Diabetes mellitus, commonly known as diabetes, is a chronic medical condition characterized by elevated levels of blood glucose, often resulting from the body’s inability to produce or effectively use insulin. It is a global health concern, affecting millions of people worldwide. Effective management of diabetes is crucial to prevent complications and ensure a good quality of life for individuals living with the condition. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore various aspects of diabetes mellitus treatment, from lifestyle modifications to medications and emerging therapies.
Contents
What is Diabetes Mellitus?
Diabetes mellitus is a chronic metabolic disorder characterized by elevated levels of glucose (sugar) in the blood. This condition arises when the body either does not produce enough insulin or is unable to effectively use the insulin it produces. Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas that plays a crucial role in regulating blood sugar levels.
There are several types of diabetes, but the two main types are Type 1 and Type 2:
Type 1 Diabetes:
- Often referred to as insulin-dependent diabetes or juvenile-onset diabetes.
- Results from the immune system mistakenly attacking and destroying the insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas.
- People with Type 1 diabetes require lifelong insulin therapy to regulate blood sugar levels.
Type 2 Diabetes:
- Commonly known as non-insulin-dependent diabetes or adult-onset diabetes.
- Occurs when the body’s cells become resistant to insulin or the pancreas doesn’t produce enough insulin.
- Often associated with lifestyle factors such as obesity, sedentary behavior, and a diet high in processed foods and sugars.
- Initially, Type 2 diabetes can often be managed with lifestyle changes, oral medications, or a combination of both. In some cases, insulin therapy may be necessary.
Different Diabetes Mellitus Treatment Methods
Diabetes mellitus treatment involves a multifaceted approach that aims to manage blood sugar levels, prevent complications, and improve the overall quality of life for individuals with diabetes. Here are various methods used in the treatment of diabetes:
1. Lifestyle Modifications

Lifestyle modifications form the cornerstone of diabetes mellitus treatment, playing a pivotal role in managing blood sugar levels and preventing complications. These changes encompass dietary adjustments, regular physical activity, and weight management.
Dietary Changes: A well-balanced diet is essential for individuals with diabetes. Emphasis is placed on whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins. Monitoring carbohydrate intake and practicing portion control are crucial strategies to regulate blood sugar levels. Limiting the consumption of processed foods, sugary beverages, and high-fat items helps maintain glycemic control. Collaborating with a registered dietitian can aid in creating a personalized meal plan tailored to individual needs and preferences.
Regular Physical Activity: Engaging in regular exercise is beneficial for both blood sugar control and overall health. Aerobic exercises like walking, cycling, and swimming improve insulin sensitivity, allowing cells to utilize glucose more effectively. Incorporating strength training helps build muscle mass, contributing to long-term weight management. Healthcare professionals can guide individuals in developing a safe and effective exercise routine based on their fitness level and health condition.
Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy weight is crucial for individuals with diabetes. Weight loss, if needed, can improve insulin sensitivity. Calorie control, mindful eating, and regular monitoring contribute to successful weight management. Healthcare providers may recommend weight loss goals based on an individual’s overall health and specific diabetes management needs.
2. Medications

When lifestyle modifications alone are insufficient, medications play a crucial role in managing diabetes mellitus. Several classes of medications address different aspects of glucose metabolism, offering a personalized approach to treatment.
Oral Medications: Metformin is often prescribed as a first-line medication. It improves insulin sensitivity and reduces glucose production in the liver. Other classes of oral medications include sulfonylureas, dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitors, and sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 (SGLT-2) inhibitors. These medications work through various mechanisms to lower blood sugar levels and may be used singly or in combination.
Insulin Therapy: Insulin therapy is essential for individuals with type 1 diabetes and may be prescribed for those with advanced type 2 diabetes. Different types of insulin, such as rapid-acting, short-acting, intermediate-acting, and long-acting, are available to address varying needs. Insulin can be administered through injections or insulin pumps, providing flexibility in managing blood sugar levels.
Combination Therapies: In some cases, a combination of oral medications and insulin therapy is necessary to achieve optimal blood sugar control. Combining medications with different mechanisms of action can enhance their effectiveness and minimize side effects. Healthcare professionals work closely with individuals to tailor treatment plans that address their specific needs and preferences.
3. Monitoring and Self-Care
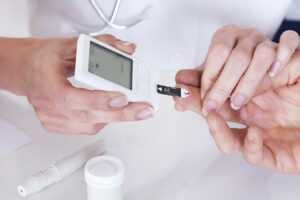
Regular monitoring and self-care practices are integral components of diabetes mellitus treatment. These activities empower individuals to actively manage their condition, track progress, and identify potential issues early on.
Blood Glucose Monitoring: Regular monitoring of blood glucose levels is fundamental to diabetes management. Glucometers and continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) systems allow individuals to track their blood sugar levels at home. Keeping a log of readings helps identify patterns and trends, enabling better-informed decisions about diet, medication, and lifestyle choices.
Foot Care: Foot care is crucial for preventing complications such as diabetic neuropathy. Regular inspection of feet, choosing proper footwear, and seeking prompt medical attention for any foot issues are essential practices. Proper foot care reduces the risk of infections and complications that can arise from impaired circulation or nerve damage.
Regular Health Check-ups: Routine check-ups with healthcare providers are vital for monitoring overall health. These check-ups include assessments of blood pressure, cholesterol levels, kidney function, and other parameters. Early detection of potential complications allows for timely intervention and better disease management.
4. Emerging Therapies
Ongoing research and technological advancements in diabetes mellitus treatment are paving the way for innovative therapies that hold the potential to transform the landscape of diabetes care.
Artificial Pancreas: The development of an artificial pancreas involves integrating insulin pumps and continuous glucose monitoring to create a closed-loop system. This automated approach aims to mimic the function of a healthy pancreas, providing real-time adjustments to insulin delivery based on glucose levels.
Gene Therapy: Gene therapy explores genetic approaches to enhance insulin production or improve insulin sensitivity. This cutting-edge field holds promise for addressing the root causes of diabetes at the genetic level, potentially offering long-term solutions.
Stem Cell Therapy: Stem cell therapy involves using stem cells to regenerate insulin-producing cells in the pancreas. Research in this area aims to restore normal pancreatic function and reduce or eliminate the need for insulin therapy in individuals with diabetes.
5. Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM)
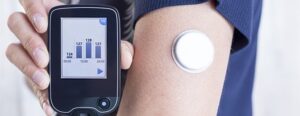
Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) is a technology that has revolutionized diabetes management by providing real-time information about blood glucose levels. Unlike traditional fingerstick testing, CGM devices continuously measure glucose levels throughout the day, offering a more comprehensive view of glycemic fluctuations.
CGM devices consist of a small sensor placed under the skin, usually on the abdomen, which measures glucose levels in the interstitial fluid. The sensor communicates with a transmitter, sending data to a receiver or a smartphone app. Users can track glucose trends, set alarms for high or low glucose levels, and make informed decisions about insulin dosing and lifestyle adjustments.
The benefits of CGM include improved glycemic control, reduced risk of hypoglycemia, and increased awareness of how various factors, such as food, exercise, and stress, affect blood sugar levels. CGM technology empowers individuals with diabetes and their healthcare providers to make timely and personalized adjustments to treatment plans, leading to better overall diabetes management.
6. Incretin-Based Therapies
Incretin-based therapies are a class of medications that leverage the body’s natural gut hormones to regulate blood sugar levels. Two main types of incretin hormones, glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) and glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP) play a crucial role in glucose metabolism.
GLP-1 Receptor Agonists:
- These medications mimic the action of GLP-1, stimulating insulin secretion in a glucose-dependent manner. They also suppress glucagon release, slow gastric emptying, and promote a feeling of fullness, leading to weight loss in some cases.
Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 (DPP-4) Inhibitors:
- DPP-4 inhibitors enhance the effects of GLP-1 by preventing its breakdown. This results in increased insulin release and decreased glucagon production.
Incretin-based therapies help as adjuncts to other diabetes medications and may be particularly beneficial for individuals with type 2 diabetes who struggle with weight management.
Sources To Get Diabetes Mellitus Treatment

Effectively managing diabetes mellitus involves a multifaceted approach, combining lifestyle modifications, medications, and vigilant self-care. With advancements in medical research and technology, the future holds promising possibilities for innovative therapies that may revolutionize diabetes treatment. However, a proactive and informed approach to current treatment options remains key to maintaining optimal health and preventing complications for individuals living with diabetes. Always consult with healthcare professionals for personalized advice and guidance based on individual health needs.
Do you want to get rid of diabetes? Join our online diabetes treatment program and reverse Diabetes naturally through lifestyle changes such as a Personalized Diet plan, Exercise, Yoga, dieticians, and health coaches.

