Glucose injections play a crucial role in the medical field, serving as a rapid and effective method to raise blood sugar levels in individuals experiencing hypoglycemia or other related conditions. This blog aims to provide a detailed exploration of glucose injections, shedding light on their uses, administration, potential side effects, and the importance of maintaining proper glucose levels in the body.
Contents
What is Glucose?
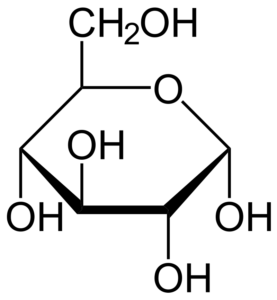
Glucose is a simple sugar, a monosaccharide, and is often referred to as blood sugar. It serves as a primary source of energy for the cells in our body. When we consume carbohydrates through food, the digestive system breaks them down into glucose, which is then absorbed into the bloodstream. This glucose is subsequently transported to cells throughout the body, providing the necessary fuel for various physiological processes.
Sources of Glucose:
- Dietary Sources: Carbohydrates are the main dietary source of glucose. Foods such as grains, fruits, vegetables, and legumes contain carbohydrates in various forms. Digestive enzymes break down these complex carbohydrates into simpler sugars, including glucose, for absorption.
- Glycogen: The body stores excess glucose in the form of glycogen, primarily in the liver and muscles. When blood glucose levels drop, glycogen can be broken down into glucose and released into the bloodstream to maintain energy balance.
Uses of Glucose Injections for Diabetes
Glucose injections are not typically used as a primary treatment for diabetes. Glucose injections can be counterproductive for people with diabetes because they can raise blood sugar levels, exacerbating the condition. However, there are situations where glucose injections may be used in the management of diabetes or related complications:
Hypoglycemia Management
Glucose injections are a crucial intervention for managing hypoglycemia in individuals with diabetes. When blood sugar levels drop too low, causing symptoms such as dizziness, confusion, or loss of consciousness, a glucose injection can rapidly raise blood sugar levels. This emergency treatment helps restore glucose to a safe range, preventing potential complications associated with severe hypoglycemia.
Emergency Situations in Hospital Settings
In hospital settings, healthcare professionals may administer glucose intravenously to individuals with diabetes who are unable to consume food orally. This may occur during critical illness, surgery, or when there is a need for precise control of blood sugar levels. Intravenous glucose ensures a controlled and swift increase in blood glucose, addressing immediate concerns in a clinical environment.
Hyperkalemia Treatment
Individuals with diabetes can occasionally experience complications like hyperkalemia, characterized by elevated potassium levels in the blood. In such cases, glucose, often administered along with insulin, can facilitate the movement of potassium back into cells, helping to lower its concentration in the bloodstream. This dual approach aids in the correction of hyperkalemia and is part of the overall management strategy for this condition.
It’s crucial to emphasize that while glucose injections play a role in specific scenarios, they are not a routine component of diabetes management. The primary focus remains on lifestyle modifications, oral medications, and insulin therapy tailored to the individual’s needs and condition severity. Adherence to the healthcare provider’s guidance ensures effective long-term control of diabetes.
How To Get Glucose Injections for Diabetes?
Glucose injections for diabetes are typically administered in a healthcare setting, and they are not something that individuals would obtain for self-use outside of a medical environment. Here’s how glucose injections are typically obtained and administered:
Emergency Medical Care:
- Glucose injections for the treatment of severe hypoglycemia are usually administered by healthcare professionals in emergency medical settings such as hospitals, clinics, or ambulances.
- If an individual with diabetes experiences a severe drop in blood sugar levels, emergency medical services should be contacted immediately.
Hospital Admission:
- In some cases, individuals with diabetes may require hospitalization for various reasons, such as surgery or critical illness.
- Healthcare providers in a hospital setting may administer glucose intravenously as part of the overall management plan.
Prescription and Supervision:
- Glucose injections are prescription medications, and their use is supervised by healthcare professionals.
- If a person with diabetes requires glucose injections as part of their treatment plan, the healthcare provider will determine the appropriate dosage and administration method based on the individual’s specific needs.
Individuals with diabetes need to work closely with their healthcare team to develop a comprehensive management plan.
Working on Glucose Injections for Diabetes
Glucose injections are not a standard diabetes treatment; rather, they are used in specific situations to address acute complications, particularly severe hypoglycemia. Here’s an overview of how glucose injections work in the context of diabetes management:
Treatment of Severe Hypoglycemia:
- Hypoglycemia occurs when blood sugar levels drop too low, leading to symptoms such as dizziness, confusion, sweating, and, in severe cases, loss of consciousness.
- Glucose injections are used in emergencies to rapidly raise blood sugar levels and counteract the effects of hypoglycemia.
Mechanism of Action:
- Glucose injections deliver a concentrated source of glucose directly into the bloodstream.
- This rapid infusion of glucose provides a quick and effective way to elevate blood sugar levels, addressing the immediate risk associated with low blood sugar.
Emergency Response:
- Glucose injections are often administered by healthcare professionals, emergency medical services, or in a hospital setting.
- The injection is usually given intravenously (IV) to ensure swift absorption and action.
Combined Approaches:
- In some cases, especially in a hospital setting, glucose injections may be combined with other interventions, such as insulin administration, to manage specific complications like hyperkalemia (high potassium levels).
Close Monitoring:
- Following the administration of glucose injections, individuals are closely monitored to ensure that blood sugar levels return to a safe range and that there are no adverse reactions.
It’s crucial to note that glucose injections are not a routine part of diabetes management.
Side Effects of Glucose Injections for Diabetes
Glucose injections are generally considered safe when administered appropriately in emergencies, particularly for the treatment of severe hypoglycemia. However, like any medical intervention, there can be potential side effects. Here are some considerations:
- Local Irritation: Injection site reactions, such as redness, swelling, or pain at the site where the injection is given, may occur. This is a common side effect of any injection and is usually mild and temporary.
- Allergic Reactions: While rare, some individuals may be allergic to components of the glucose injection. Allergic reactions can range from mild skin reactions to severe anaphylaxis, a life-threatening reaction. However, severe allergic reactions to glucose injections are uncommon.
- Fluid Overload: In cases where large amounts of glucose are administered intravenously, there is a risk of fluid overload. This can lead to swelling, shortness of breath, and other symptoms. Healthcare providers carefully monitor fluid balance during such interventions to minimize this risk.
- Electrolyte Imbalance: Glucose injections, especially when combined with insulin, can influence electrolyte levels in the body. This is usually a concern in a hospital setting where glucose and insulin may be used to address specific complications like hyperkalemia.
- Hyperglycemia Rebound: In some cases, the rapid administration of glucose may lead to a temporary rebound increase in blood sugar levels. This is generally a consideration when determining the appropriate dosage and monitoring after the injection.
It’s important to note that the decision to use glucose injections is based on a careful assessment of the individual’s condition and is typically reserved for emergencies.
Conclusion
Glucose injections play a critical role in managing hypoglycemia and ensuring optimal blood sugar levels in various medical scenarios. Understanding their uses, proper administration methods and potential side effects is crucial for healthcare professionals and individuals who may require such interventions. As with any medical treatment, it is essential to consult with healthcare providers to determine the most suitable approach for individual needs.
Do you want to get rid of diabetes? Join our online diabetes treatment program and reverse Diabetes naturally through lifestyle changes such as a Personalized Diet plan, Exercise, Yoga, dieticians, and health coaches.