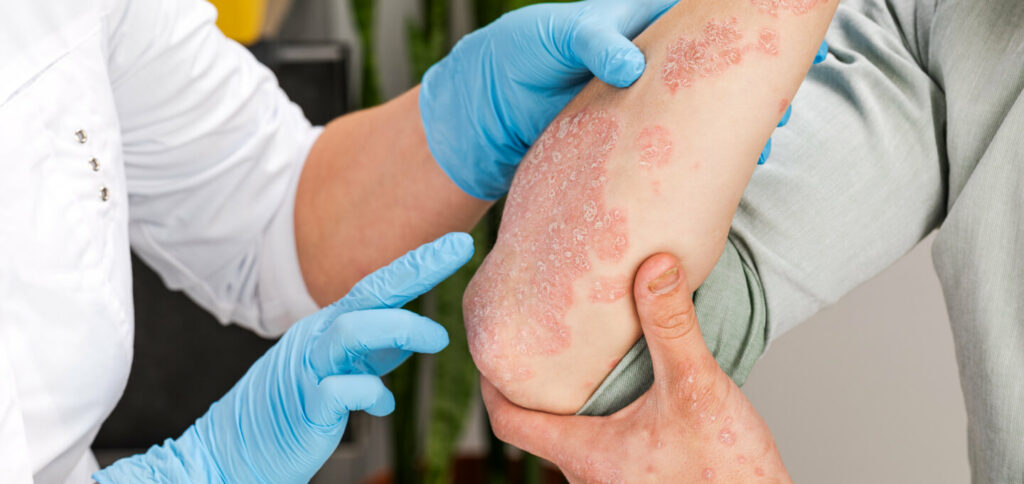
Diabetes and psoriasis are two distinct medical conditions, yet there is a significant association between them. Individuals with diabetes often find themselves grappling with psoriasis, a chronic skin condition characterized by red, itchy, and scaly patches. In this blog, we will delve into the connection between diabetes and psoriasis, explore the reasons behind their coexistence, and discuss effective treatment approaches for managing both conditions.
Contents
The Diabetes-Psoriasis Connection
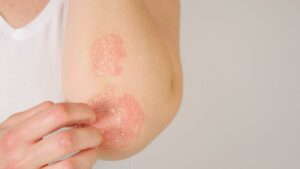
Research suggests a bidirectional relationship between diabetes and psoriasis. People with diabetes are more prone to developing psoriasis, and vice versa. The exact mechanisms linking the two conditions are not fully understood, but inflammation is believed to play a crucial role.
- Inflammation: Both diabetes and psoriasis involve chronic inflammation. Elevated levels of certain inflammatory markers, such as tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) and interleukin-6 (IL-6), are found in individuals with both conditions. This shared inflammatory pathway suggests a possible common link.
- Genetics: Genetic factors may contribute to the coexistence of diabetes and psoriasis. Research has identified specific genetic markers associated with an increased risk of both conditions. Having a family history of either disease may elevate the likelihood of developing the other.
- Immune System Dysfunction: Dysregulation of the immune system is a hallmark of psoriasis. In individuals with diabetes, the immune system may also be compromised. This immune system dysfunction could create a favorable environment for the development or exacerbation of psoriasis.
Effective Treatment Approaches for Diabetes Psoriasis
Managing both diabetes and psoriasis simultaneously requires a comprehensive approach that addresses the unique challenges posed by each condition. Here are some effective treatment approaches:
1. Lifestyle Modifications
Lifestyle modifications form the foundation for managing both diabetes and psoriasis. Adopting a healthy lifestyle can positively impact blood sugar levels, reduce inflammation, and alleviate the symptoms of psoriasis.
- Healthy Diet: A well-balanced diet is crucial for individuals with diabetes and psoriasis. Focus on whole, nutrient-dense foods such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins. Incorporate foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids, like fatty fish and flaxseeds, as these can help reduce inflammation associated with psoriasis. Limit the intake of processed foods, sugary snacks, and saturated fats, which can contribute to insulin resistance and exacerbate inflammation.
- Regular Exercise: Physical activity is a cornerstone for managing both conditions. Regular exercise helps control blood sugar levels by improving insulin sensitivity. Additionally, exercise promotes circulation, which can benefit the skin by reducing inflammation and supporting overall skin health. Aim for a combination of aerobic exercises, strength training, and flexibility exercises. Consult with healthcare providers to tailor an exercise plan that suits individual capabilities and health status.
- Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy weight is crucial for individuals with diabetes, as excess weight can contribute to insulin resistance. Weight management is also relevant for psoriasis, as obesity is a known risk factor for the development and worsening of the condition. Adopting a healthy diet and engaging in regular physical activity contribute to weight control and can positively impact both conditions.
2. Topical Treatments for Psoriasis

Topical treatments are often the first line of defense for managing psoriasis symptoms. These medications are applied directly to the affected skin, providing relief from itching, redness, and scaling.
- Corticosteroids: Topical corticosteroids are anti-inflammatory medications that help alleviate the symptoms of psoriasis. They work by suppressing the immune response in the affected skin, reducing redness and inflammation. However, long-term use should be monitored carefully, as it may lead to skin thinning and other side effects. Healthcare providers can recommend appropriate formulations and usage instructions based on the severity and location of psoriasis lesions.
- Vitamin D Analogs: Topical creams containing vitamin D analogs, such as calcitriol or calcipotriene, can be effective in slowing down the excessive growth of skin cells associated with psoriasis. These medications help normalize skin cell turnover and reduce scaling. Vitamin D analogs are often used in combination with other topical treatments or as maintenance therapy to manage psoriasis symptoms over the long term.
- Topical Retinoids: Retinoids, derived from vitamin A, can be applied topically to reduce inflammation and normalize skin cell turnover. They are especially useful for treating psoriasis on the face or areas where the skin is thinner. However, they may cause skin irritation, and their use should be guided by healthcare professionals.
3. Systemic Medications
For more severe cases of psoriasis that do not respond adequately to topical treatments, systemic medications may be prescribed. These medications work throughout the body to target the underlying causes of psoriasis.
- Biologics: Biologics are a class of medications that target specific components of the immune system involved in the development of psoriasis. They can be highly effective in managing moderate to severe psoriasis and are administered through injections or infusions. Biologics may have an impact on the immune system, necessitating close monitoring for potential side effects. They are usually reserved for cases where other treatments have not provided sufficient relief.
- Oral Medications: In cases where topical and biologic treatments are not suitable, oral medications such as methotrexate or cyclosporine may be considered. These medications work to suppress the immune response and reduce inflammation. However, they may have systemic side effects and require careful monitoring of blood parameters, especially in individuals with diabetes.
- Phototherapy (Light Therapy): Phototherapy involves exposing the skin to ultraviolet (UV) light under controlled conditions. This treatment can be effective for psoriasis by slowing down the growth of skin cells and reducing inflammation. However, it requires careful monitoring to avoid potential complications, and its use may need to be adjusted for individuals with diabetes.
4. Blood Sugar Control
Effective management of diabetes involves maintaining optimal blood sugar levels. Consistent blood sugar control not only prevents diabetes-related complications but can also positively influence the course of psoriasis.
- Medication Management: For individuals with diabetes, medication management is crucial. This may involve oral medications, insulin therapy, or a combination of both. Adherence to prescribed medications and regular monitoring of blood glucose levels are essential to keep diabetes under control.
- Continuous Glucose Monitoring: Continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) systems provide real-time data on blood sugar levels, allowing individuals with diabetes to make informed decisions about their diet, physical activity, and medication adjustments. CGM can help maintain stable blood sugar levels and reduce the risk of diabetes-related complications.
- Nutritional Planning: Consistent carbohydrate intake, distributed evenly throughout the day, can help stabilize blood sugar levels. Working with a registered dietitian can aid in developing personalized meal plans that consider both diabetes and psoriasis management goals.
5. Stress Management
Stress is a common trigger for both diabetes and psoriasis flares. Implementing stress management techniques is essential for promoting overall well-being and minimizing the impact of stress on these conditions.
- Mindfulness and Meditation: Mindfulness practices, such as meditation and deep breathing exercises, can help manage stress and promote relaxation. These techniques have been shown to reduce inflammatory markers in the body, potentially benefiting individuals with psoriasis.
- Yoga: Yoga combines physical postures, breath control, and meditation, offering a holistic approach to stress management. Engaging in regular yoga practice can contribute to improved mental well-being and may have positive effects on both diabetes and psoriasis.
- Counseling and Support Groups: Seeking professional counseling or participating in support groups can provide individuals with effective coping mechanisms for stress. Connecting with others facing similar challenges can offer emotional support and practical insights for managing the emotional aspects of living with diabetes and psoriasis.
6. Regular Monitoring and Follow-up
Regular monitoring and follow-up with healthcare providers are essential components of managing both diabetes and psoriasis. These practices ensure that treatment plans are adjusted as needed and that potential complications are identified and addressed promptly.
- Dermatological Check-ups: Individuals with psoriasis should have regular dermatological check-ups to assess the status of their skin condition. This allows healthcare providers to make timely adjustments to treatment plans based on the severity and progression of psoriasis.
- Blood Tests: Routine blood tests, including HbA1c for diabetes management and monitoring liver function for individuals on certain psoriasis medications, help track overall health. Regular blood tests are vital for detecting any potential side effects or complications related to systemic medications.
- Medication Reviews: Periodic reviews of medication effectiveness and potential side effects are crucial for optimizing treatment plans. Healthcare providers may need to adjust dosages or switch medications based on individual responses and changing health conditions.
Benefits of Diabetes-Psoriasis Treatment
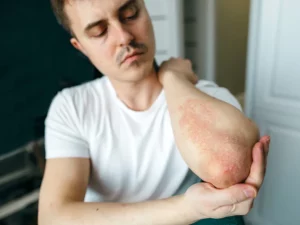
The coexistence of diabetes and psoriasis presents unique challenges, but effective treatment strategies can offer a range of benefits for individuals managing both conditions. Treating diabetes and psoriasis concurrently can lead to improvements in overall health, quality of life, and disease-specific outcomes. Here are several key benefits associated with a comprehensive approach to diabetes-psoriasis treatment:
- Improved Glycemic Control: Effective management of psoriasis can positively impact glycemic control in individuals with diabetes. Psoriasis-related inflammation and stress can contribute to insulin resistance, making it challenging to control blood sugar levels. By addressing psoriasis through various treatment modalities, including lifestyle changes and medications, individuals may experience better glycemic control, reducing the risk of diabetes-related complications.
- Reduced Cardiovascular Risk: Both diabetes and psoriasis are associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular diseases. The chronic inflammation present in psoriasis can exacerbate the cardiovascular risk already elevated in diabetes. Treating psoriasis not only improves skin symptoms but may also contribute to a reduction in systemic inflammation, potentially lowering the risk of cardiovascular events in individuals with diabetes.
- Enhanced Quality of Life: Psoriasis can significantly impact an individual’s quality of life due to visible skin symptoms, itching, and discomfort. Effective treatment of psoriasis can lead to a reduction in these symptoms, improving overall well-being and psychological health. As a result, individuals may experience less stress and anxiety related to their skin condition, positively influencing their quality of life.
- Prevention of Complications: Diabetes and psoriasis can both lead to complications if left unmanaged. Diabetes complications may include cardiovascular disease, neuropathy, and kidney damage, while psoriasis complications can involve joint inflammation (psoriatic arthritis) and an increased risk of other autoimmune conditions. Proper treatment of both conditions reduces the likelihood of complications and improves long-term health outcomes.
- Better Skin Health: Treating psoriasis effectively leads to healthier skin. Topical treatments, systemic medications, and lifestyle changes can help control the excessive growth of skin cells, reduce inflammation, and alleviate the visible symptoms of psoriasis. This not only enhances the aesthetic appearance of the skin but also prevents potential complications associated with untreated or severe psoriasis.
How To Get Diabetes-Psoriasis Treatment?
Online resources can help gather information, but the primary avenue for diagnosis and treatment should involve direct interaction with healthcare providers. Here are steps individuals can take to seek diabetes-psoriasis treatment, including some reputable online resources for information:
Consult a Healthcare Professional: Start by scheduling an appointment with your primary care physician, dermatologist, or endocrinologist, depending on your specific needs and symptoms. These healthcare professionals can conduct thorough assessments, diagnose both conditions and recommend appropriate treatment plans.
Use Reputable Medical Websites: Websites of reputable medical organizations can provide reliable information about diabetes and psoriasis. Examples include:
- American Diabetes Association (ADA)
- National Psoriasis Foundation (NPF)
- Diabetes Mantra
Telemedicine Services: Explore telemedicine services that offer virtual consultations with healthcare professionals. Platforms like Diabetes Mantra and Amwell allow individuals to consult with healthcare providers online, discuss symptoms, and receive guidance on further steps.
Health Insurance Websites: Check your health insurance provider’s website for information on covered services and network healthcare providers. Many insurance companies offer online tools to help you find in-network doctors, including specialists like dermatologists and endocrinologists.
Conclusion
Understanding the interplay between diabetes and psoriasis is essential for effective management. By adopting a holistic approach that addresses both conditions, individuals can significantly improve their quality of life. Consultation with healthcare professionals is crucial for personalized treatment plans that consider the unique needs of each patient. Through lifestyle modifications, topical treatments, systemic medications, and diligent blood sugar control, individuals can successfully navigate the challenges posed by the coexistence of diabetes and psoriasis.
Do you want to get rid of diabetes? Join our online diabetes treatment program and reverse Diabetes naturally through lifestyle changes such as a Personalized Diet plan, Exercise, Yoga, dieticians, and health coaches.