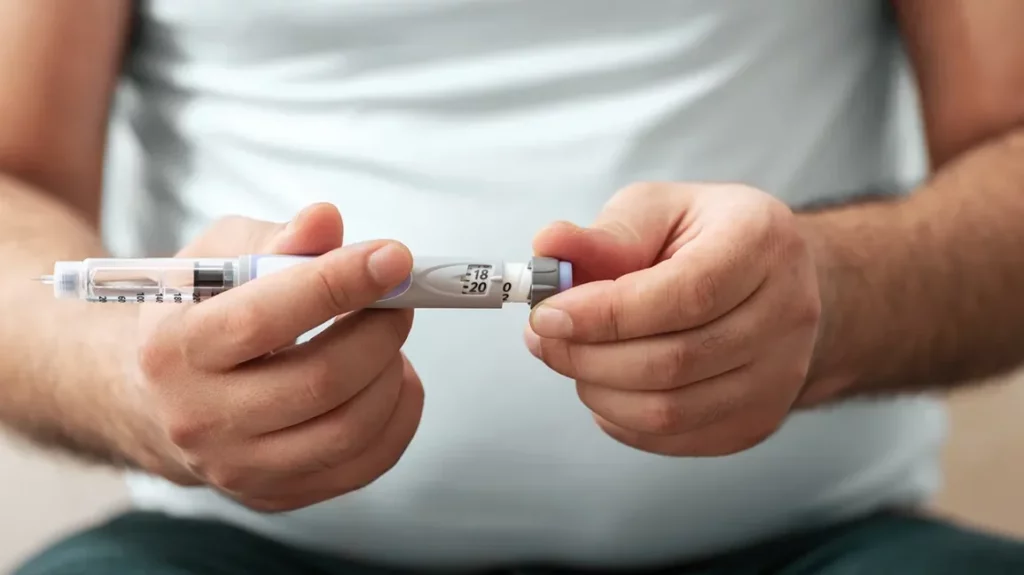
GLP-1 (Glucagon-Like Peptide-1) injections have emerged as a revolutionary tool in the management of certain health conditions, particularly type 2 diabetes and obesity. These injections mimic the natural hormone GLP-1, which plays a crucial role in regulating blood sugar levels and appetite. This guide aims to delve into the science behind GLP-1 injections, their benefits, potential side effects, and how they are transforming the landscape of modern medical treatments.
Contents
What Is A GLP Injection?
 GLP (Glucagon-Like Peptide) injections are a class of medications used primarily in the treatment of type 2 diabetes and, in some cases, for weight management in obese individuals. These injections contain synthetic versions of GLP-1, a naturally occurring hormone in the body.
GLP (Glucagon-Like Peptide) injections are a class of medications used primarily in the treatment of type 2 diabetes and, in some cases, for weight management in obese individuals. These injections contain synthetic versions of GLP-1, a naturally occurring hormone in the body.
It stimulates the pancreas to produce insulin. This helps lower blood sugar and inhibits the release of glucagon. The use of GLP-1 injections has become increasingly popular in the management of type 2 diabetes due to their effectiveness in lowering blood sugar levels and their potential benefits in weight loss.
How To Use GLP Injection?
Using a GLP-1 (Glucagon-Like Peptide-1) injection involves a series of steps to ensure proper administration and effectiveness. Here’s a general guide on how to use a GLP injection:
- Gather Supplies: Before you begin, make sure you have your GLP-1 injection pen, needles (if they are not already attached), alcohol swabs, and a sharps container for needle disposal.
- Wash Your Hands: Always wash your hands thoroughly with soap and water to reduce the risk of infection.
- Prepare the Injection Site: Choose an injection site. Common areas include the abdomen, thigh, or upper arm. Avoid areas with scars, bruises, or swelling. Clean the site with an alcohol swab and let it air dry.
- Assemble the Injection Pen: If your pen requires assembly, attach a new needle to the pen. Remove the needle cap. Depending on the type of pen, you may need to prime it to ensure it’s ready for injection.
- Set the Dose: Follow the specific instructions for your GLP-1 medication to set the correct dose on the injection pen.
- Inject the Medication: Pinch a fold of skin at the cleaned injection site. Insert the needle at a 90-degree angle (or as instructed by your healthcare provider). Press the button or plunger to inject the medication. Hold the needle in place for several seconds to ensure the full dose is delivered.
- Dispose of the Needle Safely: Remove the needle from your skin and replace the needle cap. Dispose of the used needle in a sharps container. Never reuse needles or share your injection pen with others.
- Rotate Injection Sites: To reduce the risk of tissue damage, rotate your injection sites with each dose. Don’t inject into the same spot each time.
- Store the Injection Pen Properly: Follow the storage instructions for your specific GLP-1 medication. Some pens need refrigeration, while others can be kept at room temperature.
Always follow the specific instructions provided with your GLP-1 medication and consult with your healthcare provider for personalized guidance. They can provide detailed instructions on dosage, frequency, and injection techniques tailored to your specific medication and health condition.
What Are The Benefits Of Using GLP Injections?
 GLP injections offer several benefits, particularly for individuals with type 2 diabetes and those struggling with obesity. Here are some of the key advantages:
GLP injections offer several benefits, particularly for individuals with type 2 diabetes and those struggling with obesity. Here are some of the key advantages:
- Improved Blood Sugar Control
GLP-1 injections effectively lower blood glucose levels by enhancing insulin secretion in response to meals and reducing glucagon secretion. This helps in stabilizing blood sugar levels. This is especially beneficial for people with type 2 diabetes.
- Weight Loss
Many users of GLP-1 injections experience significant weight loss. This occurs because GLP-1 reduces appetite and slows gastric emptying. It helps individuals feel fuller for longer, leading to reduced calorie intake.
- Reduced Risk of Hypoglycemia
Compared to other diabetes medications like sulfonylureas or insulin, GLP-1 injections have a lower risk of causing hypoglycemia (low blood sugar), as their insulin-releasing action is glucose-dependent.
- Cardiovascular Benefits
Some GLP-1 agonists have shown cardiovascular benefits, such as reducing the risk of heart attack, stroke, and cardiovascular death in people with type 2 diabetes who have established heart disease or are at high risk for it.
- Convenience of Use
GLP-1 injections are typically administered once daily or once weekly, depending on the specific medication. This can be more convenient than medications requiring multiple daily doses.
- Improved Pancreatic Health
By enhancing the body’s natural insulin production, GLP-1 injections can reduce the workload on the pancreas. And, potentially improving its function over time.
It’s important to note that while GLP-1 injections have these benefits, they may not be suitable for everyone and can have side effects. Consultation with a healthcare provider is essential to determine if GLP-1 therapy is appropriate for an individual’s specific health needs.
What Are The Potential Risks With It?
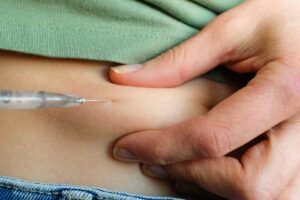 While GLP-1 (Glucagon-Like Peptide-1) injections offer significant benefits, especially for individuals with type 2 diabetes and obesity, they also come with potential risks and side effects. It’s important to be aware of these when considering GLP-1 therapy:
While GLP-1 (Glucagon-Like Peptide-1) injections offer significant benefits, especially for individuals with type 2 diabetes and obesity, they also come with potential risks and side effects. It’s important to be aware of these when considering GLP-1 therapy:
Gastrointestinal Issues
The most common side effects are gastrointestinal in nature, including nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and constipation. These symptoms are usually temporary and tend to diminish over time as the body adjusts to the medication.
Risk of Hypoglycemia
When used in combination with other diabetes medications, especially insulin or sulfonylureas, GLP-1 injections can increase the risk of hypoglycemia (low blood sugar).
Pancreatitis
There is a concern about an increased risk of pancreatitis (inflammation of the pancreas) with GLP-1 therapy, although this is relatively rare. Symptoms include severe abdominal pain that may radiate to the back, nausea, and vomiting.
Allergic Reactions
Some individuals may experience allergic reactions to GLP-1 injections. This can include rash, itching, or, in rare cases, more severe reactions like anaphylaxis.
Thyroid Tumors
In animal studies, some GLP-1 agonists have been linked to a type of thyroid tumor called medullary thyroid carcinoma. While it’s unclear if there is a direct risk to humans, these medications usually carry a warning and are not recommended for individuals with a personal or family history of certain thyroid cancers.
Gallbladder Issues
There have been reports of gallbladder-related problems, such as gallstones, in patients using GLP-1 injections. Potentially due to rapid weight loss or changes in fat metabolism.
Injection Site Reactions
As with any injectable medication, there can be reactions at the injection site, including redness, irritation, and swelling.
Psychological Impact
For some, the routine of regular injections can have a psychological impact. Potentially leading to anxiety or reluctance to continue the treatment.
Risk of Heart Rate Increase
Some patients may experience an increase in heart rate, which should be monitored, especially in those with cardiovascular conditions.
It is crucial for individuals considering GLP-1 therapy to discuss these potential risks and side effects with their healthcare provider. The decision to use GLP-1 injections should be based on a careful consideration of the benefits and risks, tailored to the individual’s health status and medical history. Regular monitoring and follow-up with a healthcare provider are important to ensure the safe and effective use of GLP-1 injections.
Conclusion
In conclusion, GLP injections offer a promising solution for individuals dealing with type 2 diabetes and obesity, providing significant benefits in blood sugar control, weight management, and potentially improving cardiovascular health. Their user-friendly administration and reduced risk of hypoglycemia make them an attractive option for many. However, it’s important to be aware of potential side effects and discuss them with a healthcare provider. They will help to ensure they are the right choice for your individual health needs.
As with any medical treatment, a balanced approach considering both the advantages and potential risks is key to achieving the best health outcomes. Do you want to get rid of diabetes? Join our online diabetes treatment program and reverse Diabetes naturally through lifestyle changes such as a Personalized Diet plan, Exercise, Yoga, dieticians, and health coaches.