may benefit from a structured meal plan with specific meal times and snacks to optimize blood sugar control.
Individualized Approach
- Diabetes management is not one-size-fits-all, and dietary recommendations should be tailored to individual needs, preferences, and lifestyle factors.
- Factors such as age, weight, activity level, medication regimen, cultural background, and food preferences influence dietary choices and meal planning.
- Working with a healthcare provider, registered dietitian, or certified diabetes educator can help individuals with diabetes develop personalized meal plans and strategies for optimizing blood sugar control and overall health.
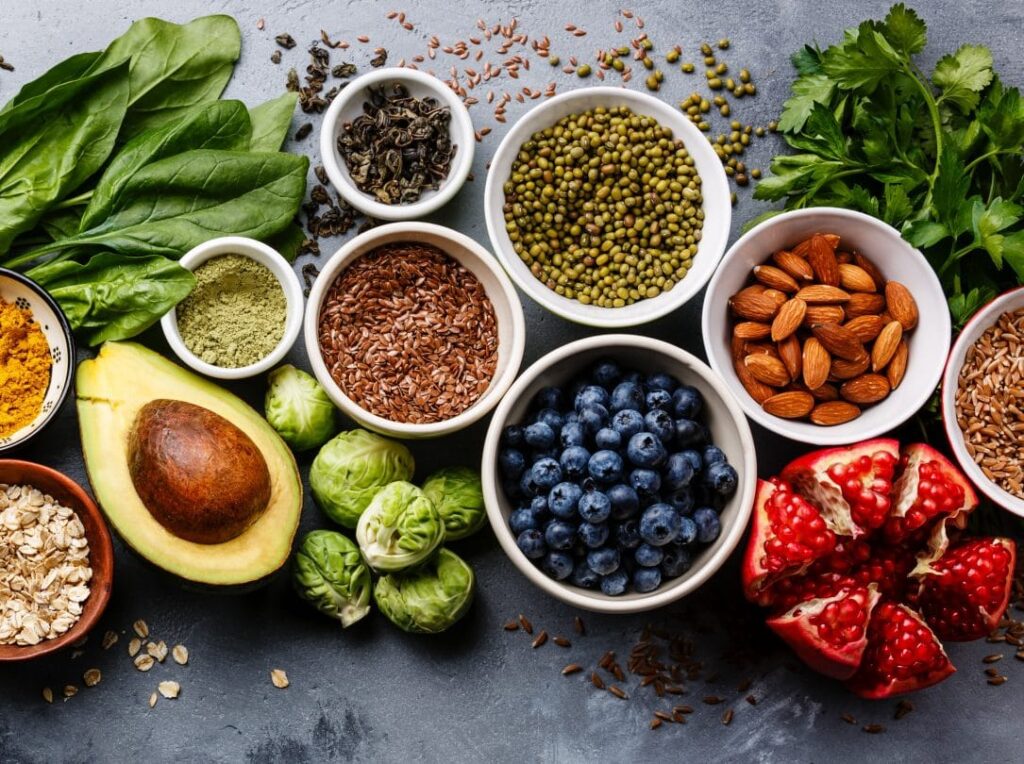
Diabetes Treatment Foods
Conclusion
Incorporating diabetes treatment foods into a balanced diet is essential for managing blood sugar levels, preventing complications, and promoting overall health and well-being. By understanding the principles of glycemic control, carbohydrate counting, and balanced nutrition, individuals with diabetes can make informed food choices to support their health goals.
Remember to consult with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian for personalized dietary recommendations tailored to your individual needs and preferences. Furthermore, with the right approach to diet and lifestyle, individuals with diabetes can take control of their health and enjoy a fulfilling life.
Do you want to get rid of diabetes? Join our online diabetes treatment program and reverse Diabetes naturally through lifestyle changes such as a Personalized Diet plan, Exercise, Yoga, dieticians, and health coaches.


