The presence of sugar in urine, also known as glucosuria or glycosuria, can be indicative of various underlying health conditions, most notably diabetes mellitus. Monitoring and managing sugar levels in urine is crucial for maintaining overall health and preventing complications associated with conditions such as diabetes. In this blog, we’ll explore the treatment options and lifestyle strategies for managing sugar in urine effectively.
Contents
What Does “Sugar in Urine” Mean?

“Sugar in urine,” also known as glucosuria or glycosuria, refers to the presence of glucose (sugar) in the urine. Under normal circumstances, the kidneys filter the blood to remove waste products while reabsorbing essential substances, including glucose, back into the bloodstream. However, when blood glucose levels are elevated, such as in diabetes mellitus or other medical conditions, the kidneys may not be able to reabsorb all the glucose, leading to its presence in the urine.
When blood sugar levels are consistently high, excess glucose spills over into the urine, causing glucosuria. Other conditions that can cause sugar in urine include certain kidney disorders, hormonal imbalances (such as Cushing’s syndrome), and rare genetic disorders affecting glucose metabolism.
Is it Easy to Treat Sugar in Urine (Glucosuria)?
The ease of treating sugar in urine, also known as glucosuria or glycosuria, depends on the underlying cause of the condition. Here’s a breakdown of the factors that influence the ease of treating sugar in urine:
- Underlying Cause: The ease of treatment often depends on identifying and addressing the underlying cause of glucosuria. The most common cause is diabetes mellitus, which requires ongoing management to control blood sugar levels through lifestyle changes, medication, and/or insulin therapy. If glucosuria is caused by a reversible condition, such as certain medications or temporary stressors, discontinuing the medication or addressing the underlying issue may resolve the problem relatively easily.
- Type of Diabetes: The type of diabetes affecting an individual can impact the ease of treatment. Type 1 diabetes, which results from the immune system attacking insulin-producing cells in the pancreas, requires lifelong insulin therapy. Managing sugar in urine in Type 1 diabetes involves regular insulin injections, blood sugar monitoring, and adherence to a healthy lifestyle. Type 2 diabetes, characterized by insulin resistance or inadequate insulin production, may initially be managed with lifestyle modifications, oral medications, or insulin therapy, depending on disease progression and individual factors.
- Lifestyle Factors: Adopting healthy lifestyle habits, such as following a balanced diet, engaging in regular physical activity, maintaining a healthy weight, and managing stress, plays a crucial role in managing sugar in urine, especially for individuals with diabetes. Making sustainable lifestyle changes can sometimes be challenging but is essential for long-term management and prevention of complications.
- Medication Adherence: Compliance with prescribed medications, including oral hypoglycemic agents or insulin therapy, is essential for controlling blood sugar levels and reducing glucosuria. Missing doses or inconsistent medication adherence can make treatment less effective and may lead to persistent sugar in the urine.
List of Treatment Methods for Sugar in Urine (Glucosuria)
Treatment methods for sugar in urine (glucosuria) primarily focus on managing the underlying condition causing elevated blood sugar levels. Here is a comprehensive list of treatment methods for glucosuria:
Dietary Changes

Dietary changes are a cornerstone of managing sugar in urine (glucosuria) effectively.
- A balanced diet rich in whole grains, fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats can help regulate blood sugar levels and minimize the amount of sugar excreted in urine.
- Monitoring carbohydrate intake is crucial, as carbohydrates have the most significant impact on blood glucose levels.
- Spacing meals evenly throughout the day and practicing portion control can prevent spikes in blood sugar levels.
- Additionally, being mindful of the glycemic index of foods can guide food choices, favoring those that have a lower glycemic index to prevent rapid fluctuations in blood sugar.
- Limiting the consumption of sugary snacks, desserts, and beverages is essential to avoid excessive intake of refined sugars.
Overall, adopting a balanced and nutrient-rich diet can contribute to better blood sugar control, promote overall health, and reduce the risk of complications associated with elevated blood glucose levels.
Regular Physical Activity
Regular physical activity plays a vital role in managing sugar in urine (glucosuria) by improving insulin sensitivity, promoting glucose uptake by muscles, and aiding in weight management.
- Engaging in consistent exercise, such as brisk walking, jogging, cycling, swimming, or strength training, helps lower blood sugar levels and reduce the risk of glucosuria-related complications.
- Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity per week, as recommended by health guidelines, supplemented with flexibility and balance exercises.
- Exercise not only helps regulate blood glucose levels but also enhances cardiovascular health, lowers blood pressure, and improves overall well-being.
- Moreover, physical activity contributes to weight loss or maintenance, which is crucial for managing diabetes and preventing insulin resistance.
- Regular exercise can also reduce stress levels, which can indirectly impact blood sugar control. Incorporating physical activity into daily routines promotes long-term adherence and fosters a healthier lifestyle.
It’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional before starting an exercise regimen, especially for individuals with existing health conditions or those who have been inactive.
Medications
Medications play a significant role in managing sugar in urine (glucosuria), particularly in cases where lifestyle modifications alone are insufficient to control blood sugar levels. Here are some common medications used in the treatment of glucosuria:
Oral Hypoglycemic Agents: These medications are taken by mouth and work to lower blood sugar levels by various mechanisms. They include:
- Metformin: Improves insulin sensitivity, decreases glucose production in the liver, and enhances glucose uptake by muscles.
- Sulfonylureas (e.g., glipizide, glyburide): Stimulate insulin secretion from the pancreas, increasing insulin levels to lower blood sugar.
- DPP-4 inhibitors (e.g., sitagliptin, saxagliptin): Inhibit the enzyme dipeptidyl peptidase-4, which increases insulin secretion and decreases glucagon release.
- SGLT2 inhibitors (e.g., dapagliflozin, empagliflozin): Block glucose reabsorption in the kidneys, leading to increased glucose excretion in urine.
Insulin Therapy: Individuals with Type 1 diabetes or advanced Type 2 diabetes may require insulin therapy to manage blood sugar levels effectively. Insulin is typically administered via injections or insulin pumps and replaces the insulin that the body is unable to produce or utilize efficiently.
Other Medications: Depending on the individual’s specific health needs and underlying conditions, other medications help to manage glucosuria or its complications. These may include:
- Blood pressure medications: If hypertension or kidney disease is present, medications such as ACE inhibitors or angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARBs) may be prescribed to protect kidney function.
- Cholesterol-lowering medications: Statins or other lipid-lowering medications may be recommended to reduce the risk of cardiovascular complications associated with diabetes.
- Medications for diabetic neuropathy or other diabetes-related complications: Depending on the presence of neuropathy, pain medications or medications to improve nerve function may be prescribed.
Blood Sugar Monitoring
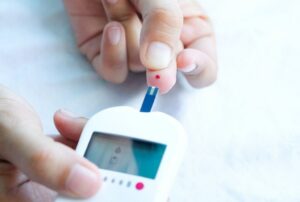
Blood sugar monitoring is a crucial aspect of managing sugar in urine (glucosuria) and overall diabetes control. Regular monitoring allows individuals to track their blood glucose levels, assess the effectiveness of treatment strategies, and make informed decisions about lifestyle adjustments and medication management.
- Using a glucometer or continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) system, individuals can measure their blood sugar levels multiple times throughout the day.
- This helps identify patterns and trends in blood glucose fluctuations, such as post-meal spikes or overnight lows, enabling proactive adjustments to diet, exercise, and medication regimens.
- Consistent monitoring is especially important for individuals with diabetes to prevent hyperglycemia (high blood sugar) or hypoglycemia (low blood sugar), both of which can have serious health consequences if left unmanaged.
- By maintaining blood sugar levels within target ranges, individuals can reduce the risk of complications associated with diabetes, such as cardiovascular disease, nerve damage, kidney problems, and vision impairment.
Hydration
Hydration plays a crucial role in managing sugar in urine (glucosuria) and supporting overall health, particularly for individuals with diabetes. Adequate hydration helps maintain kidney function, promotes the excretion of excess sugar through urine, and prevents dehydration-related complications.
Drinking plenty of water throughout the day helps dilute urine, reducing the concentration of sugar excreted and minimizing the risk of glucosuria. Additionally, proper hydration supports optimal kidney function by ensuring adequate blood flow to the kidneys and facilitating the filtration and removal of waste products from the body.
For individuals with diabetes, staying hydrated is especially important due to the increased risk of dehydration caused by high blood sugar levels and frequent urination. Dehydration can exacerbate hyperglycemia, leading to further complications such as electrolyte imbalances, urinary tract infections, and impaired kidney function.
Monitoring urine output and maintaining pale yellow urine color can serve as indicators of adequate hydration. You should drink water regularly throughout the day, aiming for at least eight 8-ounce glasses per day, or more if sweating excessively or in hot weather.
Stress Management

Stress management is integral to effectively managing sugar in the urine (glucosuria) and promoting overall well-being, especially for individuals with diabetes. Chronic stress can elevate blood sugar levels through the release of stress hormones like cortisol and adrenaline, which can exacerbate glucosuria and contribute to long-term health complications.
Implementing stress-reducing techniques can help mitigate the impact of stress on blood sugar levels and improve overall health outcomes. Here are some effective stress management strategies:
- Mindfulness Meditation: Practicing mindfulness meditation involves focusing attention on the present moment, and cultivating awareness of thoughts and emotions without judgment. Regular practice can reduce stress levels, promote relaxation, and improve emotional resilience.
- Deep Breathing Exercises: Deep breathing exercises, such as diaphragmatic breathing or progressive muscle relaxation, can activate the body’s relaxation response, counteracting the effects of stress hormones and lowering blood pressure.
- Yoga: Yoga combines physical postures, breathing techniques, and meditation to promote relaxation, flexibility, and stress relief. It can help reduce cortisol levels, improve insulin sensitivity, and enhance overall well-being.
Conclusion
In conclusion, effectively managing sugar in urine (glucosuria) requires a multifaceted approach that addresses underlying health conditions, promotes healthy lifestyle habits, and incorporates proactive strategies for stress management.
With dedication, perseverance, and a comprehensive management plan, it is possible to effectively manage glucosuria and achieve better overall health outcomes.
Do you want to get rid of diabetes? Join our online diabetes treatment program and reverse Diabetes naturally through lifestyle changes such as a Personalized Diet plan, Exercise, Yoga, dieticians, and health coaches.

