Type 1 diabetes is a chronic condition that requires careful management to maintain blood sugar levels within a healthy range. This autoimmune disease occurs when the body’s immune system attacks and destroys insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas, leading to insulin deficiency. While there is no cure for type 1 diabetes, advancements in treatment options have significantly improved the quality of life for individuals living with this condition. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the various aspects of type 1 diabetes treatment, including medication, lifestyle modifications, and emerging therapies.
Contents
What is Type 1 Diabetes?

Type 1 diabetes is a chronic autoimmune condition characterized by the body’s inability to produce insulin, a hormone essential for regulating blood sugar levels. Unlike type 2 diabetes, which is often associated with lifestyle factors such as obesity and physical inactivity, type 1 diabetes is primarily caused by the immune system mistakenly attacking and destroying insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas.
Here are the key aspects of type 1 diabetes:
- Autoimmune Disease: Type 1 diabetes is considered an autoimmune disease because the body’s immune system, which normally protects against harmful invaders like viruses and bacteria, mistakenly targets and destroys the insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas. The exact cause of this autoimmune attack is not fully understood, but genetic and environmental factors are believed to play a role.
- Insulin Deficiency: As beta cells are destroyed, the pancreas produces little to no insulin. Insulin is crucial for facilitating the uptake of glucose from the bloodstream into cells, where it is used for energy production. Without sufficient insulin, glucose accumulates in the bloodstream, leading to high blood sugar levels (hyperglycemia).
Can We Treat Type 1 Diabetes?
While there is currently no cure for type 1 diabetes, it can be effectively managed through a combination of medication, lifestyle modifications, and emerging therapies. Treatment aims to regulate blood sugar levels, minimize the risk of complications, and improve the quality of life for individuals with the condition.
While current treatments effectively manage type 1 diabetes, ongoing research aims to improve treatment options and ultimately find a cure. Emerging therapies, such as artificial pancreas systems and stem cell therapy, hold promise for enhancing diabetes care and quality of life for individuals with type 1 diabetes.
Different Type 1 Diabetes Treatment Methods
Treatment for type 1 diabetes typically involves a combination of approaches to manage blood sugar levels and prevent complications. Here are some of the different methods used in treating type 1 diabetes:
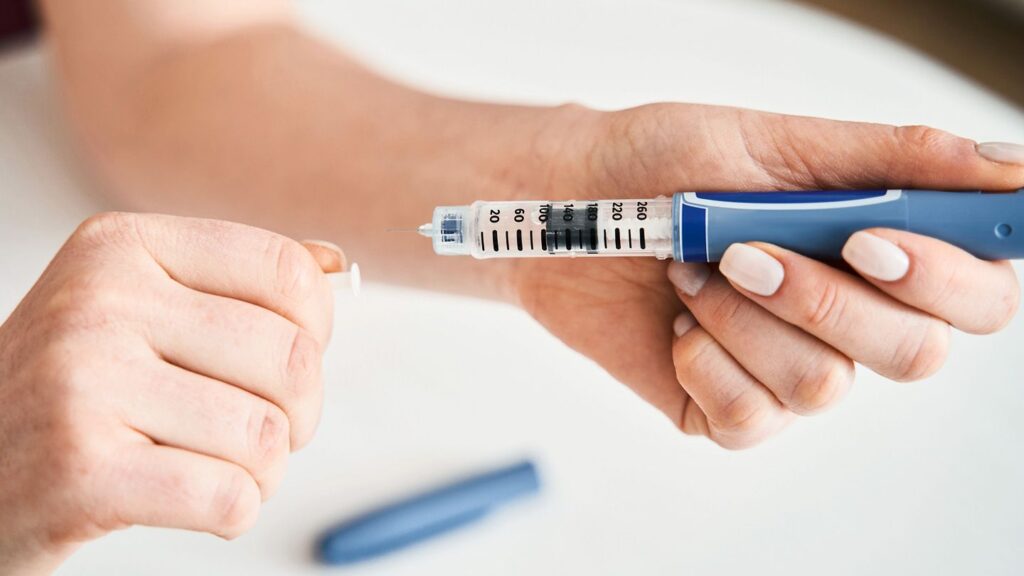
Insulin Therapy

Insulin therapy is the cornerstone of treatment for individuals with type 1 diabetes, providing the essential hormone needed to regulate blood sugar levels. In type 1 diabetes, the immune system mistakenly attacks and destroys insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas, leading to a deficiency of insulin. Insulin therapy aims to replace this lost insulin, allowing cells to absorb glucose from the bloodstream for energy production.
There are several types of insulin used in therapy, each with unique characteristics and durations of action.
- Rapid-acting insulin begins to work within minutes and is typically taken before meals to control blood sugar spikes after eating.
- Short-acting insulin takes effect within 30 minutes to an hour and is used to cover blood sugar increases during meals.
- Intermediate-acting insulin starts working within 1 to 2 hours and lasts for about 12 to 18 hours, providing basal insulin coverage between meals and overnight.
- Long-acting insulin provides a steady release of insulin over 24 hours, offering basal insulin coverage throughout the day.
Insulin therapy can be administered through injections using syringes or insulin pens, or through an insulin pump, which delivers insulin continuously through a catheter placed under the skin. Some individuals may use a combination of insulin types to mimic the body’s natural insulin production, known as basal-bolus therapy.
This approach involves taking long-acting insulin for basal (background) insulin needs and rapid-acting insulin before meals to cover carbohydrate intake.
Lifestyle Modifications

Lifestyle modifications are crucial components of type 1 diabetes treatment, complementing insulin therapy to help individuals manage their condition effectively and improve overall well-being. Here’s a breakdown of lifestyle modifications for type 1 diabetes:
Healthy Eating Habits:
- Following a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins helps regulate blood sugar levels.
- Monitoring carbohydrate intake and spacing meals and snacks evenly throughout the day can prevent blood sugar spikes and crashes.
- Limiting processed foods, sugary beverages, and high-fat foods helps maintain optimal weight and blood sugar control.
Stress Management:
- Stress can affect blood sugar levels, so it’s essential to practice stress-reduction techniques such as deep breathing, meditation, yoga, or hobbies.
- Setting realistic goals, prioritizing tasks, and seeking support from friends, family, or mental health professionals can help manage stress effectively.
Adequate Sleep:
- Getting enough sleep is vital for overall health and blood sugar management.
- Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep each night to support optimal insulin sensitivity and energy levels.
- Establishing a consistent sleep schedule and creating a relaxing bedtime routine can improve sleep quality.
Alcohol Consumption:
- Moderate alcohol consumption may be permissible, but it’s essential to monitor blood sugar levels and drink in moderation.
- Alcohol can cause hypoglycemia, especially when consumed on an empty stomach or in combination with certain diabetes medications.
- Always consume alcohol with food, and avoid excessive drinking to minimize the risk of blood sugar fluctuations.
Blood Sugar Monitoring
Blood sugar monitoring is a vital component of type 1 diabetes treatment, allowing individuals to track their blood glucose levels regularly and make informed decisions about insulin dosing, diet, and lifestyle adjustments. Here’s a breakdown of blood sugar monitoring for type 1 diabetes:
Fingerstick Blood Glucose Testing:
- Traditional fingerstick blood glucose testing involves pricking the fingertip with a lancet to obtain a small blood sample, which is then placed on a test strip and inserted into a glucometer.
- This method provides immediate results and is commonly used to monitor blood sugar levels multiple times throughout the day, including before and after meals, before exercise, and at bedtime.
Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) Systems:
- CGM systems continuously monitor glucose levels in the interstitial fluid (fluid between cells) using a tiny sensor inserted under the skin.
- The sensor measures glucose levels every few minutes and transmits data to a receiver or smartphone app, providing real-time glucose readings and trends.
- CGM systems offer insights into blood sugar fluctuations, allowing individuals to identify patterns, detect trends, and make timely adjustments to insulin dosing, diet, and physical activity.
Carbohydrate Counting and Meal Planning
Carbohydrate counting and meal planning are essential components of type 1 diabetes treatment, helping individuals manage their blood sugar levels effectively and maintain optimal health. Here’s a breakdown of carbohydrate counting and meal planning for type 1 diabetes:
Carbohydrate Counting:
- Carbohydrate counting involves estimating the amount of carbohydrates in foods and beverages and matching insulin doses to carbohydrate intake.
- Carbohydrates have the most significant impact on blood sugar levels, so accurately counting carbs allows individuals to adjust insulin doses to cover the rise in blood sugar after eating.
Understanding Carbohydrate Sources:
- Carbohydrates are found in various foods, including grains, starchy vegetables, fruits, dairy products, and sweets.
- Different foods contain different amounts of carbohydrates, so it’s essential to be familiar with common carbohydrate sources and their portion sizes.
Reading Food Labels:
- Food labels provide valuable information about the carbohydrate content of packaged foods and beverages.
- Pay attention to the serving size and total carbohydrate grams per serving. It is to calculate the carbohydrate content of a specific food item accurately.
Physical Activity

Physical activity is a crucial component of type 1 diabetes treatment. It also offers numerous benefits for blood sugar control, overall health, and well-being. Here’s a breakdown of physical activity as a treatment method for type 1 diabetes:
Improves Insulin Sensitivity:
- Regular physical activity improves insulin sensitivity, allowing cells to more efficiently absorb glucose from the bloodstream for energy production.
- Increased insulin sensitivity means that less insulin is required to lower blood sugar levels. This reduces the risk of insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes.
Lowers Blood Sugar Levels:
- Exercise helps lower blood sugar levels by increasing glucose uptake into muscles for energy during physical activity.
- Both aerobic exercise, such as walking, jogging, or cycling, and strength training exercises, such as weightlifting or resistance training, can help lower blood sugar levels.
Promotes Weight Management:
- Physical activity plays a vital role in weight management. It helps the individuals maintain a healthy body weight or achieve weight loss goals.
- Maintaining a healthy weight reduces insulin resistance and improves blood sugar control in individuals with type 1 diabetes.
Medications
Medications play a supportive role in type 1 diabetes treatment, helping manage related conditions and reducing the risk of complications. While insulin therapy remains the primary treatment for type 1 diabetes, additional medications may be prescribed to address specific health concerns. Here’s a breakdown of medications used in type 1 diabetes treatment:
Blood Pressure Medications:
- Some individuals with type 1 diabetes may develop high blood pressure (hypertension) as a complication of the condition.
- Blood pressure medications, such as angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors or angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARBs), help lower blood pressure and protect the kidneys from damage.
Cholesterol-Lowering Medications:
- High cholesterol levels are a common concern for individuals with type 1 diabetes, increasing the risk of heart disease and stroke.
- Statin medications, such as atorvastatin or simvastatin, help lower LDL (bad) cholesterol levels and reduce the risk of cardiovascular complications.
Antiplatelet Agents:
- Individuals with type 1 diabetes are at an increased risk of blood clots and cardiovascular events.
- Antiplatelet medications, such as aspirin or clopidogrel, help prevent blood clots from forming and reduce the risk of heart attacks and strokes.
Kidney-Protective Medications:
- Diabetes is a leading cause of kidney disease (diabetic nephropathy) and kidney failure.
- Medications called angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors or angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARBs) are commonly used to protect kidney function. They also slow the progression of diabetic nephropathy.
Thyroid Medications:
- Some individuals with type 1 diabetes may develop thyroid disorders, such as hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism.
- Thyroid medications, such as levothyroxine or methimazole, help regulate thyroid hormone levels and manage symptoms associated with thyroid disorders.
Psychological Support

Psychological support plays a vital role in type 1 diabetes treatment. Furthermore, the individuals cope with the emotional and mental challenges associated with managing a chronic condition. Here’s a breakdown of the importance of psychological support in type 1 diabetes treatment:
Emotional Well-being:
- Living with type 1 diabetes can be stressful and overwhelming, leading to feelings of anxiety, depression, frustration, and burnout.
- Psychological support provides individuals with coping strategies and emotional resilience to navigate the daily challenges of diabetes management.
Stress Management:
- Stress can affect blood sugar levels and overall health. This makes it essential to develop effective stress management techniques.
- Counseling, relaxation techniques, mindfulness practices, and stress-reduction exercises can help individuals manage stress and maintain stable blood sugar levels.
Education and Empowerment:
- Psychological support offers education and empowerment, helping individuals understand their condition, treatment options, and self-care practices.
- By gaining knowledge and confidence in managing their diabetes, individuals can take an active role in their treatment. It also improves their overall quality of life.
Stem Cell Therapy
Stem cell therapy holds promise as a potential treatment for type 1 diabetes. This offers the potential to regenerate insulin-producing beta cells and restore normal blood sugar regulation. Here’s a breakdown of stem cell therapy as a type 1 diabetes treatment method:
Regeneration of Beta Cells:
- Stem cells have the unique ability to differentiate into various cell types, including insulin-producing beta cells found in the pancreas.
- Stem cell therapy aims to replace damaged or destroyed beta cells with healthy, functioning beta cells generated from stem cells.
Types of Stem Cells:
- Several types of stem cells show potential for use in type 1 diabetes treatment. It is including embryonic stem cells, induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs), and adult stem cells.
- Embryonic stem cells are derived from early-stage embryos and can develop into any cell type in the body.
- iPSCs are adult cells that can behave like embryonic stem cells, offering a potentially limitless source of patient-specific stem cells.
- Adult stem cells, such as mesenchymal stem cells found in bone marrow or adipose tissue, can differentiate into certain cell types and may play a role in tissue repair and regeneration.
Conclusion
Type 1 diabetes treatment requires a multifaceted approach that encompasses insulin therapy, blood sugar monitoring, lifestyle modifications, and often the use of advanced diabetes technologies. With proper management and support, individuals with type 1 diabetes can lead full and active lives while minimizing the risk of complications associated with uncontrolled blood sugar levels. Ongoing research and advancements in diabetes care continue to improve treatment options and offer hope for a future cure.
Remember, the key to successful diabetes management lies in understanding the condition, being vigilant about monitoring, and making informed decisions about your health. Do you want to get rid of diabetes? Join our online diabetes treatment program and reverse Diabetes naturally through lifestyle changes such as a Personalized Diet plan, Exercise, Yoga, dieticians, and health coaches.