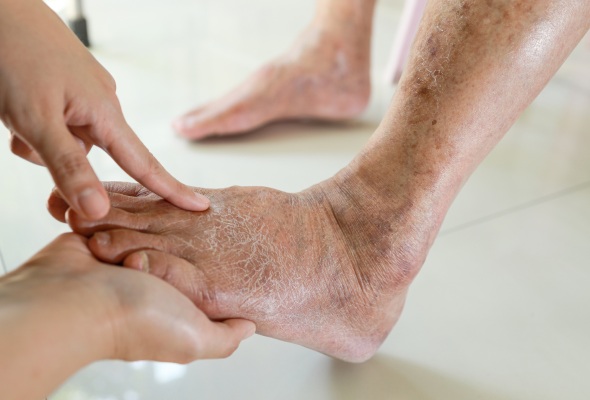
Diabetes, a chronic condition affecting millions worldwide, brings with it a range of complications, one of which is the diabetic foot. This condition, resulting from a combination of neuropathy (nerve damage) and poor circulation, can lead to severe consequences if not managed properly. Therefore, understanding and managing diabetic feet is crucial for those with diabetes. This guide aims to provide valuable insights into recognizing early symptoms and exploring the management of diabetic foot, all tailored to help you maintain healthy feet as a diabetic.
Contents
When To Consider Management Of Diabetic Foot?
 Management of diabetic foot should be considered an integral part of diabetes care from the onset of the diagnosis. However, there are specific times and scenarios when it becomes particularly critical to focus on diabetic foot management:
Management of diabetic foot should be considered an integral part of diabetes care from the onset of the diagnosis. However, there are specific times and scenarios when it becomes particularly critical to focus on diabetic foot management:
- At the Time of Diabetes Diagnosis: As soon as an individual is diagnosed with diabetes, it’s essential to start considering foot care. Early education about the risks of diabetic foot complications can lead to better preventative measures.
- Presence of Peripheral Neuropathy: If symptoms of neuropathy such as numbness, tingling, or pain in the feet are noticed, it’s crucial to begin focused foot care management. Neuropathy increases the risk of foot ulcers and infections due to decreased sensation.
- Changes in Foot Structure: Any changes in the shape of the feet, such as the development of bunions, hammertoes, or other deformities, require attention, as these can lead to uneven pressure distribution and ulcers.
- Development of Calluses or Corns: These can indicate areas of high pressure on the feet. This, in diabetics, can lead to skin breakdown and ulcers if not managed properly.
- History of Foot Ulcers or Previous Amputations: If there’s a history of foot ulcers or amputations, ongoing management and surveillance are essential to prevent recurrence.
- Occurrence of Cuts, Sores, or Blisters: Any minor injuries to the feet should be taken seriously, as they can lead to ulcers or infections due to the slowed healing process in diabetics.
It’s important for individuals with diabetes to maintain regular communication with their healthcare providers about foot care and to promptly address any concerns or changes they notice in their feet. Early intervention and proper management are key to preventing serious complications related to diabetic foot.
What Is The Management Of Diabetic Foot?
Management of diabetic foot involves a comprehensive approach that aims to prevent foot complications, such as ulcers and infections, and to treat these conditions if they occur. This management is crucial for individuals with diabetes due to their increased risk of foot problems. Here are the key components of diabetic foot management:
Regular Foot Examinations
For individuals with diabetes, regular foot examinations are crucial. These examinations should be both self-conducted and performed by healthcare professionals. Self-examination involves a daily check of the feet for any cuts, blisters, red spots, swelling, or nail problems. Using a mirror can help in checking the soles of the feet. Professional examinations, which should occur at least annually or more frequently if recommended, include a thorough check for neuropathy, changes in foot shape, dry or cracked skin, and signs of infection.
Good Foot Hygiene
This involves washing the feet daily in lukewarm water using a mild soap, which helps in preventing infections. It’s important to dry the feet gently and thoroughly, especially between the toes, to avoid moisture accumulation, which can lead to fungal infections. After washing and drying, applying a moisturizer can prevent dry skin but should be avoided between the toes to prevent excess moisture. Keeping the nails trimmed straight across and filing any sharp edges also forms part of good foot hygiene.
Proper Footwear
Proper footwear is essential in preventing diabetic foot complications. Shoes should fit well, offer good support, and protect the feet. Ill-fitting shoes can cause blisters, sores, and ulcers, especially in a diabetic foot that may not feel pain normally. Diabetic individuals should avoid walking barefoot, even indoors, to prevent injury. In some cases, special diabetic shoes or orthotics might be prescribed. These are designed to reduce pressure on the foot, provide additional support, and accommodate any specific foot deformities or needs.
Control of Blood Glucose Levels
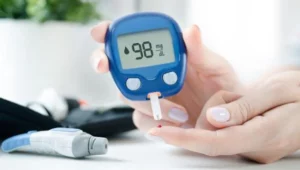 Effective management of blood glucose levels is a cornerstone of preventing and managing diabetic foot. High blood sugar levels can lead to nerve damage and poor circulation, increasing the risk of foot problems. Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels, following a diabetes-friendly diet, regular physical activity, and adhering to prescribed medications are essential strategies to maintain blood glucose within the target range. Good blood sugar control helps slow the progression of neuropathy and improves blood circulation, reducing the risk of foot ulcers and infections.
Effective management of blood glucose levels is a cornerstone of preventing and managing diabetic foot. High blood sugar levels can lead to nerve damage and poor circulation, increasing the risk of foot problems. Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels, following a diabetes-friendly diet, regular physical activity, and adhering to prescribed medications are essential strategies to maintain blood glucose within the target range. Good blood sugar control helps slow the progression of neuropathy and improves blood circulation, reducing the risk of foot ulcers and infections.
Treatment of Foot Problems
Prompt and appropriate treatment of foot problems is critical in diabetic foot care. Minor cuts, blisters, corns, or calluses can develop into serious infections if neglected. Individuals with diabetes need to treat even minor foot injuries with care. This includes cleaning the wound, applying antibiotic ointment, and covering it with a bandage. Regularly changing the bandage and monitoring the wound for signs of infection is essential. For more serious issues or if a wound does not heal, it’s important to seek medical advice promptly.
Management of Peripheral Neuropathy
Peripheral neuropathy involves damage to the nerves in the feet and legs, leading to numbness, pain, and a loss of feeling. Effective management includes maintaining optimal blood glucose levels to slow the progression of neuropathy. Pain caused by neuropathy can be managed with specific medications prescribed by healthcare providers, such as anticonvulsants and antidepressants that are effective for nerve pain. Physical therapy may also be beneficial in managing symptoms and improving function.
Improving Circulation
Good blood flow to the feet is vital for healing and preventing complications. Exercise is a key component in improving circulation. Activities like walking, swimming, or cycling can enhance blood flow, but it’s important to choose activities that do not put excessive stress on the feet. Smoking cessation is also critical as smoking impairs circulation. Patients are advised to avoid sitting with crossed legs for extended periods and to elevate their feet when sitting to promote blood flow. In some cases, doctors may prescribe medications to improve circulation.
Education and Awareness
Education plays a pivotal role in the management of diabetic foot. Understanding the risks and knowing how to care for one’s feet can significantly reduce the likelihood of serious complications. This education includes recognizing early signs of foot problems, knowing how to conduct a proper foot examination, and understanding the importance of blood glucose control in foot health. Healthcare providers often provide educational resources and may recommend attending diabetes education programs for comprehensive learning.
Surgical Interventions
In severe cases of diabetic foot, such as advanced ulcers, significant infections, or critical limb ischemia, surgical interventions may become necessary. These can range from minor procedures to remove dead tissue or ingrown toenails to more extensive surgeries to correct deformities or to amputate severely damaged tissue. Surgical interventions aim to reduce the risk of further complications, alleviate pain, and improve the overall function of the foot.
The goal of diabetic foot management is to treat existing foot problems. And also to prevent new issues from arising. It requires a proactive approach and close coordination between the individual, and healthcare providers.
How To Prevent Diabetic Foot?
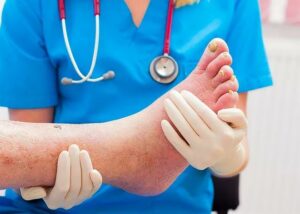 Preventing diabetic foot, a critical concern for those with diabetes involves several strategies beyond the basic foot care and medical management already discussed. Here are additional preventive measures:
Preventing diabetic foot, a critical concern for those with diabetes involves several strategies beyond the basic foot care and medical management already discussed. Here are additional preventive measures:
- Avoiding Foot Trauma: It’s important to protect the feet from injuries, especially in activities that may pose risks. This includes being cautious about walking barefoot and being mindful of potential hazards, like sharp objects or hot surfaces.
- Skin Care: Beyond just moisturizing, paying attention to the skin on the feet can prevent problems. This includes avoiding exposure to extreme temperatures that can cause burns or frostbite, especially since neuropathy can diminish the sensation of temperature.
- Manage Other Health Conditions: Controlling other health conditions that can exacerbate foot problems is vital. This includes managing blood pressure and cholesterol levels, as these can impact circulation. Regularly monitoring and managing these conditions can contribute significantly to diabetic foot prevention.
- Hydration: Staying well-hydrated is important for overall health and can also help in keeping the skin on the feet supple and less prone to cracking.
- Regular Podiatrist Visits: Regular visits to a podiatrist for professional foot care can help in the early detection and management of potential foot problems. A podiatrist can also provide specialized care and advice tailored to individual needs.
By integrating these preventive strategies into daily routines, individuals with diabetes can significantly reduce their risk of developing diabetic foot complications. Thereby maintaining better overall health and quality of life.
Conclusion
In conclusion, management of diabetic foot and prevention is an essential aspect of living well with diabetes. It involves a combination of regular foot care, such as daily inspections and maintaining good hygiene, wearing appropriate footwear, and controlling blood glucose levels. Additionally, incorporating a healthy lifestyle, protecting the feet from injuries, managing other health conditions, and staying hydrated is crucial.
By taking these steps, individuals with diabetes can greatly reduce their risk of foot complications. Ultimately, ensuring a healthier and more comfortable life. Do you want to get rid of diabetes? Join our online diabetes treatment program and reverse Diabetes naturally through lifestyle changes such as a Personalized Diet plan, Exercise, Yoga, dieticians, and health coaches.