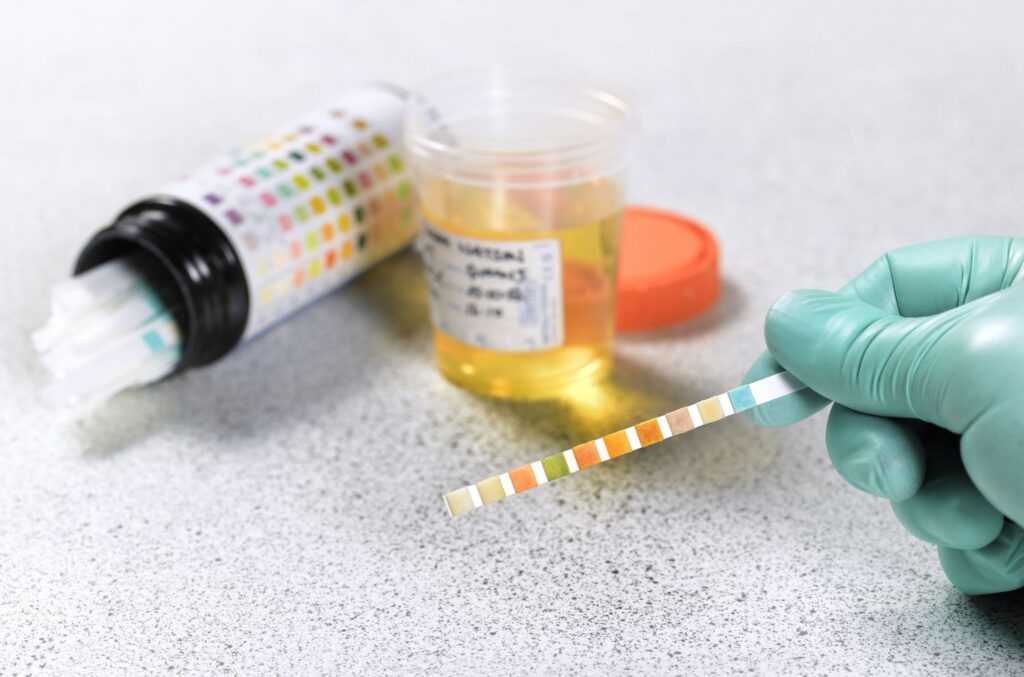
Glycosuria, also known as glucosuria, is a condition characterized by glucose in the urine. This occurrence indicates that the kidneys are excreting glucose into the urine rather than reabsorbing it as they normally would. While mild glycosuria may not always be a cause for concern, persistent or severe cases can indicate underlying health issues that require attention. In this blog post, we’ll delve into the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for glycosuria to help you better understand and manage this condition.
Contents
What is Glycosuria?

Glycosuria can occur due to various reasons, but it primarily stems from abnormalities in glucose metabolism or kidney function. Normally, the kidneys filter waste products from the blood, including glucose. However, they typically reabsorb almost all of the filtered glucose back into the bloodstream. When this reabsorption mechanism fails, glucose spills into the urine, resulting in glycosuria.
Causes of Glycosuria:
- Diabetes Mellitus: One of the most common causes of glycosuria is diabetes mellitus. In individuals with diabetes, either the body does not produce enough insulin (Type 1 diabetes) or it cannot effectively use the insulin it produces (Type 2 diabetes). As a result, glucose levels in the bloodstream remain elevated, leading to spillage of glucose into the urine.
- Renal Glycosuria: In some cases, glycosuria can occur due to a condition known as renal glycosuria, where the kidneys are unable to reabsorb glucose efficiently despite normal blood sugar levels. This condition is usually benign and may not require treatment unless accompanied by other symptoms or complications.
- Medications: Certain medications, such as some diuretics and antiretroviral drugs, can interfere with glucose reabsorption in the kidneys, leading to glycosuria as a side effect.
Symptoms of Glycosuria
Glycosuria itself may not cause noticeable symptoms in mild cases. However, when associated with underlying conditions like diabetes, symptoms may include:
- Increased thirst (polydipsia)
- Frequent urination (polyuria)
- Fatigue
- Weight loss
- Blurred vision
- Recurrent infections, especially urinary tract infections (UTIs)
List of Different Glycosuria Treatment Options Available
Treatment options for glycosuria vary depending on its underlying cause and severity, aiming primarily to regulate blood glucose levels and minimize urinary glucose excretion.
The treatment of glycosuria depends on its underlying cause and severity. Here are some common approaches:
Lifestyle Modifications

Lifestyle modifications serve as crucial treatment options for glycosuria, aiming to regulate blood glucose levels and minimize urinary glucose excretion.
Dietary changes are fundamental, emphasizing a balanced diet low in refined sugars and carbohydrates while prioritizing whole foods rich in fiber to promote gradual glucose absorption and enhance insulin sensitivity. Portion control and meal timing are essential strategies to prevent spikes in blood sugar levels.
Regular exercise plays a pivotal role in glycosuria management by improving glucose metabolism and insulin sensitivity. Aerobic exercises like walking, jogging, and cycling, along with strength training, help lower blood glucose levels and reduce the need for urinary glucose excretion. Healthcare providers recommend at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity per week, supplemented with muscle-strengthening exercises.
Weight management is crucial, particularly for individuals with obesity or overweight, as excess body fat contributes to insulin resistance and dysregulated glucose metabolism. Caloric restriction, combined with regular exercise, is key to achieving and maintaining a healthy weight. Behavioral interventions, such as setting realistic weight loss goals and monitoring food intake, support successful weight management.
Stress management techniques, including mindfulness meditation and deep breathing exercises, help mitigate the impact of chronic stress on glycemic control. By reducing cortisol levels and improving insulin sensitivity, stress management contributes to better glucose regulation and minimizes glycosuria episodes.
Additionally, smoking cessation and limiting alcohol intake are important lifestyle modifications. Smoking and excessive alcohol consumption adversely affect glucose metabolism and increase the risk of complications in individuals with glycosuria.
Symptomatic Treatment
Symptomatic treatment options for glycosuria aim to address specific symptoms or complications associated with the condition. While addressing the underlying cause of glycosuria is essential, symptomatic treatment plays a crucial role in alleviating discomfort and preventing complications. Here are some symptomatic treatment options available for glycosuria:
- Treatment of Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs): Glycosuria increases the risk of urinary tract infections due to the presence of excess glucose in the urine, creating a favorable environment for bacterial growth. Symptomatic treatment for UTIs typically involves antibiotic therapy to eliminate the infection and alleviate symptoms such as urinary frequency, urgency, and discomfort. Healthcare providers may prescribe antibiotics based on the type of bacteria causing the infection and the patient’s medical history.
- Management of Polyuria and Polydipsia: Polyuria (excessive urination) and polydipsia (excessive thirst) are common symptoms of glycosuria, especially in individuals with uncontrolled diabetes. Symptomatic treatment focuses on managing these symptoms to improve quality of life and prevent dehydration. Patients are advised to maintain adequate fluid intake to prevent dehydration while monitoring their urine output and adjusting fluid intake accordingly. Additionally, addressing the underlying cause of glycosuria, such as optimizing blood sugar control in diabetes, can help reduce polyuria and polydipsia over time.
- Monitoring for Complications: Glycosuria can lead to complications such as electrolyte imbalances, dehydration, and kidney damage if left untreated. Symptomatic treatment involves regular monitoring of electrolyte levels, kidney function, and hydration status to detect and address any complications promptly. Healthcare providers may recommend laboratory tests, such as blood tests and urinalysis, to assess kidney function and electrolyte levels and guide appropriate management.
Medications

Medications play a crucial role in the treatment of glycosuria, particularly when addressing underlying conditions such as diabetes mellitus or renal glycosuria. These medications aim to regulate blood glucose levels, improve insulin sensitivity, and reduce urinary glucose excretion. Here are some medication options commonly used in the management of glycosuria:
Insulin Therapy: Insulin therapy is a cornerstone treatment for individuals with diabetes mellitus, especially those with Type 1 diabetes or advanced Type 2 diabetes. Insulin injections or insulin pump therapy help regulate blood sugar levels by facilitating glucose uptake into cells and reducing glucose production by the liver. By controlling blood glucose levels, insulin therapy effectively reduces glycosuria episodes and prevents complications associated with uncontrolled diabetes.
Oral Antidiabetic Medications: Oral medications are prescribed to individuals with Type 2 diabetes to improve insulin secretion, reduce insulin resistance, and lower blood glucose levels. Common classes of oral antidiabetic medications include:
- Sulfonylureas: Stimulate insulin secretion from pancreatic beta cells.
- Biguanides (e.g., Metformin): Decrease glucose production by the liver and improve insulin sensitivity in peripheral tissues.
- Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 (DPP-4) Inhibitors: Increase insulin secretion and reduce glucagon production.
- Thiazolidinediones (TZDs): Enhance insulin sensitivity in muscle and adipose tissue.
SGLT2 Inhibitors: Sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors are a newer class of medications that work by blocking glucose reabsorption in the kidneys, leading to increased urinary glucose excretion and lower blood sugar levels. By reducing renal glucose reabsorption, SGLT2 inhibitors effectively lower glycosuria levels and improve glycemic control in individuals with Type 2 diabetes.
SGLT1/SGLT2 Inhibitors: Dual inhibitors of SGLT1 and SGLT2 receptors offer a combined approach to reducing glucose reabsorption in the kidneys, resulting in enhanced glycosuria and glycemic control. These medications may be particularly beneficial for individuals with diabetes who have inadequate glycemic control with other treatments.
Monitoring and Follow-Up
Monitoring and follow-up are essential components of glycosuria treatment, allowing healthcare providers to assess treatment efficacy, adjust management strategies, and prevent complications. Regular monitoring of blood glucose levels, kidney function, and urinary glucose excretion provides valuable insights into the patient’s response to treatment and helps guide further management decisions.
Blood Glucose Monitoring
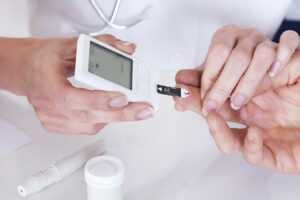
Regular monitoring of blood glucose levels is paramount in the management of glycosuria, particularly in individuals with diabetes mellitus. Patients are advised to perform self-monitoring of blood glucose using glucometers to track their blood sugar levels throughout the day.
Healthcare providers may recommend specific targets for fasting, preprandial, and postprandial glucose levels based on individual patient factors and treatment goals. By monitoring blood glucose levels regularly, patients and healthcare providers can identify trends, adjust treatment regimens as needed, and prevent episodes of hyperglycemia or hypoglycemia.
Kidney Function Tests
Monitoring kidney function is essential in individuals with glycosuria, as persistent urinary glucose excretion can increase the risk of renal damage and impairment. Kidney function tests, such as serum creatinine and estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR), are performed periodically to assess renal function and detect any signs of kidney dysfunction or damage.
close monitoring of kidney function allows healthcare providers to intervene early and prevent progression to more severe kidney-related complications.
Urine Glucose Monitoring
In addition to blood glucose monitoring, urinary glucose excretion is assessed through urine glucose testing. Patients may be instructed to perform periodic urine glucose tests at home using dipstick tests or urine test strips. Elevated urinary glucose levels indicate poor glycemic control and may necessitate adjustments to the treatment regimen, such as medication changes or lifestyle modifications.
Healthcare providers interpret urine glucose results in conjunction with blood glucose levels and other clinical parameters to optimize glycosuria management.
Regular Follow-Up Visits
Scheduled follow-up visits with healthcare providers are essential for individuals with glycosuria to monitor treatment progress, address any concerns or complications, and provide ongoing support and education. During follow-up visits, healthcare providers review blood glucose logs, assess medication adherence, perform physical examinations, and discuss any changes in symptoms or health status.
These visits offer opportunities to reinforce treatment goals, adjust management strategies, and empower patients to take an active role in their glycosuria management.
How To Get Glycosuria Treatment?

While online resources can offer valuable information and support, they should complement, not replace, professional medical care. Here are some reputable online resources where you can find information about glycosuria treatment and connect with healthcare providers:
- DiabetesMantra (diabetesmantra.com): DiabetesMantra offers comprehensive information on various medical conditions, including glycosuria. You can find articles, expert advice, and resources to learn more about glycosuria treatment options and management strategies.
- Mayo Clinic (www.mayoclinic.org): The Mayo Clinic’s website provides reliable information on glycosuria, including causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment. You can access articles, patient resources, and educational materials to understand glycosuria and its management better.
- National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK) (www.niddk.nih.gov): The NIDDK website offers evidence-based information on diabetes and related conditions, including glycosuria. You can find patient education materials, research updates, and resources to support glycosuria management and self-care.
Conclusion
Glycosuria is a condition characterized by the presence of glucose in the urine, often indicative of underlying health issues such as diabetes or renal dysfunction. While mild cases may not always require treatment, proper management is essential to prevent complications and improve overall health.
By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for glycosuria, individuals can work with healthcare providers to develop personalized treatment plans aimed at optimizing their health and well-being. If you experience symptoms suggestive of glycosuria or have concerns about your urinary glucose levels, consult a healthcare professional for proper evaluation and guidance.
Do you want to get rid of diabetes? Join our online diabetes treatment program and reverse Diabetes naturally through lifestyle changes such as a Personalized Diet plan, Exercise, Yoga, dieticians, and health coaches.