Type 2 Diabetes is a condition that affects millions worldwide. Living with diabetes can be challenging, but with the right knowledge and tools, it’s possible to lead a healthy and fulfilling life. This blog is designed to provide you with valuable insights into the latest type 2 diabetes treatment options, lifestyle changes, and supportive measures that can help you effectively manage your diabetes.
Contents
Can I Live a Normal Life With Type 2 Diabetes?
 Absolutely, you can live a normal and active life with Type 2 diabetes. The key to managing this condition effectively lies in maintaining a balance between medical management, lifestyle changes, and regular monitoring of your health. Proper management and staying in close communication with your healthcare provider. Moreover, living with Type 2 diabetes also involves adapting to certain lifestyle modifications, but these changes can positively impact overall health and well-being.
Absolutely, you can live a normal and active life with Type 2 diabetes. The key to managing this condition effectively lies in maintaining a balance between medical management, lifestyle changes, and regular monitoring of your health. Proper management and staying in close communication with your healthcare provider. Moreover, living with Type 2 diabetes also involves adapting to certain lifestyle modifications, but these changes can positively impact overall health and well-being.
Embracing a diet rich in whole foods and maintaining a healthy weight is not only beneficial for diabetes management but also for general health. Additionally, many people find that their diagnosis is a motivating factor to make healthier choices and develop stronger coping strategies. With the right support, education, and care, individuals with Type 2 diabetes can lead fulfilling, active lives, successfully managing their condition while enjoying a wide range of activities and pursuits.
What Are The Effective Type 2 Diabetes Treatment?
Effective Type 2 diabetes treatment primarily involves a combination of lifestyle changes and medical interventions. The medical treatment options for Type 2 diabetes are diverse and are often tailored to individual needs based on various factors like the severity of the disease, the patient’s overall health, and response to treatments. Here’s an overview:
Oral Medications
- Metformin is often the first medication prescribed for Type 2 diabetes. It works by decreasing the amount of sugar produced by the liver and improving the body’s sensitivity to insulin. This drug has the added benefit of potentially aiding in weight loss and has a low risk of causing hypoglycemia.
- Sulfonylureas, such as glipizide, glyburide, and glimepiride, stimulate the pancreas to produce more insulin. These are some of the oldest diabetes drugs still in use and can be quite effective, though they may increase the risk of weight gain and hypoglycemia.
- DPP-4 Inhibitors (such as sitagliptin, linagliptin, and alogliptin) work by blocking the action of DPP-4, an enzyme that destroys the hormone incretin. Incretins help the body produce more insulin only when needed and reduce the amount of glucose being produced by the liver when it’s not needed.
- Thiazolidinediones, like pioglitazone and rosiglitazone, make the body’s tissues more sensitive to insulin. These medications can be very effective but may carry risks, such as increased risk of heart failure and fractures.
- SGLT2 Inhibitors, such as canagliflozin and empagliflozin, work by preventing the kidneys from reabsorbing glucose back into the blood. This results in more glucose being excreted in the urine, lowering blood glucose levels.
Insulin Therapy
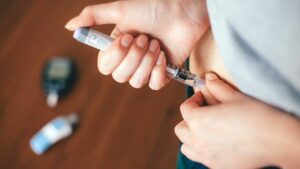
- Basal Insulin: This type of insulin is administered once or twice daily to provide a steady baseline level of insulin. It helps control blood glucose levels overnight and between meals. Long-acting insulin analogs like glargine and detemir are commonly used.
- Bolus Insulin: This includes rapid-acting insulin like lispro, aspart, and glulisine, or short-acting insulins like regular human insulin. They are taken before meals to manage the spike in blood sugar that occurs after eating.
Combination Therapy
- In many cases, a single medication may not be sufficient to control blood glucose levels, necessitating a combination of drugs. For instance, a doctor may prescribe a mix of metformin and a DPP-4 inhibitor. Combination therapies can target different aspects of diabetes management, such as insulin resistance, insulin production, and glucose excretion.
Bariatric Surgery
- For individuals with severe obesity and Type 2 diabetes, bariatric surgery can be a viable option. Procedures like gastric bypass or sleeve gastrectomy have been shown to significantly improve blood sugar levels in severely obese patients, often leading to remission of diabetes. This effect is partly due to weight loss. But these surgeries also impact gut hormones that influence blood sugar levels.
Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM)
- CGM systems provide real-time data on blood glucose levels. And, helping patients make more informed decisions about their diet, activity, and medications. Insulin pumps, often used in conjunction with CGM systems, deliver insulin continuously through a small catheter placed under the skin, simplifying insulin management and potentially improving blood sugar control.
Each of these treatment options plays a critical role in the overall management of Type 2 diabetes. Patients need to work closely with their healthcare team to determine the best treatment plan for their individual needs and to adjust this plan as needed over time.
What Are Some Lifestyle Changes For Type 2 Diabetes?
 Lifestyle changes play a crucial role in managing Type 2 diabetes effectively. These changes not only help in controlling blood sugar levels but also contribute to overall health improvement. Here are some key lifestyle modifications:
Lifestyle changes play a crucial role in managing Type 2 diabetes effectively. These changes not only help in controlling blood sugar levels but also contribute to overall health improvement. Here are some key lifestyle modifications:
Healthy Eating
Adopting a balanced diet is vital. Focus on foods low in sugar and fat but high in fiber, such as fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. Portion control is also important to manage weight and blood sugar levels. Understanding carbohydrate counting and the glycemic index of foods can further refine dietary choices to maintain stable blood glucose levels.
Regular Physical Activity
Exercise is a powerful tool for managing diabetes. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity per week, such as walking, swimming, or cycling, along with muscle-strengthening activities on two or more days a week. Exercise helps increase insulin sensitivity and can lead to better blood sugar control.
Weight Management
If you’re overweight, losing even a small amount of weight can significantly impact your diabetes management. Weight loss can improve blood sugar levels, reduce the need for medication, and lower the risk of complications.
Stress Management
Stress can affect blood sugar levels. So, it’s important to find ways to relieve stress. Techniques such as deep breathing, meditation, yoga, or engaging in hobbies can be effective.
Quit Smoking and Limit Alcohol
Smoking can increase the risk of diabetes complications, including heart disease, stroke, and nerve damage. Limiting alcohol intake is also important as alcohol can affect blood sugar levels.
Regular Health Check-ups
Regular visits to your healthcare provider are essential to monitor your diabetes and check for complications. These check-ups often include blood pressure monitoring, cholesterol checks, eye exams, and foot inspections.
Good Sleep Hygiene
Poor sleep can affect blood sugar levels and insulin sensitivity. Aim for 7-8 hours of quality sleep per night and maintain a regular sleep schedule.
Stay Educated
Keeping informed about diabetes and its management can empower you to make better health decisions. Diabetes education programs and support groups can be valuable resources.
Implementing these lifestyle changes can be challenging, but they’re crucial for managing Type 2 diabetes effectively. It’s often helpful to start with small, achievable goals and gradually incorporate more changes. Remember, every positive lifestyle change, no matter how small, can make a significant difference in managing diabetes and improving overall health.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Type 2 Diabetes treatment involves a blend of informed medical treatments and lifestyle modifications. By understanding and utilizing the various medications available, including oral drugs, insulin therapy, and emerging technologies like CGM systems, individuals can effectively manage their blood sugar levels. Alongside medical interventions, incorporating healthy lifestyle choices plays a pivotal role in controlling diabetes.
It’s important to remember that with the right approach, dedication, and support, living a fulfilling life with Type 2 Diabetes is not just possible, but highly achievable. Do you want to get rid of diabetes? Join our online diabetes treatment program and reverse Diabetes naturally through lifestyle changes such as a Personalized Diet plan, Exercise, Yoga, dieticians, and health coaches.

